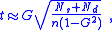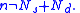Gamma test (statistics)
Encyclopedia
In statistics
, a gamma test tests the strength of association
of the cross tabulated
data when both variables
are measured at the ordinal level. It makes no adjustment for either table size or ties. Values range from −1 (100% negative association, or perfect inversion) to +1 (100% positive association, or perfect agreement). A value of zero indicates the absence of association.
This test statistic is also known as Goodman and Kruskal's gamma (which is distinct from Goodman and Kruskal's lambda
), after Leo Goodman and William Kruskal
who proposed it in a series of papers from 1954 to 1972.
where "ties" are dropped. That is cases where either of the two variables in the pair are equal.
Then
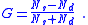
The test statistic can be regarded as the maximum likelihood estimator for the theoretical quantity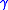 , where
, where
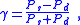
and where Ps and Pd are the probabilities that a randomly selected pair of observations will place in the same or opposite order respectively, when ranked by both variables.
Critical values for the gamma tests statistic are sometimes found by using an approximation, whereby a transformed value, t of the test statistic is referred to Student t distribution, where
and where n is the number of observations (not the number of pairs):
http://www.psych.cornell.edu/Darlington/crosstab/TABLE5.HTM
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
, a gamma test tests the strength of association
Association (statistics)
In statistics, an association is any relationship between two measured quantities that renders them statistically dependent. The term "association" refers broadly to any such relationship, whereas the narrower term "correlation" refers to a linear relationship between two quantities.There are many...
of the cross tabulated
Cross tabulation
Cross tabulation is the process of creating a contingency table from the multivariate frequency distribution of statistical variables. Heavily used in survey research, cross tabulations can be produced by a range of statistical packages, including some that are specialised for the task. Survey...
data when both variables
Variable (mathematics)
In mathematics, a variable is a value that may change within the scope of a given problem or set of operations. In contrast, a constant is a value that remains unchanged, though often unknown or undetermined. The concepts of constants and variables are fundamental to many areas of mathematics and...
are measured at the ordinal level. It makes no adjustment for either table size or ties. Values range from −1 (100% negative association, or perfect inversion) to +1 (100% positive association, or perfect agreement). A value of zero indicates the absence of association.
This test statistic is also known as Goodman and Kruskal's gamma (which is distinct from Goodman and Kruskal's lambda
Goodman and Kruskal's lambda
In probability theory and statistics, Goodman & Kruskal's lambda is a measure of proportional reduction in error in cross tabulation analysis...
), after Leo Goodman and William Kruskal
William Kruskal
William Henry Kruskal was an American mathematician and statistician. He is best known for having formulated the Kruskal–Wallis one-way analysis of variance , a widely-used nonparametric statistical method.Kruskal was born in New York City to a successful fur wholesaler...
who proposed it in a series of papers from 1954 to 1972.
Definition
The value of a gamma test statistic, G, depends on two quantities:- Ns, the number of pairs of cases ranked in the same order on both variables (number of concordant pairs),
- Nd, the number of pairs of cases ranked differently on the variables (number of discordant pairs),
where "ties" are dropped. That is cases where either of the two variables in the pair are equal.
Then
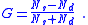
The test statistic can be regarded as the maximum likelihood estimator for the theoretical quantity
 , where
, where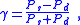
and where Ps and Pd are the probabilities that a randomly selected pair of observations will place in the same or opposite order respectively, when ranked by both variables.
Critical values for the gamma tests statistic are sometimes found by using an approximation, whereby a transformed value, t of the test statistic is referred to Student t distribution, where
and where n is the number of observations (not the number of pairs):
Further reading
Sheskin, D.J. (2007) The Handbook of Parametric and Nonparametric Statistical Procedures. Chapman & Hall/CRC, ISBN 9781584888147http://www.psych.cornell.edu/Darlington/crosstab/TABLE5.HTM