
Fle3
Encyclopedia
Fle3 is a Web
-based learning environment or virtual learning environment
. More precisely Fle3 is server
software for computer supported collaborative learning (CSCL).
Fle3 is designed to support learner and group centered work that concentrates on creating and developing expressions of knowledge (i.e. knowledge artefacts). Fle3 supports study groups to implement knowledge building
, creative problem solving
and scientific method
in an inquiry learning process, for example the progressive inquiry
method.
Fle3 user interface is translated to more than 20 languages including most of the European languages and Chinese. Fle3 is used in more than 70 countries.
Fle3 is a Zope
product, written in Python
. Fle3 is open source
and free software
released under the GNU General Public Licence (GPL).
When Fle3 was released in 2002 the developers were claiming that the name comes from "Fle3 is a Learning Environment", with intertextual reference to the name GNU
(GNU is Not Unix).
Fle3 WebTops can be used by teachers and students to store different items (documents, files, links, knowledge building notes) related to their studies, organize them to folders and share them with others.
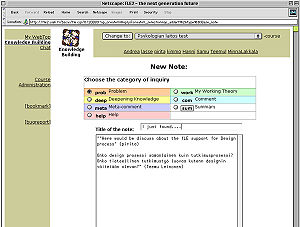
Fle3 Knowledge Building is group tool for having knowledge building dialogues, theory building and debates in a shared database. Knowledge Building tool includes Knowledge Types to scaffold and structure the process.
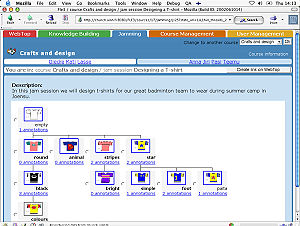
Fle3 Jamming tool is a shared space for collaborative construction of digital artefacts (pictures, text, audio, video). A study group may work together with some digital artefacts by simply uploading and downloading files. Versions are tracked automatically and different versions are displayed graphically.
For teachers and administrators Fle3 offers tools to manage users and study projects.
The knowledge types guides pupils to think adequate and important things related to the process, and this way helps them to write more substantial notes to the discussion forum. As an aid for users to follow the knowledge building discourse, users may take different views to the knowledge building discussion by sorting the notes as a discussion thread, by writer, by knowledge type, or by date.
The Knowledge Building tool contains two default knowledge type sets: (1) Progressive Inquiry, and (2) Design Thinking. Depending on the selected knowledge types set, users get guidelines and a checklist on how to write their notes to the discussion forum. Each knowledge type is also color-coded making them fast to recognize and learn.
, Helsinki, Finland. Fle3 software is based on the Future Learning Environment concept promoting learning process, which differs from traditional teacher and didactic-based teaching by emphasising students active role in a learning process.
The objective was to study alternative approaches of using information and communication technologies (ICT) in teaching and learning, and to design alternative learning practices and tools. At that time, the strong e-learning movement was seen to promote rather naïve conception of human learning. The acquisition metaphor of learning, which emphasizes learning as a process where students are supplied with pieces of knowledge (Sfard 1998), was getting stronger.
The researchers of the FLE project brought to the discussion more advanced conceptions of learning, such as participation metaphor (Sfard 1998) and knowledge creation metaphor (Paavola et al. 2002). However, the objective of the FLE project was not only to bring new theoretical approaches to the discussion, but also to design learning practices and technology based on the theories. The results of this work culminated in the progressive inquiry learning model (Hakkarainen et al. 2001; Muukkonen et al. 1999; 2005) and in the Fle3 software (http://fle3.uiah.fi).
The history of virtual learning environments
shows how the e-learning and Learning Management Systems (LMS), with course-centred outlook and focus on delivery of learning content, was, and is probably still, the mainstream approach to use of ICT in education. Although in mid-2000 the growing popularity of blogs and wikis and the consideration how they could be used in teaching and learning has led the mainstream research and development community of virtual learning to re-consider the existing e-learning paradigms.
and Marlene Scardamalia
, and their concept of Knowledge building
. In the design of FLE software, Bereiter's and Scardamalia's Computer-Supported Intentional Learning Environment (CSILE) was used as a reference.
