Federal Enterprise Architecture
Encyclopedia
A federal enterprise architecture (FEA) is the enterprise architecture
of a federal government
. It provides a common methodology for information technology (IT) acquisition, use, and disposal in the Federal government.
 Enterprise architecture (EA) is a management practice for aligning resources to improve business performance and help government agencies better execute their core mission
Enterprise architecture (EA) is a management practice for aligning resources to improve business performance and help government agencies better execute their core mission
s. An EA describes the current and future state of the agency, and lays out a plan for transitioning from the current state to the desired future state. A federal enterprise architecture is a work in progress to achieve these goals.
The U.S. federal enterprise architecture (FEA) is an initiative of the U.S. Office of Management and Budget that aims to comply with the Clinger-Cohen Act
and provide a common methodology for IT acquisition in the United States federal government
. It is designed to ease sharing of information and resources across federal agencies, reduce costs, and improve citizen services.
(EA) within any Federal Agency for a system that transcends multiple inter-agency boundaries. It builds on common business practices and designs that cross organizational boundaries, among others the NIST Enterprise Architecture Model
. The FEAF provides an enduring standard for developing and documenting architecture descriptions of high-priority areas. It provides guidance in describing architectures for multi-organizational functional segments of the Federal Government.
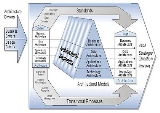
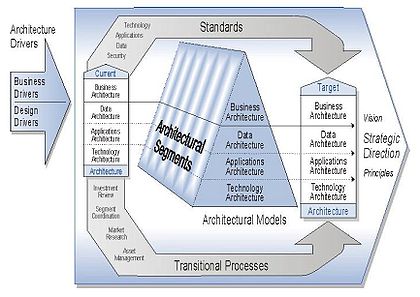
These federal architectural segments collectively constitute the federal enterprise architecture. In 2001, the Federal Architecture Working Group (FAWG) was sponsoring the development of Enterprise Architecture products for trade and grant Federal architecture segments. Methoda prescribed way of approaching a particular problem. As shown in the figure, the FEAF partitions a given architecture into business, data, applications, and technology architectures. The FEAF overall framework created that time, see image, includes the first three columns of the Zachman Framework
and the Spewak
's Enterprise Architecture Planning
methodology.
 The FEA is built using an assortment of reference model
The FEA is built using an assortment of reference model
s, that develop a common taxonomy
and ontology for describing IT resources. These include the, (see image):
It is designed to ease sharing of information and resources across federal agencies, reduce costs, and improve citizen services. It is an initiative of the US Office of Management and Budget that aims to comply with the Clinger-Cohen Act
.
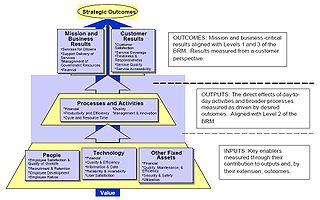 The PRM is a standardized framework to measure the performance of major IT investments and their contribution to program performance. The PRM has three main purposes:
The PRM is a standardized framework to measure the performance of major IT investments and their contribution to program performance. The PRM has three main purposes:
The PRM uses a number of existing approaches to performance measurement, including the Balanced Scorecard
, Baldrige Criteria, value measuring methodology
, program logic models
, the value chain, and the Theory of Constraints
. In addition, the PRM was informed by what agencies are currently measuring through PART assessments, GPRA, enterprise architecture
, and Capital Planning and Investment Control. The PRM is currently composed of four measurement areas:
 The "FEA Business Reference Model" is business reference model
The "FEA Business Reference Model" is business reference model
, a function-driven framework for describing the business operations of the Federal Government independent of the agencies that perform them. This business reference model provides an organized, hierarchical construct for describing the day-to-day business operations of the Federal government using a functionally driven approach. The BRM is the first layer of the Federal Enterprise Architecture and it is the main viewpoint for the analysis of data, service components and technology.
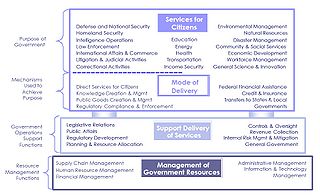
The BRM is broken down into four areas:
The Business Reference Model provides a framework that facilitates a functional (as opposed to organizational) view of the federal government’s LoBs, including its internal operations and its services for the citizens, independent of the agencies, bureaus and offices that perform them. By describing the federal government around common business areas instead of by a stovepiped, agency-by-agency view, the BRM promotes agency collaboration and serves as the underlying foundation for the FEA and E-Gov strategies.
While the BRM does provide an improved way of thinking about government operations, it is only a model; its true utility can only be realized when it is effectively used. The functional approach promoted by the BRM will do little to help accomplish the goals of E-Government if it is not incorporated into EA business architectures and the management processes of all Federal agencies and OMB.
 The Service Component Reference Model (SRM) is a business and performance-driven, functional framework that classifies Service Components with respect to how they support business and/or performance objectives. The SRM is intended for use to support the discovery of government-wide business and application Service Components in IT investments and assets. The SRM is structured across horizontal and vertical service domains that, independent of the business functions, can provide a leverage-able foundation to support the reuse of applications, application capabilities, components, and business services.
