
Feline odontoclastic resorptive lesion
Encyclopedia

Cat
The cat , also known as the domestic cat or housecat to distinguish it from other felids and felines, is a small, usually furry, domesticated, carnivorous mammal that is valued by humans for its companionship and for its ability to hunt vermin and household pests...
s characterized by resorption of the tooth
Tooth
Teeth are small, calcified, whitish structures found in the jaws of many vertebrates that are used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores, also use teeth for hunting or for defensive purposes. The roots of teeth are embedded in the Mandible bone or the Maxillary bone and are...
by odontoclasts, cells similar to osteoclast
Osteoclast
An osteoclast is a type of bone cell that removes bone tissue by removing its mineralized matrix and breaking up the organic bone . This process is known as bone resorption. Osteoclasts were discovered by Kolliker in 1873...
s. A FORL is also known as a neck lesion, cervical neck lesion, cervical line erosion, feline caries, or feline cavity. It is one of the most common disease of domestic cats, affecting up to two-thirds. FORLs have been seen more recently in the history of feline medicine due to the advancing ages of cats, but 800-year-old cat skeletons have shown evidence of this disease. Purebred cats, especially Siamese
Siamese (cat)
The Siamese is one of the first distinctly recognized breeds of Oriental cat. The origins of the breed are unknown, but it is believed to be from Thailand. In Thailand, where they are one of several native breeds, they are called Wichian Mat...
and Persians, may be more susceptible.
Gingiva
The gingiva , or gums, consists of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth.-General description:...
l border. They are often covered with calculus
Calculus (dental)
In dentistry, calculus or tartar is a form of hardened dental plaque. It is caused by the continual accumulation of minerals from saliva on plaque on the teeth...
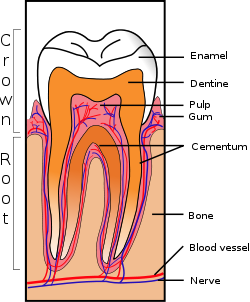
or gingival tissue. It is a progressive disease, usually starting with loss of cementum
Cementum
Cementum is a specialized calcified substance covering the root of a tooth. Cementum is excreted by cells called cementoblasts within the root of the tooth and is thickest at the root apex. These cementoblasts develop from undifferentiated mesenchymal cells in the connective tissue of the dental...
and dentin
Dentin
Dentine is a calcified tissue of the body, and along with enamel, cementum, and pulp is one of the four major components of teeth. Usually, it is covered by enamel on the crown and cementum on the root and surrounds the entire pulp...
and leading to penetration of the pulp
Pulp (tooth)
The dental pulp is the part in the center of a tooth made up of living connective tissue and cells called odontoblasts.- Anatomy :Each person can have a total of up to 52 pulp organs, 32 in the permanent and 20 in the primary teeth....
cavity. Resorption continues up the dentinal tubules
Dental canaliculi
The dental canaliculi are the blood supply of a tooth. The number and size of the canaliculi decrease as the tubules move away from the pulp and toward the enamel or cementum....
into the tooth crown. The enamel
Tooth enamel
Tooth enamel, along with dentin, cementum, and dental pulp is one of the four major tissues that make up the tooth in vertebrates. It is the hardest and most highly mineralized substance in the human body. Tooth enamel is also found in the dermal denticles of sharks...
is also resorbed or undermined to the point of tooth fracture. Resorbed cementum and dentin is replaced with bone-like tissue.
Symptoms
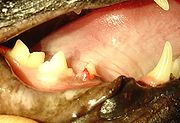
Premolar
The premolar teeth or bicuspids are transitional teeth located between the canine and molar teeth. In humans, there are two premolars per quadrant, making eight premolars total in the mouth. They have at least two cusps. Premolars can be considered as a 'transitional tooth' during chewing, or...
is the most commonly affected tooth.
Cause
The definitive cause of FORLs is unknown, but histologicallyHistology
Histology is the study of the microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues of plants and animals. It is performed by examining cells and tissues commonly by sectioning and staining; followed by examination under a light microscope or electron microscope...
destruction of the cementum and other mineralized tissue of the tooth root by odontoclasts is seen. It occurs secondary to the loss of the protective covering of the root (the periodontal ligament
Periodontal ligament
The periodontal fiber or periodontal ligament, commonly abbreviated as the PDL, is a group of specialized connective tissue fibers that essentially attach a tooth to the alveolar bone within which it sits...
s) and possibly to a stimulus such as periodontal disease
Periodontal disease
Periodontitis is a set of inflammatory diseases affecting the periodontium, i.e., the tissues that surround and support the teeth. Periodontitis involves progressive loss of the alveolar bone around the teeth, and if left untreated, can lead to the loosening and subsequent loss of teeth...
and the release of cytokine
Cytokine
Cytokines are small cell-signaling protein molecules that are secreted by the glial cells of the nervous system and by numerous cells of the immune system and are a category of signaling molecules used extensively in intercellular communication...
s, leading to odontoclast migration. However, FORLs can develop in the absence of inflammation. The natural inhibition to root resorption provided by the lining of the root may be altered by increased amounts of Vitamin D
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of fat-soluble secosteroids. In humans, vitamin D is unique both because it functions as a prohormone and because the body can synthesize it when sun exposure is adequate ....
, in cats supplied by their diet.
Treatment
Treatment for FORLs is limited to tooth extractionExtraction (dental)
A dental extraction is the removal of a tooth from the mouth. Extractions are performed for a wide variety of reasons, including tooth decay that has destroyed enough tooth structure to render the tooth non-restorable...
to create a mouth free of pain. Amputation of the tooth crown without root removal has also been advocated in cases free of periodontal disease because the roots often completely resorb. However, X-ray
Radiography
Radiography is the use of X-rays to view a non-uniformly composed material such as the human body. By using the physical properties of the ray an image can be developed which displays areas of different density and composition....
s are recommended prior to this treatment to document root resorption and lack of the periodontal ligament.
Tooth restoration
Dental restoration
A dental restoration or dental filling is a dental restorative material used to restore the function, integrity and morphology of missing tooth structure. The structural loss typically results from caries or external trauma. It is also lost intentionally during tooth preparation to improve the...
is not recommended because resorption of the tooth will continue underneath the restoration. Use of alendronate
Alendronate
Alendronic acid or alendronate sodium — sold as Fosamax by Merck — is a bisphosphonate drug used for osteoporosis and several other bone diseases. It is marketed alone as well as in combination with vitamin D . Merck's U.S...
has been studied to prevent FORLs and decrease progression of existing lesions.
Differential diagnosis: dental caries
True dental cariesDental caries
Dental caries, also known as tooth decay or a cavity, is an irreversible infection usually bacterial in origin that causes demineralization of the hard tissues and destruction of the organic matter of the tooth, usually by production of acid by hydrolysis of the food debris accumulated on the...
is uncommon among companion animals. Although rarely seen in cats, the incidence of caries in dogs has been estimated at approximately 5%. The term feline cavities is commonly used to refer to FORLs, however, sacchrolytic acid-producing bacteria are not involved in this condition.
External links
- Felipedia
- Feline odontoclastic resorption lesions - American Veterinary Dental College position statement.
- Feline Oral Resorptive Lesions (FORL) from Veterinary Partner