However, there are also many differences between the two software. For instance, already in the early design specifications of FLE there was the idea of shared artefacts that are collaboratively constructed alongside the knowledge building activities. In FLE vocabulary the activity, and the tool supporting it, is called “jamming”. Also the idea of archiving the results of the study work and to make them then available for other study groups makes FLE very different from the CSILE, which was primary designed to be a system used in a classroom. Another difference is related to the Web. From the very beginning FLE has been web-based system, and has taken in use all the advantages the flexible platform is offering, whereas the original CSILE was a client-sever system.
The first prototype server with FLE software was set up in 1998 and announced in early 1999. The software was named to be Fle-Tools. The software was designed in Media Lab
in Helsinki but programmed by a Finnish company called NSD Consulting Oy.
Fle-Tools was developed in a Future Learning Environment project funded by Tekes
- the National Technology Agency of Finland. The project partners were Media Lab
of the University of Art and Design Helsinki
(coordinator), Centre for Research on Networked Learning and Knowledge Building in the Department of Psychology of the University of Helsinki
, Finnish Ministry of Education, Finnish new media company Grey Interactive, Finnish teleoperator Sonera, and Finnish educational publisher SanomaWSOY
.
Fle-Tools was described to be: (1) www-based service for computer supported collaborative learning (CSCL); (2) on-line learning community and teamwork environment; (3) collection of server-based applications and databases and (4) cross-platform for end users (www-browser in Linux, Mac, Win PC, WebTV, Nokia Communicator, etc.). The tools of Fle3-Tools were:
In 1999 Fle-Tools was tested in several university course at the University of Helsinki and the University of Art and Design Helsinki. The results form the pilots were published in scientific conferences and journals.
In the end of 1999, The Finnish operator Sonera, who was a key partner in the Future Learning Environment project, decided to draw back from the project and started to develop their own product based on Fle-Tools. This resulted as a breakdown of the original Future Learning Environment research and development project.
 The next generation FLE software was developed during the years 1999-2001. Because of the collapse of the original Future Learning Environment project consortium in 1999 the research and design partners felt that they must continue the FLE development on their own.
The next generation FLE software was developed during the years 1999-2001. Because of the collapse of the original Future Learning Environment project consortium in 1999 the research and design partners felt that they must continue the FLE development on their own.
In 2000 the Fle2 project got funding from the Nordic Council of Ministers NordUnet 2 program. The partners of the project were Media Lab in Helsinki, Department of Communication, Journalism and Computer Science of Roskilde University in Denmark, and Department of Psychology of the University of Helsinki.
The new software was named Fle2 and released online for free downloading in April 2001. Fle2 was based on the design of Fle-Tools, but this time the software development and programming was carried-out in Media Lab Helsinki. The Fle2 was built on top of the BSCW - Basic Support for Cooperative Work software developed by the Fraunhofer Society
in Germany.
The tools of Fle2 were personal WebTops and Knowledge Building. Th Fle2 did not have Jam Session or Library tools of the earlier Fle-Tools. In the Fle2 WebTop there were two new features compared to the earlier Fle-Tools: (1) "yellow notes" made it possible to add notes to other people WebTops when visiting them, and (2) chat with whiteboard for chating and drawing with other users online.
In 2002 the design and development team in Helsinki realized that BSCW was not the right platform for developing the FLE software. The main reason for giving up the development of Fle2 on top of the BSCW was the fact that BSCW was not an Open Source / Free Software.
 Fle3 is the third and the latest version of FLE software. The first version of Fle3 was released on February 15, 2002. The latest version 1.5 was released in April 2005.
Fle3 is the third and the latest version of FLE software. The first version of Fle3 was released on February 15, 2002. The latest version 1.5 was released in April 2005.
