Feed-forward
Encyclopedia
Feed-forward is a term describing an element or pathway within a control system
which passes a controlling signal from a source in the control system's external environment, often a command signal from an external operator, to a load elsewhere in its external environment. A control system which has only feed-forward behavior responds to its control signal in a pre-defined way without responding to how the load reacts; it is in contrast with a system that also has feedback
, which adjusts the output to take account of how it affects the load, and how the load itself may vary unpredictably; the load is considered to belong to the external environment of the system.
Some prerequisites are needed for control scheme to be reliable by pure feed-forward without feedback: the external command or controlling signal must be available, and the effect of the output of the system on the load should be known (that usually means that the load must be predictably unchanging with time). Sometimes pure feed-forward control without feedback is called 'ballistic', because once a control signal has been sent, it cannot be further adjusted; any corrective adjustment must be by way of a new control signal. In contrast 'cruise control' adjusts the output in response to the load that it encounters, by a feedback mechanism.
These systems could be in control theory
, physiology
or computing
.
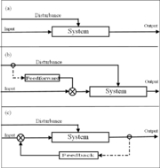
 There are three types of control systems: open loop, feed-forward, and feedback.
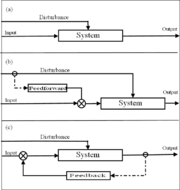
There are three types of control systems: open loop, feed-forward, and feedback.
An example of a pure open loop control system is manual non-power-assisted steering of a motor car; the steering system does not have access to an auxiliary power source and does not respond to varying resistance to turning of the direction wheels; the driver must make that response without help from the steering system. In comparison, power steering
has access to a controlled auxiliary power source, which depends on the engine speed. When the steering wheel is turned, a valve is opened which allows fluid under pressure to turn the driving wheels. A sensor monitors that pressure so that the valve only opens enough to cause the correct pressure to reach the wheel turning mechanism. This is feed-forward control where the output of the system, the change in direction of travel of the vehicle, plays no part in the system. See Model predictive control
.
If you include the driver in the system, then he does provide a feedback path by observing the direction of travel and compensating for errors by turning the steering wheel. In that case you have a feedback system, and the block labeled "System" in Figure(c) is a feed-forward system.
In other words, systems of different types can be nested, and the overall system regarded as a black-box.
, feed-forward control is exemplified by the normal anticipatory regulation of heartbeat in advance of actual physical exertion. Feed-forward control can be likened to learned anticipatory responses to known cues. Feedback regulation of the heartbeat provides further adaptiveness to the running eventualities of physical exertion.
A pure feed-forward system is distinct from a homeostatic control system, which has the function of keeping the internal environment of the body steady or constant or in a prolonged steady state of readiness, and relies mainly on feedback, indeed on negative feedback, in addition to the feedforward elements of the system.
for the latter. A motif which predominantly appears in all known networks (E. coli, Yeast
,...) is A activates B, A and B activate C. This motif has been shown to be a feed forward system, detecting non-temporary change of environment. This feed forward control theme is commonly observed in hematopoietic cell lineage development, where irreversible commitments are made.
In computing
, feed-forward normally refers to a perceptron
network in which the outputs from all neuron
s go to following but not preceding layers, so there are no feedback loops. The connections are set up during a training phase, which in effect is when the system is a feedback system.
, used feed-forward amplifiers to diminish linear distortion. This more complex method allowed wider bandwidth than earlier feedback
systems. Optical fiber
, however, made such systems obsolete before many were built.
is a discipline within the field of automatic controls used in automation.
Control system
A control system is a device, or set of devices to manage, command, direct or regulate the behavior of other devices or system.There are two common classes of control systems, with many variations and combinations: logic or sequential controls, and feedback or linear controls...
which passes a controlling signal from a source in the control system's external environment, often a command signal from an external operator, to a load elsewhere in its external environment. A control system which has only feed-forward behavior responds to its control signal in a pre-defined way without responding to how the load reacts; it is in contrast with a system that also has feedback
Feedback
Feedback describes the situation when output from an event or phenomenon in the past will influence an occurrence or occurrences of the same Feedback describes the situation when output from (or information about the result of) an event or phenomenon in the past will influence an occurrence or...
, which adjusts the output to take account of how it affects the load, and how the load itself may vary unpredictably; the load is considered to belong to the external environment of the system.
Some prerequisites are needed for control scheme to be reliable by pure feed-forward without feedback: the external command or controlling signal must be available, and the effect of the output of the system on the load should be known (that usually means that the load must be predictably unchanging with time). Sometimes pure feed-forward control without feedback is called 'ballistic', because once a control signal has been sent, it cannot be further adjusted; any corrective adjustment must be by way of a new control signal. In contrast 'cruise control' adjusts the output in response to the load that it encounters, by a feedback mechanism.
These systems could be in control theory
Control theory
Control theory is an interdisciplinary branch of engineering and mathematics that deals with the behavior of dynamical systems. The desired output of a system is called the reference...
, physiology
Physiology
Physiology is the science of the function of living systems. This includes how organisms, organ systems, organs, cells, and bio-molecules carry out the chemical or physical functions that exist in a living system. The highest honor awarded in physiology is the Nobel Prize in Physiology or...
or computing
Computing
Computing is usually defined as the activity of using and improving computer hardware and software. It is the computer-specific part of information technology...
.
Overview
With feed-forward control, the disturbances are measured and accounted for before they have time to affect the system. In the house example, a feed-forward system may measure the fact that the door is opened and automatically turn on the heater before the house can get too cold. The difficulty with feed-forward control is that the effect of the disturbances on the system must be accurately predicted, and there must not be any unmeasured disturbances. For instance, if a window were opened that was not being measured, the feed-forward-controlled thermostat might still let the house cool down.
