
Fourier shell correlation
Encyclopedia
In applied mathematics
, the three-dimensional Fourier shell correlation (FSC) measures the normalised cross-correlation
coefficient between two 3-dimensional volumes over corresponding shells in Fourier
space (i.e., as a function of spatial frequency), a three-dimensional extension of the Fourier ring correlation (FRC).
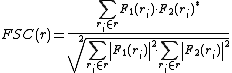
where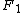 is the complex structure Factor for volume 1,
is the complex structure Factor for volume 1, 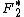 is the complex conjugate of the structure Factor for volume 2, and
is the complex conjugate of the structure Factor for volume 2, and 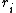 is the individual voxel element at radius
is the individual voxel element at radius  . In this form, the FSC takes two three-dimensional data sets and converts them into a one-dimensional array.
. In this form, the FSC takes two three-dimensional data sets and converts them into a one-dimensional array.
, the resolution of a structure is typically measured by the Fourier shell correlation (FSC). To measure the FSC, the data needs to be separated into two groups. Typically, the even particles form the first group and odd particles the second based on their order. This is commonly referred to as the even-odd test. Most publications quote the FSC 0.5 cutoff, which refers to the when correlation coefficient of the Fourier shells is equal to 0.5. Determining the resolution threshold remains a controversial topic: fixed-value thresholds were argued to be based on incorrect statistical assumptions. Many other criteria using the FSC curve exist, including 3-σ criterion, 5-σ criterion, and the 0.143 cutoff. The half-bit criterion indicates at which resolution we have collected enough information to reliably interpret the 3-dimensional volume, and the (modified) 3-sigma
criterion indicates where the FSC systematically emerges above the expected random correlations of the background noise.
Applied mathematics
Applied mathematics is a branch of mathematics that concerns itself with mathematical methods that are typically used in science, engineering, business, and industry. Thus, "applied mathematics" is a mathematical science with specialized knowledge...
, the three-dimensional Fourier shell correlation (FSC) measures the normalised cross-correlation
Cross-correlation
In signal processing, cross-correlation is a measure of similarity of two waveforms as a function of a time-lag applied to one of them. This is also known as a sliding dot product or sliding inner-product. It is commonly used for searching a long-duration signal for a shorter, known feature...
coefficient between two 3-dimensional volumes over corresponding shells in Fourier
Fourier
Fourier most commonly refers to Joseph Fourier , French mathematician and physicist, or the mathematics, physics, and engineering terms named in his honor for his work on the concepts underlying them:In mathematics:...
space (i.e., as a function of spatial frequency), a three-dimensional extension of the Fourier ring correlation (FRC).
Calculation
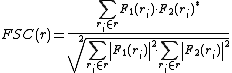
where
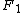 is the complex structure Factor for volume 1,
is the complex structure Factor for volume 1, 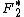 is the complex conjugate of the structure Factor for volume 2, and
is the complex conjugate of the structure Factor for volume 2, and 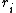 is the individual voxel element at radius
is the individual voxel element at radius  . In this form, the FSC takes two three-dimensional data sets and converts them into a one-dimensional array.
. In this form, the FSC takes two three-dimensional data sets and converts them into a one-dimensional array.Application in Cryo-electron microscopy
In cryo-electron microscopyCryo-electron microscopy
Cryo-electron microscopy , or electron cryomicroscopy, is a form of transmission electron microscopy where the sample is studied at cryogenic temperatures...
, the resolution of a structure is typically measured by the Fourier shell correlation (FSC). To measure the FSC, the data needs to be separated into two groups. Typically, the even particles form the first group and odd particles the second based on their order. This is commonly referred to as the even-odd test. Most publications quote the FSC 0.5 cutoff, which refers to the when correlation coefficient of the Fourier shells is equal to 0.5. Determining the resolution threshold remains a controversial topic: fixed-value thresholds were argued to be based on incorrect statistical assumptions. Many other criteria using the FSC curve exist, including 3-σ criterion, 5-σ criterion, and the 0.143 cutoff. The half-bit criterion indicates at which resolution we have collected enough information to reliably interpret the 3-dimensional volume, and the (modified) 3-sigma
Sigma
Sigma is the eighteenth letter of the Greek alphabet, and carries the 'S' sound. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 200. When used at the end of a word, and the word is not all upper case, the final form is used, e.g...
criterion indicates where the FSC systematically emerges above the expected random correlations of the background noise.

