Gamma motoneurons
Encyclopedia
Gamma motoneurons also called gamma motor neurons, are the efferent component of the fusimotor system, the system by which the central nervous system
controls and modifies muscle spindle
sensitivity. The fusimotor system refers to the combination of muscle spindle
s and γ-motoneurons. The function of the muscle spindle
is to provide proprioceptive feedback for the movement, position and extension of muscle
s.
γ-motoneurons are located in the brainstem and spinal cord
and are smaller than their α-motoneuron counterparts, which are responsible for controlling skeletal muscle
.
from a γ-motoneuron is myelinated and has a slower conduction velocity than α-motoneuron axons. The typical conduction velocity for a γ-motoneuron axon is in the region of 4 to 24 m/s.
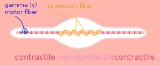
by adjusting the level of tension
in the intrafusal muscle fiber
s of the muscle spindle. This mechanism sets the baseline level of activity in α-motoneurons and helps to regulate muscle length and tone. For example, stimulation of a γ-motoneuron from higher centers contracts the ends of the intrafusal fibres and consequently stretches the middle part of the muscle spindle. This part of the spindle is innervated by type Ia sensory fiber
that go on to synapse with alpha-motoneurons, completing the gamma-loop.
of around 60 Hz in a linear fashion, above which the discharge can become irregular. The activities of bag2 fibres show an initial sharp peak in discharge, which gets less as the receptor adapts. Bag2 fibres also reduce the dynamic sensitivity of the Ia afferent and sometimes also reduce the length sensitivity. Activation of bag1 fibres has the effect of increasing both the length sensitivity and the dynamic sensitivity of the primary ending.
It is believed that the secondary sensory endings serve to measure length and muscle contraction
s of nuclear chain fibres at the pole via the static γ-motoneurons both excite the ending and increase its length sensitivity. Bag1 and bag2 fibres receive very little innervation from secondary endings, and activation of these fibres has a minimal effect on the discharge of the secondary ending.
Central nervous system
The central nervous system is the part of the nervous system that integrates the information that it receives from, and coordinates the activity of, all parts of the bodies of bilaterian animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and radially symmetric animals such as jellyfish...
controls and modifies muscle spindle
Muscle spindle
Muscle spindles are sensory receptors within the belly of a muscle, which primarily detect changes in the length of this muscle. They convey length information to the central nervous system via sensory neurons. This information can be processed by the brain to determine the position of body parts...
sensitivity. The fusimotor system refers to the combination of muscle spindle
Muscle spindle
Muscle spindles are sensory receptors within the belly of a muscle, which primarily detect changes in the length of this muscle. They convey length information to the central nervous system via sensory neurons. This information can be processed by the brain to determine the position of body parts...
s and γ-motoneurons. The function of the muscle spindle
Muscle spindle
Muscle spindles are sensory receptors within the belly of a muscle, which primarily detect changes in the length of this muscle. They convey length information to the central nervous system via sensory neurons. This information can be processed by the brain to determine the position of body parts...
is to provide proprioceptive feedback for the movement, position and extension of muscle
Muscle
Muscle is a contractile tissue of animals and is derived from the mesodermal layer of embryonic germ cells. Muscle cells contain contractile filaments that move past each other and change the size of the cell. They are classified as skeletal, cardiac, or smooth muscles. Their function is to...
s.
γ-motoneurons are located in the brainstem and spinal cord
Spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular bundle of nervous tissue and support cells that extends from the brain . The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system...
and are smaller than their α-motoneuron counterparts, which are responsible for controlling skeletal muscle
Skeletal muscle
Skeletal muscle is a form of striated muscle tissue existing under control of the somatic nervous system- i.e. it is voluntarily controlled. It is one of three major muscle types, the others being cardiac and smooth muscle...
.
Conduction velocity
The axonAxon
An axon is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body or soma....
from a γ-motoneuron is myelinated and has a slower conduction velocity than α-motoneuron axons. The typical conduction velocity for a γ-motoneuron axon is in the region of 4 to 24 m/s.
