
Fractional order control
Encyclopedia
Fractional order control or (FOC) is a field of control theory
that uses the fractional order integrator
as part of the control system design toolkit.
The fundamental advantage of FOC is that the fractional order integrator weights history using a function that decays with a power-law tail. The effect is that the effects of all time are computed for each iteration of the control algorithm. This creates a 'distribution of time constants,' the upshot of which is there is no particular time constant, or resonance frequency, for the system.
In fact, the fractional integral operator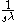 is different from any integer-order rational transfer function
is different from any integer-order rational transfer function 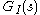 , in the sense that it is a non-local operator that possesses an infinite memory and takes into account the whole history of its input signal.
, in the sense that it is a non-local operator that possesses an infinite memory and takes into account the whole history of its input signal.
Fractional order control shows promise in many controlled environments that suffer from the classical problems of overshoot and resonance, as well as time diffuse applications such as thermal dissipation and chemical mixing.
Control theory
Control theory is an interdisciplinary branch of engineering and mathematics that deals with the behavior of dynamical systems. The desired output of a system is called the reference...
that uses the fractional order integrator
Fractional order integrator
A fractional order integrator or just simply fractional integrator is an integrator device that calculates the fractional order integral or derivative of an input. Differentiation or integration is a real or complex parameter...
as part of the control system design toolkit.
The fundamental advantage of FOC is that the fractional order integrator weights history using a function that decays with a power-law tail. The effect is that the effects of all time are computed for each iteration of the control algorithm. This creates a 'distribution of time constants,' the upshot of which is there is no particular time constant, or resonance frequency, for the system.
In fact, the fractional integral operator
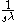 is different from any integer-order rational transfer function
is different from any integer-order rational transfer function 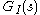 , in the sense that it is a non-local operator that possesses an infinite memory and takes into account the whole history of its input signal.
, in the sense that it is a non-local operator that possesses an infinite memory and takes into account the whole history of its input signal. Fractional order control shows promise in many controlled environments that suffer from the classical problems of overshoot and resonance, as well as time diffuse applications such as thermal dissipation and chemical mixing.
External links
- Dr. YangQuan Chen's page about fractional calculus on Google Sites
- 4th IFAC Workshop on Fractional Differentiation and Its Applications University of Extremadura, Badajoz, Spain, October 18-20, 2010
- 3rd IFAC Workshop on Fractional Differentiation and its Applications, Ankara, Turkey, 05 - 07 November, 2008
- 2nd IFAC Workshop on Fractional Differentiation and its Applications, Porto, Portugal, 19 - 21 July, 2006
- 1st IFAC Workshop on Fractional Differentiation and its Applications, Bordeaux, France, 19 - 21 July, 2004