Fle3 was largely developed in the Innovative Technology for Collaborative Learning and Knowledge Building (ITCOLE) project, funded by the European Commission
in the Information Society Technologies (IST) framework's 'School of Tomorrow' program.
The ITCOLE project was coordinated by the Media Lab in Helsinki. The technical development partners included the developers of BSCW - Basic Support for Cooperative Work in Fraunhofer Society
and Department of Computer Science of the University of Murcia in Spain. Testing of different software in schools was coordinated by Helsinki City Education Department and pedagogical research was carried out by researcher from University of Helsinki, University of Amsterdam, University of Salerno, University of Rome La Sapienza, University of Athens and University of Utrecht.
In the ITCOLE project there were several parallel software development projects. At first Fle3 was developed in Media Lab in Helsinki as a user interface and interaction demonstration for the main software development taking place in Fraunhofer and based on their BSCW system. The University of Murcia's main task was to develop the synchronous communications tools, which were then integrated experimentally to BSCW and Fle3. The software based on BSCW was named at first Synergeia and later BSCL (Basic Support for Collaborative Learning).
During the course of the project Fle3 was found user friendly, accessible, and technically reliable for a wider use. This way it ended up to be not only a UI and interaction prototype but also software of its own. Finally Fle3 became one of the main results of the ITCOLE project.
There has been no noticeable development in the Fle3 project since 2006.
World Wide Web
The World Wide Web is a system of interlinked hypertext documents accessed via the Internet...
-based learning environment or virtual learning environment
Virtual learning environment
Defined largely by usage, the term virtual learning environment has most, if not all, of the following salient properties:* It is Web-based* It uses Web 2.0 tools for rich 2-way interaction* It includes a content management system...
. More precisely Fle3 is server
Server (computing)
In the context of client-server architecture, a server is a computer program running to serve the requests of other programs, the "clients". Thus, the "server" performs some computational task on behalf of "clients"...
software for computer supported collaborative learning (CSCL).
Fle3 is designed to support learner and group centered work that concentrates on creating and developing expressions of knowledge (i.e. knowledge artefacts). Fle3 supports study groups to implement knowledge building
Knowledge building
The Knowledge Building theory was created and developed by Carl Bereiter and Marlene Scardamalia for describing what a community of learners needs to accomplish in order to create knowledge...
, creative problem solving
Creative problem solving
Creative problem solving is the mental process of creating a solution to a problem. It is a special form of problem solving in which the solution is independently created rather than learned with assistance.Creative problem solving always involves creativity....
and scientific method
Scientific method
Scientific method refers to a body of techniques for investigating phenomena, acquiring new knowledge, or correcting and integrating previous knowledge. To be termed scientific, a method of inquiry must be based on gathering empirical and measurable evidence subject to specific principles of...
in an inquiry learning process, for example the progressive inquiry
Progressive inquiry
Progressive inquiry is a pedagogical model which aims at facilitating the same kind of productive knowledge practices of working with knowledge in education that characterize scientific research communities...
method.
Fle3 user interface is translated to more than 20 languages including most of the European languages and Chinese. Fle3 is used in more than 70 countries.
Fle3 is a Zope
Zope
Zope is a free and open-source, object-oriented Web application server written in the Python programming language. Zope stands for "Z Object Publishing Environment", and was the first system using the now common object publishing methodology for the Web...
product, written in Python
Python (programming language)
Python is a general-purpose, high-level programming language whose design philosophy emphasizes code readability. Python claims to "[combine] remarkable power with very clear syntax", and its standard library is large and comprehensive...
. Fle3 is open source
Open source
The term open source describes practices in production and development that promote access to the end product's source materials. Some consider open source a philosophy, others consider it a pragmatic methodology...
and free software
Free software
Free software, software libre or libre software is software that can be used, studied, and modified without restriction, and which can be copied and redistributed in modified or unmodified form either without restriction, or with restrictions that only ensure that further recipients can also do...
released under the GNU General Public Licence (GPL).
