
Foveated imaging
Encyclopedia
Foveated imaging is a digital image processing
technique in which the image resolution
, or amount of detail, varies across the image
according to one or more "fixation points."
A fixation point indicates the highest resolution region of the image and corresponds to the center of the eye
's retina
, the fovea
.
The location of a fixation point may be specified in many ways.
For example, when viewing an image on a computer monitor, one may specify a fixation using a pointing device
, like a computer mouse.
Eye trackers which precisely measure the eye's position and movement are also commonly used to determine fixation points in perception experiments.
When the display is manipulated with the use of an eye tracker, this is known as a gaze contingent display
.
Fixations may also be determined automatically using computer algorithms.
Some common applications of foveated imaging include imaging sensor hardware
and image compression.
For descriptions of these and other applications, see the list below.
Foveated imaging is also commonly referred to as space variant imaging or gaze contingent imaging.

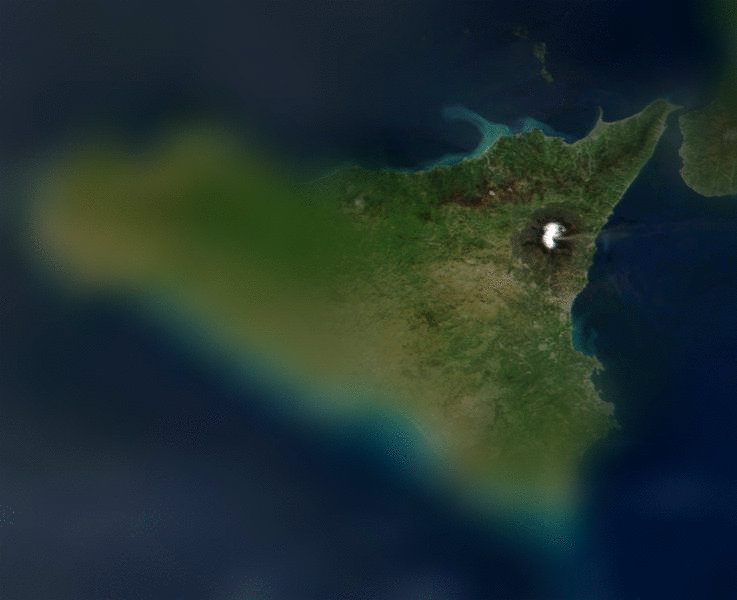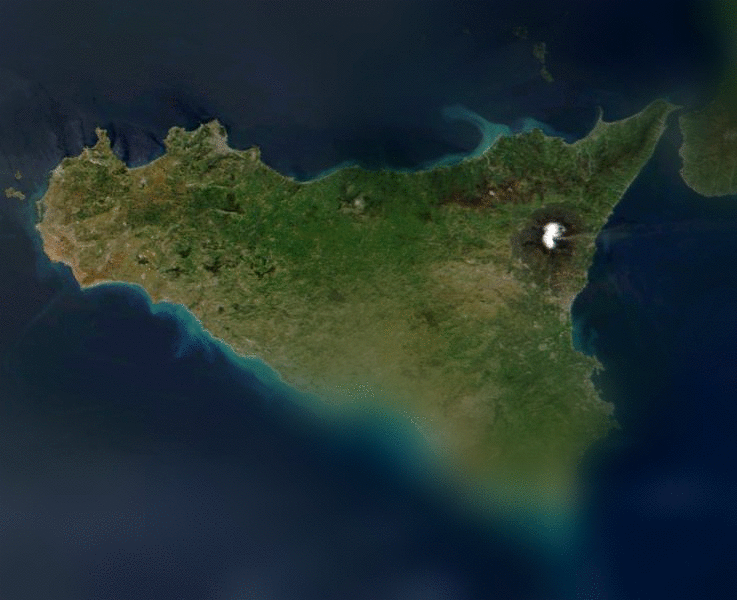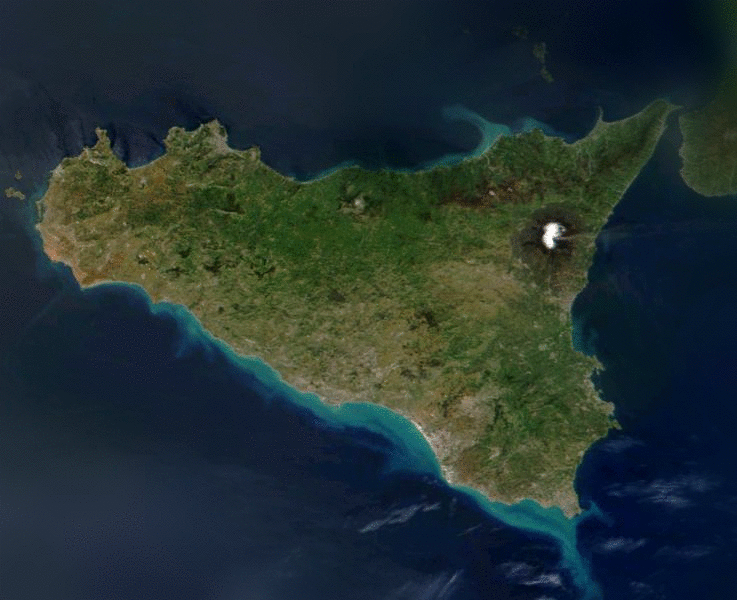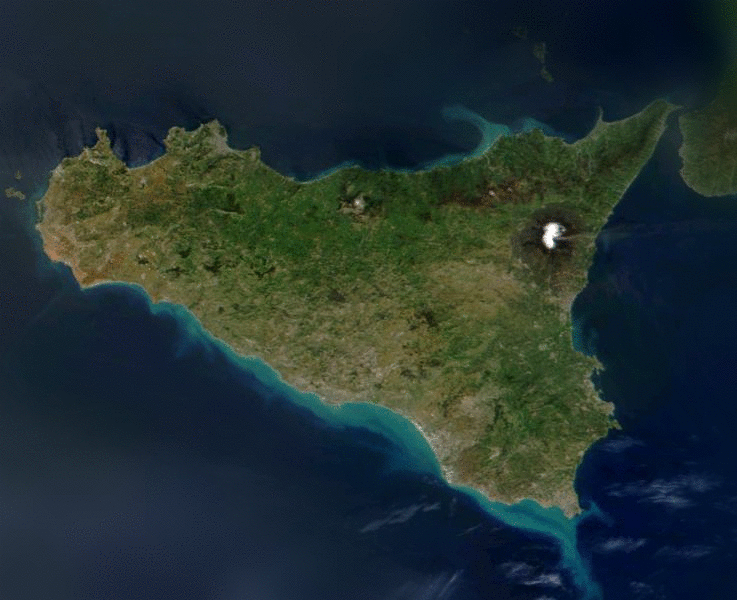
One may take advantage of this fact in order to compactly code images.
If one knows the viewer's approximate point of gaze, one may reduce the amount of information contained in the image as the distance from the point of gaze increases. Because the fall-off in the eye's resolution is dramatic, the potential reduction in display information can be substantial. Also, foveation encoding may be applied to the image before other types of image compression are applied and therefore can result in a multiplicative reduction.