An example of a pure open loop control system is manual non-power-assisted steering of a motor car; the steering system does not have access to an auxiliary power source and does not respond to varying resistance to turning of the direction wheels; the driver must make that response without help from the steering system. In comparison, power steering
Power steering
Power steering helps drivers steer vehicles by augmenting steering effort of the steering wheel.Hydraulic or electric actuators add controlled energy to the steering mechanism, so the driver needs to provide only modest effort regardless of conditions. Power steering helps considerably when a...
has access to a controlled auxiliary power source, which depends on the engine speed. When the steering wheel is turned, a valve is opened which allows fluid under pressure to turn the driving wheels. A sensor monitors that pressure so that the valve only opens enough to cause the correct pressure to reach the wheel turning mechanism. This is feed-forward control where the output of the system, the change in direction of travel of the vehicle, plays no part in the system. See Model predictive control
Model predictive control
Model Predictive Control, or MPC, is an advanced method of process control that has been in use in the process industries such as chemical plants and oil refineries since the 1980s...
.
If you include the driver in the system, then he does provide a feedback path by observing the direction of travel and compensating for errors by turning the steering wheel. In that case you have a feedback system, and the block labeled "System" in Figure(c) is a feed-forward system.
In other words, systems of different types can be nested, and the overall system regarded as a black-box.
Physiological feed-forward system
In physiologyPhysiology
Physiology is the science of the function of living systems. This includes how organisms, organ systems, organs, cells, and bio-molecules carry out the chemical or physical functions that exist in a living system. The highest honor awarded in physiology is the Nobel Prize in Physiology or...
, feed-forward control is exemplified by the normal anticipatory regulation of heartbeat in advance of actual physical exertion. Feed-forward control can be likened to learned anticipatory responses to known cues. Feedback regulation of the heartbeat provides further adaptiveness to the running eventualities of physical exertion.
A pure feed-forward system is distinct from a homeostatic control system, which has the function of keeping the internal environment of the body steady or constant or in a prolonged steady state of readiness, and relies mainly on feedback, indeed on negative feedback, in addition to the feedforward elements of the system.
Gene regulation and feed-forward
The cross regulation of genes can be represented by a graph, where genes are the nodes and one node is linked to another if the former is a transcription factorTranscription factor
In molecular biology and genetics, a transcription factor is a protein that binds to specific DNA sequences, thereby controlling the flow of genetic information from DNA to mRNA...
for the latter. A motif which predominantly appears in all known networks (E. coli, Yeast
Yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic micro-organisms classified in the kingdom Fungi, with 1,500 species currently described estimated to be only 1% of all fungal species. Most reproduce asexually by mitosis, and many do so by an asymmetric division process called budding...
,...) is A activates B, A and B activate C. This motif has been shown to be a feed forward system, detecting non-temporary change of environment. This feed forward control theme is commonly observed in hematopoietic cell lineage development, where irreversible commitments are made.
Feed-forward systems in computing
Main article: PerceptronPerceptron
The perceptron is a type of artificial neural network invented in 1957 at the Cornell Aeronautical Laboratory by Frank Rosenblatt. It can be seen as the simplest kind of feedforward neural network: a linear classifier.- Definition :...
In computing
Computing
Computing is usually defined as the activity of using and improving computer hardware and software. It is the computer-specific part of information technology...
, feed-forward normally refers to a perceptron
Perceptron
The perceptron is a type of artificial neural network invented in 1957 at the Cornell Aeronautical Laboratory by Frank Rosenblatt. It can be seen as the simplest kind of feedforward neural network: a linear classifier.- Definition :...
network in which the outputs from all neuron
Neuron
A neuron is an electrically excitable cell that processes and transmits information by electrical and chemical signaling. Chemical signaling occurs via synapses, specialized connections with other cells. Neurons connect to each other to form networks. Neurons are the core components of the nervous...
s go to following but not preceding layers, so there are no feedback loops. The connections are set up during a training phase, which in effect is when the system is a feedback system.
Long distance telephony
In the early 1970s, intercity coaxial transmission systems, including L-carrierL-carrier
SystemYearFrequencyCoax per cableDistance between repeatersVoice circuits per coax tubeL-119413 MHz48 miles600L-21942840 kHz416 miles360L-319508 MHz84 miles1,860L-4196717 MHz202 miles3,600L-5197257 MHz221 mile10,800L-5E197566 MHz221 mile13,200...
, used feed-forward amplifiers to diminish linear distortion. This more complex method allowed wider bandwidth than earlier feedback
Feedback
Feedback describes the situation when output from an event or phenomenon in the past will influence an occurrence or occurrences of the same Feedback describes the situation when output from (or information about the result of) an event or phenomenon in the past will influence an occurrence or...
systems. Optical fiber
Optical fiber
An optical fiber is a flexible, transparent fiber made of a pure glass not much wider than a human hair. It functions as a waveguide, or "light pipe", to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber. The field of applied science and engineering concerned with the design and application of...
, however, made such systems obsolete before many were built.
Automation and Machine Control
Feedforward controlFeedforward Control
Feedforward control is a term that has specific meaning within the field of CPU based Automatic Controls. The discipline of “feedforward controls” as it relates to modern, CPU based automatic controls is widely discussed, but is seldom practiced due to the difficulty and expense of developing or...
is a discipline within the field of automatic controls used in automation.
Further reading
- S. Mangan A. Zaslaver & U. Alon, "The coherent feed-forward loop serves as a sign-sensitive delay element in transcription networks", J. Molecular Biology 334:197-204 (2003).
- Foss, S., Foss, K., & Trapp. (2002). Contemporary Perspectives on Rhetoric (3rd ed.). Waveland Press, Inc.

