
Fita
Encyclopedia
- For other meanings see FITAFITA-Acronyms:* Friendly Islands Teachers' Association, a trade union in Tonga* Federación Argentina de Industrias Textiles* Fédération Internationale de Tir à l'Arc, the World Archery Federation...
.
Fita is a letter of the Early Cyrillic alphabet
Early Cyrillic alphabet
The Early Cyrillic alphabet is a writing system developed in the First Bulgarian Empire in the 9th or 10th century to write the Old Church Slavonic liturgical language...
. The shape and the name of the letter are derived from the Greek letter Theta (Θ θ).
In the Cyrillic numeral system
Cyrillic numerals
The Cyrillic numerals are a numbering system derived from the Cyrillic script, used by South and East Slavic peoples. The system was used in Russia as late as the early 18th century when Peter the Great replaced it with Arabic numerals....
, Fita has a value of 9.
Shape
In traditional (Church Slavonic) fonts, the central line is typically about twice the width of letter's body and has serifs similar to ones on the letter T: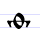 . Sometimes the line is drawn as low as the baseline which makes the letter almost identical to Д and may cause reading difficulties.
. Sometimes the line is drawn as low as the baseline which makes the letter almost identical to Д and may cause reading difficulties.In modern-style (Petrine or civil) fonts, depending on the typeface, the centre line may be either straight or waving. In regular textfonts, both ends of the line touch the "O". Stylish fonts may use a shorter line, either placed entirely inside the "O" (a standard shape for Greek uppercase Theta) or touching the circle at one point.
Old Russian and Church Slavonic
The traditional Russian name of the letter is fita (or, in pre-1918 spelling). Fita was mainly used to write proper names and loanwords derived from or via Greek. RussiansRussians
The Russian people are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Russia, speaking the Russian language and primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries....
pronounced these names with the sound /f/ instead of /θ/ (like the pronunciation of ⟨th⟩ in "thin"), for example "Theodore" was pronounced as "Feodor" (now "Fyodor").
Early texts in Russian
Russian language
Russian is a Slavic language used primarily in Russia, Belarus, Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan. It is an unofficial but widely spoken language in Ukraine, Moldova, Latvia, Turkmenistan and Estonia and, to a lesser extent, the other countries that were once constituent republics...
(and in the Russian recension of Church Slavonic) demonstrate an increasing interchangeability of and Ф. Some scribes preferred one of the two letters and ignored the other. There existed an orthographical system to write in an initial position and Ф elsewhere. Since the middle of the 17th century, selection between and Ф was re-adjusted to exactly follow the Greek origin, the system still in use in Church Slavonic orthography.
Russian
In the first variant of the Petrine Russian alphabet (1707–1708), the letter Ф was eliminated and Fita became the only way to represent /f/. Later (1710) the letter Ф (with the same etymological rule of spelling and Ф) was restored and both letters co-existed until the 1918 spelling reform, when Fita was eliminated and replaced by the letter Ef (Ф ф).Note that many Greek words with Theta were adopted in Russian with Te (Т т) instead of Fita (mostly through Latin or other Western European languages): театръ (theatre), теорема (theorem), атлетъ (athlete), пантера (panther), фталевый (phthalic), etc. Sometimes dual spelling/pronunciation existed: /атеизмъ (atheism), /алгоритмъ (algorithm), /католическiй (Catholic), etc.; the variants with Fita (in modern spelling with Ф) are typically more archaic or special.
Other Slavic languages
In most other Slavic languagesSlavic languages
The Slavic languages , a group of closely related languages of the Slavic peoples and a subgroup of Indo-European languages, have speakers in most of Eastern Europe, in much of the Balkans, in parts of Central Europe, and in the northern part of Asia.-Branches:Scholars traditionally divide Slavic...
, Fita was pronounced /t/ and was replaced with Te (Т т). For example, the Bulgarian and Serbian version of Theodore is Тодор Todor or Теодор Teodor.
Romanian
Called thita, ⟨⟩ is part of the Romanian Cyrillic alphabetRomanian Cyrillic alphabet
The Romanian Cyrillic alphabet was used to write the Romanian language before 1860–1862, when it was officially replaced by a Latin-based Romanian alphabet. Cyrillic remained in occasional use until circa 1920...
, which was used until about 1860.
Aleut
Fita is used in the Cyrillic version of the AleutAleut language
Aleut is a language of the Eskimo–Aleut language family. It is the heritage language of the Aleut people living in the Aleutian Islands, Pribilof Islands, and Commander Islands. As of 2007 there were about 150 speakers of Aleut .- Dialects :Aleut is alone with the Eskimo languages in the...
alphabet, typically in loanwords.
Related letters and other similar characters
- Θ θ/ϑ : Greek letter Theta : Cyrillic letter Barred O, currently used in the KazakhKazakh languageKazakh is a Turkic language which belongs to the Kipchak branch of the Turkic languages, closely related to Nogai and Karakalpak....
, TuvanTuvan languageTuvan , also known as Tuvinian, Tyvan or Tuvin, is a Turkic language spoken in the Republic of Tuva in south-central Siberia in Russia. The language has borrowed a great number of roots from the Mongolian language and more recently from the Russian language...
, and MongolianMongolian languageThe Mongolian language is the official language of Mongolia and the best-known member of the Mongolic language family. The number of speakers across all its dialects may be 5.2 million, including the vast majority of the residents of Mongolia and many of the Mongolian residents of the Inner...
languages
Computing codes
| character | ||||
| Unicode name | CYRILLIC CAPITAL LETTER FITA | CYRILLIC SMALL LETTER FITA | ||
| character encoding | decimal | hex | decimal | hex |
| Unicode Unicode Unicode is a computing industry standard for the consistent encoding, representation and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems... |
1138 | 0472 | 1139 | 0473 |
| UTF-8 UTF-8 UTF-8 is a multibyte character encoding for Unicode. Like UTF-16 and UTF-32, UTF-8 can represent every character in the Unicode character set. Unlike them, it is backward-compatible with ASCII and avoids the complications of endianness and byte order marks... |
209 178 | D1 B2 | 209 179 | D1 B3 |
| Numeric character reference Numeric character reference A numeric character reference is a common markup construct used in SGML and other SGML-related markup languages such as HTML and XML. It consists of a short sequence of characters that, in turn, represent a single character from the Universal Character Set of Unicode... |
Ѳ | Ѳ | ѳ | ѳ |