The Service Component Reference Model (SRM) is a business and performance-driven, functional framework that classifies Service Components with respect to how they support business and/or performance objectives. The SRM is intended for use to support the discovery of government-wide business and application Service Components in IT investments and assets. The SRM is structured across horizontal and vertical service domains that, independent of the business functions, can provide a leverage-able foundation to support the reuse of applications, application capabilities, components, and business services.
The SRM establishes the following domains:
Each Service Domain is decomposed into Service Types. For example, the three Service Types associated with the Customer Services Domain are: Customer Preferences; Customer Relationship Management; and Customer Initiated Assistance. And each Service Type is decomposed further into components. For example, the four components within the Customer Preferences Service Type include: Personalization; Subscriptions; Alerts and Notifications; and Profile Management.
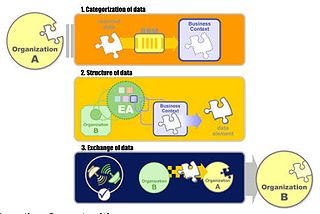 The Data Reference Model
The Data Reference Model
(DRM) describes, at an aggregate level, the data and information that support government program and business line operations. This model enables agencies to describe the types of interaction and exchanges that occur between the Federal Government and citizens. The DRM categorizes government information into greater levels of detail. It also establishes a classification for Federal data and identifies duplicative data resources. A common data model will streamline information exchange processes within the Federal government and between government and external stakeholders.
Volume One of the DRM provides a high-level overview of the structure, usage, and data-identification constructs. This document:
The DRM is the starting point from which data architects should develop modeling standards and concepts. The combined volumes of the DRM support data classification and enable horizontal and vertical information sharing.
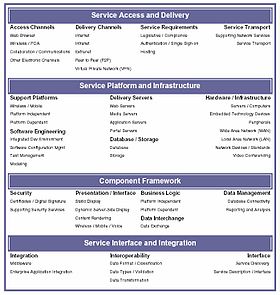 The TRM is a component-driven, technical framework categorizing the standards and technologies to support and enable the delivery of Service Components and capabilities. It also unifies existing agency TRMs and E-Gov guidance by providing a foundation to advance the reuse and standardization of technology and Service Components from a government-wide perspective.
The TRM is a component-driven, technical framework categorizing the standards and technologies to support and enable the delivery of Service Components and capabilities. It also unifies existing agency TRMs and E-Gov guidance by providing a foundation to advance the reuse and standardization of technology and Service Components from a government-wide perspective.
The TRM consists of:
The figure on the right provides a high-level depiction of the TRM.
Aligning agency capital investments to the TRM leverages a common, standardized vocabulary, allowing interagency discovery, collaboration, and interoperability. Agencies and the federal government will benefit from economies of scale by identifying and reusing the best solutions and technologies to support their business functions, mission, and target architecture. Organized in a hierarchy, the TRM categorizes the standards and technologies that collectively
support the secure delivery, exchange, and construction of business and application Service Components that may be used and leveraged in a component-based
or service-oriented architecture
.
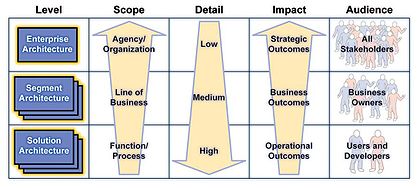
By definition, Enterprise Architecture
(EA) is fundamentally concerned with identifying common or shared assets – whether they are strategies, business processes, investments, data, systems, or technologies. EA is driven by strategy; it helps an agency identify whether its resources are properly aligned to the agency mission and strategic goals and objectives. From an investment perspective, EA is used to drive decisions about the IT investment portfolio as a whole. Consequently, the primary stakeholders of the EA are the senior managers and executives tasked with ensuring the agency fulfills its mission as effectively and efficiently as possible.
By contrast, "segment architecture
" defines a simple roadmap for a core mission area, business service, or enterprise service. Segment architecture is driven by business management and delivers products that improve the delivery of services to citizens and agency staff. From an investment perspective, segment architecture drives decisions for a business case or group of business cases supporting a core mission area or common or shared service. The primary stakeholders for segment architecture are business owners and managers. Segment architecture is related to EA through three principles:
"Solution architecture
" defines agency IT assets such as applications or components used to automate and improve individual agency business functions. The scope of a solution architecture is typically limited to a single project and is used to implement all or part of a system or business solution. The primary stakeholders for solution architecture are system users and developers. Solution architecture is commonly related to segment architecture and enterprise architecture through definitions and constraints. For example, segment architecture provides definitions of data or service interfaces used within a core mission area or service, which are accessed by individual solutions. Equally, a solution may be constrained to specific technologies and standards that are defined at the enterprise level.
The CIO Council's ET.gov site can be used to identify technical specifications (standards) that are not yet included in the TRM but should be. Those that have been identified thus far can be discovered using the advanced ET.gov search service hosted by IntelligenX.
Enterprise architecture
An enterprise architecture is a rigorous description of the structure of an enterprise, which comprises enterprise components , the externally visible properties of those components, and the relationships between them...
of a federal government
Federal government
The federal government is the common government of a federation. The structure of federal governments varies from institution to institution. Based on a broad definition of a basic federal political system, there are two or more levels of government that exist within an established territory and...
