
Galilei number
Encyclopedia
In fluid dynamics
, the Galilei number (Ga), sometimes also referred to as Galileo number (see discussion), is a dimensionless number named after Italian scientist Galileo Galilei
(1564-1642).
It may be regarded as proportional to gravity forces divided by viscous forces. The Galilei number is used in viscous flow and thermal expansion calculations, for example to describe fluid film flow over walls. These flows apply to condensors or chemical columns.
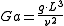
Fluid dynamics
In physics, fluid dynamics is a sub-discipline of fluid mechanics that deals with fluid flow—the natural science of fluids in motion. It has several subdisciplines itself, including aerodynamics and hydrodynamics...
, the Galilei number (Ga), sometimes also referred to as Galileo number (see discussion), is a dimensionless number named after Italian scientist Galileo Galilei
Galileo Galilei
Galileo Galilei , was an Italian physicist, mathematician, astronomer, and philosopher who played a major role in the Scientific Revolution. His achievements include improvements to the telescope and consequent astronomical observations and support for Copernicanism...
(1564-1642).
It may be regarded as proportional to gravity forces divided by viscous forces. The Galilei number is used in viscous flow and thermal expansion calculations, for example to describe fluid film flow over walls. These flows apply to condensors or chemical columns.
-
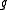 : gravitational accelerationGravitational accelerationIn physics, gravitational acceleration is the acceleration on an object caused by gravity. Neglecting friction such as air resistance, all small bodies accelerate in a gravitational field at the same rate relative to the center of mass....
: gravitational accelerationGravitational accelerationIn physics, gravitational acceleration is the acceleration on an object caused by gravity. Neglecting friction such as air resistance, all small bodies accelerate in a gravitational field at the same rate relative to the center of mass....
, (SISiSi, si, or SI may refer to :- Measurement, mathematics and science :* International System of Units , the modern international standard version of the metric system...
units: m/s2) -
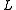 : characteristic length, (SISiSi, si, or SI may refer to :- Measurement, mathematics and science :* International System of Units , the modern international standard version of the metric system...
: characteristic length, (SISiSi, si, or SI may refer to :- Measurement, mathematics and science :* International System of Units , the modern international standard version of the metric system...
units: m) -
 : characteristic kinematic viscosity, (SISiSi, si, or SI may refer to :- Measurement, mathematics and science :* International System of Units , the modern international standard version of the metric system...
: characteristic kinematic viscosity, (SISiSi, si, or SI may refer to :- Measurement, mathematics and science :* International System of Units , the modern international standard version of the metric system...
units: m2/s)

