Gamma globulin
Encyclopedia

Globulin
Globulin is one of the three types of serum proteins, the others being albumin and fibrinogen. Some globulins are produced in the liver, while others are made by the immune system. The term globulin encompasses a heterogeneous group of proteins with typical high molecular weight, and both...
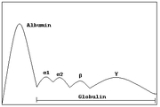
s, identified by their position after serum protein electrophoresis
Serum protein electrophoresis
Serum protein electrophoresis is a laboratory test that examines specific proteins in the blood called globulins. Blood must first be collected, usually into an airtight vial or syringe...
. The most significant gamma globulins are immunoglobulins
Antibody
An antibody, also known as an immunoglobulin, is a large Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique part of the foreign target, termed an antigen...
("Igs"), more commonly known as antibodies, although some Igs are not gamma globulins, and some gamma globulins are not Igs.
Use as medical treatment
Gamma globulin injections are usually given in an attempt to temporarily boost a patient's immunity against disease. Injections are most commonly used on patients who have been exposed to hepatitis AHepatitis A
Hepatitis A is an acute infectious disease of the liver caused by the hepatitis A virus , an RNA virus, usually spread the fecal-oral route; transmitted person-to-person by ingestion of contaminated food or water or through direct contact with an infectious person...
or measles
Measles
Measles, also known as rubeola or morbilli, is an infection of the respiratory system caused by a virus, specifically a paramyxovirus of the genus Morbillivirus. Morbilliviruses, like other paramyxoviruses, are enveloped, single-stranded, negative-sense RNA viruses...
, or to make a kidney donor and recipient compatible regardless of blood type of tissue match. Injections are also used to boost immunity in patients who cannot produce gamma globulins naturally because of an immune deficiency, such as X-linked agammaglobulinemia
X-linked agammaglobulinemia
X-linked agammaglobulinemia is a rare X-linked genetic disorder that was discovered in 1952 which affects the body's ability to fight infection. XLA is an X-linked disorder, and therefore is more common in males...
and hyper IgM syndrome
Hyper IgM syndrome
Hyper IgM syndrome is a family of genetic disorders in which the level of Immunoglobulin M antibodies is relatively high. The most common type is a result of a defect in a Th2 cell protein . The disorder causes immunodeficiencies, including a higher than normal susceptibility to various types of...
. Such injections are less common in modern medical practice than they were previously, and injections of gamma globulin previously recommended for travelers have largely been replaced by the use of hepatitis A
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is an acute infectious disease of the liver caused by the hepatitis A virus , an RNA virus, usually spread the fecal-oral route; transmitted person-to-person by ingestion of contaminated food or water or through direct contact with an infectious person...
vaccine
Vaccine
A vaccine is a biological preparation that improves immunity to a particular disease. A vaccine typically contains an agent that resembles a disease-causing microorganism, and is often made from weakened or killed forms of the microbe or its toxins...
.
Gamma globulin infusions are also used to treat some immunological diseases, such as idiopathic thrombocytopenia purpura (ITP), a disease in which the platelets are being attacked by antibodies, leading to seriously low platelet counts. Gamma globulin apparently causes the spleen to ignore the antibody-tagged platelets, thus allowing them to survive and function.
A recent clinical trial of gamma globulin in chronic fatigue syndrome patients had no recognizable benefit, while an older trial showed improvement. The success of this treatment remains uncertain.
Another theory on how gamma globulin administration works in autoimmune disease is by overloading the mechanisms which degrade gamma globulins. Overloading the degradation mechanism causes the harmful gamma globulins to have a much shorter halflife in sera.
IVIG may be used in Kawasaki disease.
Intravenous Gamma globulin was FDA approved in 2004 to reduce antibodies in a patient with kidney failure to allow that person to accept a kidney from a donor who has a different blood type, (ABO incompatible) or is an unacceptable tissue match. Stanley Jordan at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles pioneered this treatment.
Pathology
An excess is known as hypergammaglobulinemiaHypergammaglobulinemia
Hypergammaglobulinemia is a medical condition with elevated levels of gamma globulin.It is a type of immunoproliferative disorder.- Types :...
. A deficiency is known as hypogammaglobulinemia
Hypogammaglobulinemia
Hypogammaglobulinemia is a type of immune disorder characterized by a reduction in all types of gamma globulins.Hypogammaglobulinemia is a characteristic of common variable immunodeficiency.-Terminology:...
.
A disease of gamma globulins is called a "gammopathy" (for example, in monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance
Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance
Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance , formerly benign monoclonal gammopathy, is a condition in which a paraprotein is found in the blood during standard laboratory tests...
.)