. By utilizing an eye-tracker and holding the blurred region fixed relative to the viewer's gaze, the viewer will have a visual experience similar to that of a person with an actual scotoma. The figure on the right shows a frame from a simulation of a glaucoma patient with the eye fixated on the word "similar."
Digital image processing
Digital image processing is the use of computer algorithms to perform image processing on digital images. As a subcategory or field of digital signal processing, digital image processing has many advantages over analog image processing...
technique in which the image resolution
Image resolution
Image resolution is an umbrella term that describes the detail an image holds. The term applies to raster digital images, film images, and other types of images. Higher resolution means more image detail....
, or amount of detail, varies across the image
Digital image
A digital image is a numeric representation of a two-dimensional image. Depending on whether or not the image resolution is fixed, it may be of vector or raster type...
according to one or more "fixation points."
A fixation point indicates the highest resolution region of the image and corresponds to the center of the eye
Human eye
The human eye is an organ which reacts to light for several purposes. As a conscious sense organ, the eye allows vision. Rod and cone cells in the retina allow conscious light perception and vision including color differentiation and the perception of depth...
's retina
Retina
The vertebrate retina is a light-sensitive tissue lining the inner surface of the eye. The optics of the eye create an image of the visual world on the retina, which serves much the same function as the film in a camera. Light striking the retina initiates a cascade of chemical and electrical...
, the fovea
Fovea
The fovea centralis, also generally known as the fovea , is a part of the eye, located in the center of the macula region of the retina....
.
The location of a fixation point may be specified in many ways.