Origin of the name
The abbreviation FLE comes from the words Future Learning Environment. The number 3 in the name refers to the number of times the software has been built from scratch.When Fle3 was released in 2002 the developers were claiming that the name comes from "Fle3 is a Learning Environment", with intertextual reference to the name GNU
GNU
GNU is a Unix-like computer operating system developed by the GNU project, ultimately aiming to be a "complete Unix-compatible software system"...
(GNU is Not Unix).
Features
Fle3 contains three learning tools for collaborative learning and several administration tools.Fle3 WebTops can be used by teachers and students to store different items (documents, files, links, knowledge building notes) related to their studies, organize them to folders and share them with others.
Fle3 Knowledge Building is group tool for having knowledge building dialogues, theory building and debates in a shared database. Knowledge Building tool includes Knowledge Types to scaffold and structure the process.
Fle3 Jamming tool is a shared space for collaborative construction of digital artefacts (pictures, text, audio, video). A study group may work together with some digital artefacts by simply uploading and downloading files. Versions are tracked automatically and different versions are displayed graphically.
For teachers and administrators Fle3 offers tools to manage users and study projects.
Knowledge type sets
An important feature of the Knowledge Building tool is the knowledge type sets that are scaffolding and structuring the discussions. For instance, for a progressive inquiry learning teachers may use knowledge type set designed for this purpose. Progressive Inquiry knowledge type set contains the following five knowledge types: Problem, My Explanation, Scientific Explanation, Evaluation of the Process and Summary. Every time a pupil is posting something to the discussion, she must choose what knowledge type her note represents.The knowledge types guides pupils to think adequate and important things related to the process, and this way helps them to write more substantial notes to the discussion forum. As an aid for users to follow the knowledge building discourse, users may take different views to the knowledge building discussion by sorting the notes as a discussion thread, by writer, by knowledge type, or by date.
The Knowledge Building tool contains two default knowledge type sets: (1) Progressive Inquiry, and (2) Design Thinking. Depending on the selected knowledge types set, users get guidelines and a checklist on how to write their notes to the discussion forum. Each knowledge type is also color-coded making them fast to recognize and learn.
History
Development of Fle3 software was started in 1998 in a Future Learning Environment (http://fle.uiah.fi) research and development project in Media LabMedia Lab Helsinki
The Media Lab is a unit focusing on digital design within the Department of Media at the School of Art and Design, Aalto University in Helsinki, Finland. The lab provides MA and Doctoral education, and does research on design and production of digital culture, digital media, interaction design and...
, Helsinki, Finland. Fle3 software is based on the Future Learning Environment concept promoting learning process, which differs from traditional teacher and didactic-based teaching by emphasising students active role in a learning process.
The objective was to study alternative approaches of using information and communication technologies (ICT) in teaching and learning, and to design alternative learning practices and tools. At that time, the strong e-learning movement was seen to promote rather naïve conception of human learning. The acquisition metaphor of learning, which emphasizes learning as a process where students are supplied with pieces of knowledge (Sfard 1998), was getting stronger.
The researchers of the FLE project brought to the discussion more advanced conceptions of learning, such as participation metaphor (Sfard 1998) and knowledge creation metaphor (Paavola et al. 2002). However, the objective of the FLE project was not only to bring new theoretical approaches to the discussion, but also to design learning practices and technology based on the theories. The results of this work culminated in the progressive inquiry learning model (Hakkarainen et al. 2001; Muukkonen et al. 1999; 2005) and in the Fle3 software (http://fle3.uiah.fi).
The history of virtual learning environments
History of virtual learning environments
A virtual learning environment is a system that creates an environment designed to facilitate teachers in the management of educational courses for their students, especially a system using computer hardware and software, which involves distance learning...
shows how the e-learning and Learning Management Systems (LMS), with course-centred outlook and focus on delivery of learning content, was, and is probably still, the mainstream approach to use of ICT in education. Although in mid-2000 the growing popularity of blogs and wikis and the consideration how they could be used in teaching and learning has led the mainstream research and development community of virtual learning to re-consider the existing e-learning paradigms.
