
Gadolinium(III) oxide
Encyclopedia
Gadolinium oxide is a inorganic compound
with the formula
Gd2
O3
. It is one of the most commonly available forms of the rare earth element
gadolinium, derivatives of which are potential contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging
.
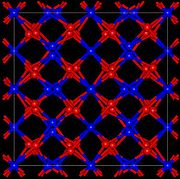 Gadolinium oxide has two most common structures: monoclinic (Pearson symbol
Gadolinium oxide has two most common structures: monoclinic (Pearson symbol
mS30, space group
C2/m, No. 12) and cubic (cI80
, Ia, No. 206). The cubic structure is similar to that of manganese(III) oxide
, which, as a mineral, is also called bixbyite
(then with a minor iron(III) content). There are two types of gadolinium sites in the cubic structure, both with a coordination number of 6 but with different geometry of the surrounding oxygen atoms. At room temperature, the cubic structure is the most stable and a phase change to the monoclinic structure takes place at 1200 °C. From 2100 °C and up to the melting point at 2420 °C, a hexagonal phase dominates.
Gadolinium oxide is a rather basic oxide, indicated by its ready reaction with carbon dioxide to give carbonates. It dissolves readily in the common mineral acids with the complication that the oxalate
, fluoride, sulfate and phosphate are very insoluble in water and may coat the grains of oxide, thereby preventing the complete dissolution.
Nanoparticles of gadolinium oxide is a potential contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging
(MRI). A dextran
-coated preparation of 20–40 nm sized gadolinium oxide particles had a relaxivity of 4.8 s−1mM−1 per gadolinium ion at 7.05 T (an unusually high field compared to the clinically used MRI scanners which mostly range from 0.5 to 3 T). Smaller particles, between 2 and 7 nm, were tested as a MRI agent in.
Inorganic compound
Inorganic compounds have traditionally been considered to be of inanimate, non-biological origin. In contrast, organic compounds have an explicit biological origin. However, over the past century, the classification of inorganic vs organic compounds has become less important to scientists,...
with the formula
Chemical formula
A chemical formula or molecular formula is a way of expressing information about the atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound....
Gd2
Gadolinium
Gadolinium is a chemical element with the symbol Gd and atomic number 64. It is a silvery-white, malleable and ductile rare-earth metal. It is found in nature only in combined form. Gadolinium was first detected spectroscopically in 1880 by de Marignac who separated its oxide and is credited with...
O3
Oxide
An oxide is a chemical compound that contains at least one oxygen atom in its chemical formula. Metal oxides typically contain an anion of oxygen in the oxidation state of −2....
. It is one of the most commonly available forms of the rare earth element
Rare earth element
As defined by IUPAC, rare earth elements or rare earth metals are a set of seventeen chemical elements in the periodic table, specifically the fifteen lanthanides plus scandium and yttrium...
gadolinium, derivatives of which are potential contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging , nuclear magnetic resonance imaging , or magnetic resonance tomography is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to visualize detailed internal structures...
.
Structure

Pearson symbol
The Pearson symbol, or Pearson notation, is used in crystallography as a means of describing a crystal structure, and was originated by W.B. Pearson. The symbol is made up of two letters followed by a number. For example:* Diamond structure, cF8...
mS30, space group
Space group
In mathematics and geometry, a space group is a symmetry group, usually for three dimensions, that divides space into discrete repeatable domains.In three dimensions, there are 219 unique types, or counted as 230 if chiral copies are considered distinct...
C2/m, No. 12) and cubic (cI80
Pearson symbol
The Pearson symbol, or Pearson notation, is used in crystallography as a means of describing a crystal structure, and was originated by W.B. Pearson. The symbol is made up of two letters followed by a number. For example:* Diamond structure, cF8...
, Ia, No. 206). The cubic structure is similar to that of manganese(III) oxide
Manganese(III) oxide
Manganese oxide is the chemical compound of formula Mn2O3.-Preparation and chemistry:Heating MnO2 in air at below 800°C α-Mn2O3 is produced . γ-Mn2O3 can be produced by oxidation followed by dehydration of manganese hydroxide...
, which, as a mineral, is also called bixbyite
Bixbyite
Bixbyite is a manganese iron oxide mineral with formula: 2O3. The iron:manganese ratio is quite variable and many specimens have almost no iron. It is a metallic dark black with a Mohs hardness of 6.0 - 6.5...
(then with a minor iron(III) content). There are two types of gadolinium sites in the cubic structure, both with a coordination number of 6 but with different geometry of the surrounding oxygen atoms. At room temperature, the cubic structure is the most stable and a phase change to the monoclinic structure takes place at 1200 °C. From 2100 °C and up to the melting point at 2420 °C, a hexagonal phase dominates.
Preparation and chemistry
Gadolinium oxide can be formed by thermal decomposition of the hydroxide, nitrate, carbonate, or oxalates. Gadolinium oxide forms on the surface of gadolinium metal.Gadolinium oxide is a rather basic oxide, indicated by its ready reaction with carbon dioxide to give carbonates. It dissolves readily in the common mineral acids with the complication that the oxalate
Oxalate
Oxalate , is the dianion with formula C2O42− also written 22−. Either name is often used for derivatives, such as disodium oxalate, 2C2O42−, or an ester of oxalic acid Oxalate (IUPAC: ethanedioate), is the dianion with formula C2O42− also written (COO)22−. Either...
, fluoride, sulfate and phosphate are very insoluble in water and may coat the grains of oxide, thereby preventing the complete dissolution.
Nanoparticles of Gd2O3
Several methods are known for the synthesis of gadolinium oxide nanoparticles, mostly based on precipitation of the hydroxide by the reaction of gadolinium ions with hydroxide, followed by thermal dehydration to the oxide. The nanoparticles are always coated with a protective material to avoid the formation of larger polycrystalline aggregates.Nanoparticles of gadolinium oxide is a potential contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging , nuclear magnetic resonance imaging , or magnetic resonance tomography is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to visualize detailed internal structures...
(MRI). A dextran
Dextran
Dextran is a complex, branched glucan composed of chains of varying lengths...
-coated preparation of 20–40 nm sized gadolinium oxide particles had a relaxivity of 4.8 s−1mM−1 per gadolinium ion at 7.05 T (an unusually high field compared to the clinically used MRI scanners which mostly range from 0.5 to 3 T). Smaller particles, between 2 and 7 nm, were tested as a MRI agent in.