Function
Gamma-motoneurons regulate the gain of the stretch reflexStretch reflex
The stretch reflex is a muscle contraction in response to stretching within the muscle. It is a monosynaptic reflex which provides automatic regulation of skeletal muscle length....
by adjusting the level of tension
Muscle tone
In physiology, medicine, and anatomy, muscle tone is the continuous and passive partial contraction of the muscles, or the muscle’s resistance to passive stretch during resting state. It helps maintain posture, and it declines during REM sleep.-Purpose:Unconscious nerve impulses maintain the...
in the intrafusal muscle fiber
Intrafusal muscle fiber
Intrafusal muscle fibers are skeletal muscle fibers that comprise the muscle spindle and are innervated by gamma motor neurons. These fibers are a proprioceptor that detect the amount and rate of change of length in a muscle. These fibers are walled off from the rest of the muscle by a collagen...
s of the muscle spindle. This mechanism sets the baseline level of activity in α-motoneurons and helps to regulate muscle length and tone. For example, stimulation of a γ-motoneuron from higher centers contracts the ends of the intrafusal fibres and consequently stretches the middle part of the muscle spindle. This part of the spindle is innervated by type Ia sensory fiber
Type Ia sensory fiber
Type Ia Sensory Fiber also called Primary Afferent Fiber is a type of sensory fiber. It is a component of a muscle fiber's muscle spindle which keeps track of how fast a muscle stretch changes .-Function of muscle spindles:...
that go on to synapse with alpha-motoneurons, completing the gamma-loop.
Populations of neurons
There are two distinct populations of γ-motoneuron: dynamic γ-motoneurons and static γ-motoneurons.- Dynamic γ-motoneurons have axons that innervate only dynamic nuclear bag fibres (bag1) .
- Static γ-motoneurons innervate both nuclear chain fibres and static nuclear bag (bag2) fibres.
Effects of nuclear chain fibers
The effect of nuclear chain fibres on primary endings is to drive the discharge up to a frequencyFrequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
of around 60 Hz in a linear fashion, above which the discharge can become irregular. The activities of bag2 fibres show an initial sharp peak in discharge, which gets less as the receptor adapts. Bag2 fibres also reduce the dynamic sensitivity of the Ia afferent and sometimes also reduce the length sensitivity. Activation of bag1 fibres has the effect of increasing both the length sensitivity and the dynamic sensitivity of the primary ending.
It is believed that the secondary sensory endings serve to measure length and muscle contraction
Muscle contraction
Muscle fiber generates tension through the action of actin and myosin cross-bridge cycling. While under tension, the muscle may lengthen, shorten, or remain the same...
s of nuclear chain fibres at the pole via the static γ-motoneurons both excite the ending and increase its length sensitivity. Bag1 and bag2 fibres receive very little innervation from secondary endings, and activation of these fibres has a minimal effect on the discharge of the secondary ending.
See also
- Alpha motor neuronAlpha motor neuronAlpha motor neurons are large lower motor neurons of the brainstem and spinal cord. They innervate extrafusal muscle fibers of skeletal muscle and are directly responsible for initiating their contraction...
- Beta motor neuronBeta motor neuronA beta motor neuron is a kind of lower motor neuron, along with alpha motor neuron and gamma motor neuron. These motor neurons innervate intrafusal fibers of muscle spindles with collaterals to extrafusal fibers . Axons of beta motor neurons are myelinated...
- Muscle spindleMuscle spindleMuscle spindles are sensory receptors within the belly of a muscle, which primarily detect changes in the length of this muscle. They convey length information to the central nervous system via sensory neurons. This information can be processed by the brain to determine the position of body parts...
- Intrafusal muscle fibre
- Extrafusal muscle fiberExtrafusal muscle fiberExtrafusal muscle fiber is a term given to standard muscle fibers as to distinguish them from intrafusal muscle fibers. Extrafusal muscle fibers are innervated by alpha motor neurons and generate tension by contracting, thereby allowing for skeletal movement...
External links
- http://www.lib.mcg.edu/edu/eshuphysio/program/section8/8ch3/s8ch3_20.htm
- NIF Search - Gamma Motor Neuron via the Neuroscience Information FrameworkNeuroscience Information FrameworkThe Neuroscience Information Framework is a repository of global neuroscience web resources, including experimental, clinical, and translational neuroscience databases, knowledge bases, atlases, and genetic/genomic resources.-Description:...