Fle-Tools (1998-1999)
In the late 1990s the research, development and design team members of the first FLE project were greatly influenced by the work of Carl BereiterCarl Bereiter
Carl Bereiter is an education researcher, professor emeritus at the Ontario Institute for Studies in Education, University of Toronto and co-director of the Education Commons at OISE/UofT, a division that integrates all information and technology services from this institute.His areas of research...
and Marlene Scardamalia
Marlene Scardamalia
Marlene Scardamalia is an education researcher, professor at the Ontario Institute for Studies in Education, University of Toronto.-Contributions:She is considered one of the pioneers in Computer-supported collaborative learning...
, and their concept of Knowledge building
Knowledge building
The Knowledge Building theory was created and developed by Carl Bereiter and Marlene Scardamalia for describing what a community of learners needs to accomplish in order to create knowledge...
. In the design of FLE software, Bereiter's and Scardamalia's Computer-Supported Intentional Learning Environment (CSILE) was used as a reference.
However, there are also many differences between the two software. For instance, already in the early design specifications of FLE there was the idea of shared artefacts that are collaboratively constructed alongside the knowledge building activities. In FLE vocabulary the activity, and the tool supporting it, is called “jamming”. Also the idea of archiving the results of the study work and to make them then available for other study groups makes FLE very different from the CSILE, which was primary designed to be a system used in a classroom. Another difference is related to the Web. From the very beginning FLE has been web-based system, and has taken in use all the advantages the flexible platform is offering, whereas the original CSILE was a client-sever system.
The first prototype server with FLE software was set up in 1998 and announced in early 1999. The software was named to be Fle-Tools. The software was designed in Media Lab
Media Lab Helsinki
The Media Lab is a unit focusing on digital design within the Department of Media at the School of Art and Design, Aalto University in Helsinki, Finland. The lab provides MA and Doctoral education, and does research on design and production of digital culture, digital media, interaction design and...
in Helsinki but programmed by a Finnish company called NSD Consulting Oy.
Fle-Tools was developed in a Future Learning Environment project funded by Tekes
Tekes
Tekes – the Finnish Funding Agency for Technology and Innovation, a part of Finnish Ministry of Employment and the Economy, is the most important public funding agency for research funding in Finland...
- the National Technology Agency of Finland. The project partners were Media Lab
Media Lab Helsinki
The Media Lab is a unit focusing on digital design within the Department of Media at the School of Art and Design, Aalto University in Helsinki, Finland. The lab provides MA and Doctoral education, and does research on design and production of digital culture, digital media, interaction design and...
of the University of Art and Design Helsinki
University of Art and Design Helsinki
Aalto University School of Art and Design , known commonly as TaiK, is the largest art university in the Nordic countries, and was founded in 1871. Media Centre Lume – the National Research and Development Center of audiovisual media – is also located in the university...
(coordinator), Centre for Research on Networked Learning and Knowledge Building in the Department of Psychology of the University of Helsinki
University of Helsinki
The University of Helsinki is a university located in Helsinki, Finland since 1829, but was founded in the city of Turku in 1640 as The Royal Academy of Turku, at that time part of the Swedish Empire. It is the oldest and largest university in Finland with the widest range of disciplines available...
, Finnish Ministry of Education, Finnish new media company Grey Interactive, Finnish teleoperator Sonera, and Finnish educational publisher SanomaWSOY
SanomaWSOY
Sanoma Oyj is a leading media group in the Nordic countries with operations in 20 European countries, based in Helsinki...
.
Fle-Tools was described to be: (1) www-based service for computer supported collaborative learning (CSCL); (2) on-line learning community and teamwork environment; (3) collection of server-based applications and databases and (4) cross-platform for end users (www-browser in Linux, Mac, Win PC, WebTV, Nokia Communicator, etc.). The tools of Fle3-Tools were:
- WebTop: Personal open desk top in the web to store and share digital materials;
- Knowledge Building: Asynchronous conferencing system with 'Categories of Inquiry' and different searching capabilities (by date, person, category of inquiry, users own notes, answers to own notes);
- Jam Session: Asynchronous multi-user environment for collaborative design, writing, software development, etc.;
- Library: Adaptive medium to publish and browse multimedia course materials
- Administration: Tools for administer users, groups, courses and course materials.
