Four-tensor
Encyclopedia
Syntax
General four-tensors are usually written as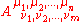 , with the indices taking integral values from 0 to 3. Such a tensor is said to have contravariant rank n and covariant rank m .
, with the indices taking integral values from 0 to 3. Such a tensor is said to have contravariant rank n and covariant rank m .Examples
One of the simplest non-trivial examples of a four-tensor is the four-displacement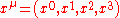 , a four-tensor with contravariant rank 1 and covariant rank 0. Four-tensors of this kind are usually known as four-vectors. Here the component
, a four-tensor with contravariant rank 1 and covariant rank 0. Four-tensors of this kind are usually known as four-vectors. Here the component  gives the displacement of a body in time (time is multiplied by the speed of light
gives the displacement of a body in time (time is multiplied by the speed of light  so that
so that 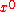 has units of length). The remaining components of the four-displacement form the spatial displacement vector
has units of length). The remaining components of the four-displacement form the spatial displacement vector 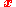 .
.Similarly, the four-momentum
Four-momentum
In special relativity, four-momentum is the generalization of the classical three-dimensional momentum to four-dimensional spacetime. Momentum is a vector in three dimensions; similarly four-momentum is a four-vector in spacetime...
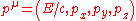 of a body is equivalent to the energy-momentum tensor of said body. The element
of a body is equivalent to the energy-momentum tensor of said body. The element 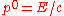 represents the momentum
represents the momentumMomentum
In classical mechanics, linear momentum or translational momentum is the product of the mass and velocity of an object...
of the body as a result of it travelling through time (directly comparable to the internal energy of the body). The elements
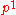 ,
, 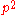 and
and 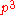 correspond to the momentum
correspond to the momentumMomentum
In classical mechanics, linear momentum or translational momentum is the product of the mass and velocity of an object...
of the body as a result of it travelling through space, written in vector notation as
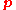 .
.The electromagnetic field tensor is an example of a rank two contravariant tensor :