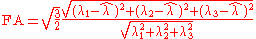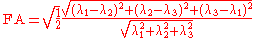Fractional anisotropy
Encyclopedia
Fractional anisotropy is a scalar
value between zero and one that describes the degree of anisotropy
of a diffusion
process. A value of zero means that diffusion is isotropic, i.e. it is unrestricted (or equally restricted) in all directions. A value of one means that diffusion occurs only along one axis and is fully restricted along all other directions. FA is a measure often used in diffusion imaging where it is thought to reflect fiber density, axon
al diameter, and myelination in white matter
. The FA is an extension of the concept of eccentricity of conic sections in 3 dimensions, normalized to the unit range.
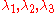 ) of the diffusion tensor
) of the diffusion tensor
.. The eigenvectors give the directions in which the ellipsoid has major axes, and the corresponding eigenvalues
give the directions in which the ellipsoid has major axes, and the corresponding eigenvalues 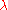 give the magnitude of the peak in that direction.
give the magnitude of the peak in that direction.
with the trace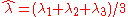
Alternatively, FA can be calculated as
It can be noted that if all the eigenvalues are equal, which happens in the case of a sphere, the FA becomes 0. The FA can go to a maximum value of 1, and this rarely happens in real data, and the ellipsoid then reduces to a line in the direction of that eigenvector. This means that the diffusion is confined to that direction alone.
A drawback of the Diffusion Tensor model is that it can account only for Gaussian
diffusion processes, which has been found to be inadequate in accurately representing the true diffusion process in the human brain. Due to this, higher order models using spherical harmonics and Orientation Diffusion Functions (ODF) have been used to define newer and richer estimates of the anisotropy, called Generalized Fractional Anisotropy. GFA computations use samples of the ODF to evaluate the anisotropy in diffusion. They can also be easily calculated by using the Spherical Harmonic coefficients of the ODF model.
Scalar (mathematics)
In linear algebra, real numbers are called scalars and relate to vectors in a vector space through the operation of scalar multiplication, in which a vector can be multiplied by a number to produce another vector....
value between zero and one that describes the degree of anisotropy
Anisotropy
Anisotropy is the property of being directionally dependent, as opposed to isotropy, which implies identical properties in all directions. It can be defined as a difference, when measured along different axes, in a material's physical or mechanical properties An example of anisotropy is the light...
of a diffusion
Diffusion
Molecular diffusion, often called simply diffusion, is the thermal motion of all particles at temperatures above absolute zero. The rate of this movement is a function of temperature, viscosity of the fluid and the size of the particles...
process. A value of zero means that diffusion is isotropic, i.e. it is unrestricted (or equally restricted) in all directions. A value of one means that diffusion occurs only along one axis and is fully restricted along all other directions. FA is a measure often used in diffusion imaging where it is thought to reflect fiber density, axon
Axon
An axon is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body or soma....
al diameter, and myelination in white matter
White matter
White matter is one of the two components of the central nervous system and consists mostly of myelinated axons. White matter tissue of the freshly cut brain appears pinkish white to the naked eye because myelin is composed largely of lipid tissue veined with capillaries. Its white color is due to...
. The FA is an extension of the concept of eccentricity of conic sections in 3 dimensions, normalized to the unit range.
Definition
A Diffusion Ellipsoid is completely represented by the Diffusion Tensor, D. FA is calculated from the eigenvalues (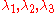 ) of the diffusion tensor
) of the diffusion tensorTensor
Tensors are geometric objects that describe linear relations between vectors, scalars, and other tensors. Elementary examples include the dot product, the cross product, and linear maps. Vectors and scalars themselves are also tensors. A tensor can be represented as a multi-dimensional array of...
.. The eigenvectors
 give the directions in which the ellipsoid has major axes, and the corresponding eigenvalues
give the directions in which the ellipsoid has major axes, and the corresponding eigenvalues 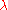 give the magnitude of the peak in that direction.
give the magnitude of the peak in that direction.with the trace

Alternatively, FA can be calculated as
It can be noted that if all the eigenvalues are equal, which happens in the case of a sphere, the FA becomes 0. The FA can go to a maximum value of 1, and this rarely happens in real data, and the ellipsoid then reduces to a line in the direction of that eigenvector. This means that the diffusion is confined to that direction alone.
Details
This can be visualized well with an ellipsoid, which is defined by the tensor whose eigenvectors and eigenvalues are used for it's numerical calculation. The FA of a sphere is 0 since the diffusion is anisotropic, and there is equal probability of diffusion in all directions. The eigenvectors and eigenvalues of the Diffusion Tensor give a complete representation of the diffusion process. FA quantifies the pointedness of the ellipsoid, but does not give information about which direction it is pointing to.A drawback of the Diffusion Tensor model is that it can account only for Gaussian
GAUSSIAN
Gaussian is a computational chemistry software program initially released in 1970 by John Pople and his research group at Carnegie-Mellon University as Gaussian 70. It has been continuously updated since then...
diffusion processes, which has been found to be inadequate in accurately representing the true diffusion process in the human brain. Due to this, higher order models using spherical harmonics and Orientation Diffusion Functions (ODF) have been used to define newer and richer estimates of the anisotropy, called Generalized Fractional Anisotropy. GFA computations use samples of the ODF to evaluate the anisotropy in diffusion. They can also be easily calculated by using the Spherical Harmonic coefficients of the ODF model.