For example, when viewing an image on a computer monitor, one may specify a fixation using a pointing device
Pointing device
A pointing device is an input interface that allows a user to input spatial data to a computer...
, like a computer mouse.
Eye trackers which precisely measure the eye's position and movement are also commonly used to determine fixation points in perception experiments.
When the display is manipulated with the use of an eye tracker, this is known as a gaze contingent display
Gaze-contingency paradigm
The gaze-contingency paradigm is a general term for techniques allowing to change the display on a computer screen in function of where the viewer is looking.Gaze-contingent techniques are part of the eye movement field of study in psychology...
.
Fixations may also be determined automatically using computer algorithms.
Some common applications of foveated imaging include imaging sensor hardware
and image compression.
For descriptions of these and other applications, see the list below.
Foveated imaging is also commonly referred to as space variant imaging or gaze contingent imaging.
Applications


Compression
Contrast sensitivity falls off dramatically as one moves from the center of the retina to the periphery.One may take advantage of this fact in order to compactly code images.
If one knows the viewer's approximate point of gaze, one may reduce the amount of information contained in the image as the distance from the point of gaze increases. Because the fall-off in the eye's resolution is dramatic, the potential reduction in display information can be substantial. Also, foveation encoding may be applied to the image before other types of image compression are applied and therefore can result in a multiplicative reduction.
Foveated sensors
Foveated sensors are multiresolution hardware devices that allow image data to be collected with higher resolution concentrated at a fixation point. An advantage to using foveated sensor hardware is that the image collection and encoding can occur much faster than in a system that post-processes a high resolution image in software.Simulation
Foveated imaging has been used to simulate visual fields with arbitrary spatial resolution. For example, one may present video containing a blurred region representing a scotomaScotoma
A scotoma is an area of partial alteration in one's field of vision consisting of a partially diminished or entirely degenerated visual acuity which is surrounded by a field of normal - or relatively well-preserved - vision.Every normal mammalian eye has a scotoma in its field of vision, usually...
. By utilizing an eye-tracker and holding the blurred region fixed relative to the viewer's gaze, the viewer will have a visual experience similar to that of a person with an actual scotoma. The figure on the right shows a frame from a simulation of a glaucoma patient with the eye fixated on the word "similar."
Quality assessment
Foveated imaging may be useful in providing a subjective image quality measure. Traditional image quality measures, such as peak signal-to-noise ratio, are typically performed on fixed resolution images and do not take into account some aspects of the human visual system, like the change in spatial resolution across the retina. A foveated quality index may therefore more accurately determine image quality as perceived by humans.Image database retrieval
In databases that contain very high resolution images, such as a satellite image database, it may be desirable to interactively retrieve images in order to reduce retrieval time. Foveated imaging allows one to scan low resolution images and retrieve only high resolution portions as they are needed. This is sometimes called progressive transmission.See also
- FoveaFoveaThe fovea centralis, also generally known as the fovea , is a part of the eye, located in the center of the macula region of the retina....
- Gaze-contingency paradigmGaze-contingency paradigmThe gaze-contingency paradigm is a general term for techniques allowing to change the display on a computer screen in function of where the viewer is looking.Gaze-contingent techniques are part of the eye movement field of study in psychology...
- Human visual system modelHuman Visual System ModelA human visual system model is used by image processing, video processing and computer vision experts to deal with biological and psychological processes that are not yet fully understood. Such a model is used to simplify the behaviours of what is a very complex system...
- Low visionLow visionLow vision is a subspecialty within the professions of optometry and ophthalmology dealing with individuals who have reduced vision even when using the best possible spectacle or contact lens correction available. It can be a result of either congenital disease Low vision is a subspecialty within...
- Image compressionImage compressionThe objective of image compression is to reduce irrelevance and redundancy of the image data in order to be able to store or transmit data in an efficient form.- Lossy and lossless compression :...
- Digital image processingDigital image processingDigital image processing is the use of computer algorithms to perform image processing on digital images. As a subcategory or field of digital signal processing, digital image processing has many advantages over analog image processing...
- Eye tracker
- Eye movement in language readingEye movement in language readingEye movement in reading involves visual processing of words. This was first described by the French ophthalmologist Louis Émile Javal in the late 19th century. He reported that eyes do not move continuously along a line of text, but make short rapid movements intermingled with short stops...
External links
- http://live.ece.utexas.edu
- http://svi.cps.utexas.edu
- http://webvision.med.utah.edu/