In 1999 Fle-Tools was tested in several university course at the University of Helsinki and the University of Art and Design Helsinki. The results form the pilots were published in scientific conferences and journals.
In the end of 1999, The Finnish operator Sonera, who was a key partner in the Future Learning Environment project, decided to draw back from the project and started to develop their own product based on Fle-Tools. This resulted as a breakdown of the original Future Learning Environment research and development project.
Fle2 (1999-2001)

In 2000 the Fle2 project got funding from the Nordic Council of Ministers NordUnet 2 program. The partners of the project were Media Lab in Helsinki, Department of Communication, Journalism and Computer Science of Roskilde University in Denmark, and Department of Psychology of the University of Helsinki.
The new software was named Fle2 and released online for free downloading in April 2001. Fle2 was based on the design of Fle-Tools, but this time the software development and programming was carried-out in Media Lab Helsinki. The Fle2 was built on top of the BSCW - Basic Support for Cooperative Work software developed by the Fraunhofer Society
Fraunhofer Society
The Fraunhofer Society is a German research organization with 60 institutes spread throughout Germany, each focusing on different fields of applied science . It employs around 18,000, mainly scientists and engineers, with an annual research budget of about €1.65 billion...
in Germany.
The tools of Fle2 were personal WebTops and Knowledge Building. Th Fle2 did not have Jam Session or Library tools of the earlier Fle-Tools. In the Fle2 WebTop there were two new features compared to the earlier Fle-Tools: (1) "yellow notes" made it possible to add notes to other people WebTops when visiting them, and (2) chat with whiteboard for chating and drawing with other users online.
In 2002 the design and development team in Helsinki realized that BSCW was not the right platform for developing the FLE software. The main reason for giving up the development of Fle2 on top of the BSCW was the fact that BSCW was not an Open Source / Free Software.
Fle3 (2002 - 2006)

Fle3 was largely developed in the Innovative Technology for Collaborative Learning and Knowledge Building (ITCOLE) project, funded by the European Commission
European Commission
The European Commission is the executive body of the European Union. The body is responsible for proposing legislation, implementing decisions, upholding the Union's treaties and the general day-to-day running of the Union....
in the Information Society Technologies (IST) framework's 'School of Tomorrow' program.
The ITCOLE project was coordinated by the Media Lab in Helsinki. The technical development partners included the developers of BSCW - Basic Support for Cooperative Work in Fraunhofer Society
Fraunhofer Society
The Fraunhofer Society is a German research organization with 60 institutes spread throughout Germany, each focusing on different fields of applied science . It employs around 18,000, mainly scientists and engineers, with an annual research budget of about €1.65 billion...
and Department of Computer Science of the University of Murcia in Spain. Testing of different software in schools was coordinated by Helsinki City Education Department and pedagogical research was carried out by researcher from University of Helsinki, University of Amsterdam, University of Salerno, University of Rome La Sapienza, University of Athens and University of Utrecht.
In the ITCOLE project there were several parallel software development projects. At first Fle3 was developed in Media Lab in Helsinki as a user interface and interaction demonstration for the main software development taking place in Fraunhofer and based on their BSCW system. The University of Murcia's main task was to develop the synchronous communications tools, which were then integrated experimentally to BSCW and Fle3. The software based on BSCW was named at first Synergeia and later BSCL (Basic Support for Collaborative Learning).
During the course of the project Fle3 was found user friendly, accessible, and technically reliable for a wider use. This way it ended up to be not only a UI and interaction prototype but also software of its own. Finally Fle3 became one of the main results of the ITCOLE project.
There has been no noticeable development in the Fle3 project since 2006.