. It provides a common methodology for information technology (IT) acquisition, use, and disposal in the Federal government.

Core business
The core business of an organization is an idealized construct intended to express that organization's "main" or "essential" activity.The corporate trend in the mid-20th Century of acquiring new enterprises and forming conglomerates enabled corporations to reduce costs funds and similar investment...
s. An EA describes the current and future state of the agency, and lays out a plan for transitioning from the current state to the desired future state. A federal enterprise architecture is a work in progress to achieve these goals.
The U.S. federal enterprise architecture (FEA) is an initiative of the U.S. Office of Management and Budget that aims to comply with the Clinger-Cohen Act
Clinger-Cohen Act
The Clinger–Cohen Act , formerly the Information Technology Management Reform Act of 1996 , is a 1996 United States federal law, designed to improve the way the federal government acquires, uses and disposes information technology ....
and provide a common methodology for IT acquisition in the United States federal government
Federal government of the United States
The federal government of the United States is the national government of the constitutional republic of fifty states that is the United States of America. The federal government comprises three distinct branches of government: a legislative, an executive and a judiciary. These branches and...
. It is designed to ease sharing of information and resources across federal agencies, reduce costs, and improve citizen services.
History
In September 1999, the Federal CIO Council published the "Federal Enterprise Architecture Framework" (FEAF) Version 1.1 for developing an Enterprise ArchitectureEnterprise architecture
An enterprise architecture is a rigorous description of the structure of an enterprise, which comprises enterprise components , the externally visible properties of those components, and the relationships between them...
(EA) within any Federal Agency for a system that transcends multiple inter-agency boundaries. It builds on common business practices and designs that cross organizational boundaries, among others the NIST Enterprise Architecture Model
NIST Enterprise Architecture Model
NIST Enterprise Architecture Model is a reference model for Enterprise Architecture, that illustrates the interrelationship of enterprise business, information, and technology environments....
. The FEAF provides an enduring standard for developing and documenting architecture descriptions of high-priority areas. It provides guidance in describing architectures for multi-organizational functional segments of the Federal Government.
These federal architectural segments collectively constitute the federal enterprise architecture. In 2001, the Federal Architecture Working Group (FAWG) was sponsoring the development of Enterprise Architecture products for trade and grant Federal architecture segments. Methoda prescribed way of approaching a particular problem. As shown in the figure, the FEAF partitions a given architecture into business, data, applications, and technology architectures. The FEAF overall framework created that time, see image, includes the first three columns of the Zachman Framework
Zachman framework
The Zachman Framework is an Enterprise Architecture framework for enterprise architecture, which provides a formal and highly structured way of viewing and defining an enterprise...
and the Spewak
Steven Spewak
Steven H. Spewak was an American management consultant, author, and lecturer on enterprise architectures, who influenced the direction of enterprise architecture thinking, especially in government.- Biography :...
's Enterprise Architecture Planning
Enterprise Architecture Planning
Enterprise Architecture Planning in Enterprise Architecture is the planning process of defining architectures for the use of information in support of the business and the plan for implementing those architectures.- Overview :...
methodology.
Reference models

Reference Model
A reference model in systems, enterprise, and software engineering is a model of something that embodies the basic goal or idea of something and can then be looked at as a reference for various purposes.- Overview :...
s, that develop a common taxonomy
Taxonomy
Taxonomy is the science of identifying and naming species, and arranging them into a classification. The field of taxonomy, sometimes referred to as "biological taxonomy", revolves around the description and use of taxonomic units, known as taxa...
and ontology for describing IT resources. These include the, (see image):
- performance reference model,
- business reference model,
- service component reference model,
- data reference model and
- technical reference model.
It is designed to ease sharing of information and resources across federal agencies, reduce costs, and improve citizen services. It is an initiative of the US Office of Management and Budget that aims to comply with the Clinger-Cohen Act
Clinger-Cohen Act
The Clinger–Cohen Act , formerly the Information Technology Management Reform Act of 1996 , is a 1996 United States federal law, designed to improve the way the federal government acquires, uses and disposes information technology ....
.
Performance Reference Model (PRM)

- Help produce enhanced performance information to improve strategic and daily decision-making;
- Improve the alignment — and better articulate the contribution of — inputs to outputs and outcomes, thereby creating a clear “line of sight” to desired results; and
- Identify performance improvement opportunities that span traditional organizational structures and boundaries
The PRM uses a number of existing approaches to performance measurement, including the Balanced Scorecard
Balanced scorecard
The Balanced Scorecard is a strategic performance management tool - a semi-standard structured report, supported by proven design methods and automation tools, that can be used by managers to keep track of the execution of activities by the staff within their control and to monitor the...
, Baldrige Criteria, value measuring methodology
Value Measuring Methodology
Value measuring methodology is a tool that helps planners balance both tangible and intangible values when making investment decisions, and monitor benefits....
, program logic models
Logic model
A logic model sets out how an intervention is understood or intended to produce particular results....
, the value chain, and the Theory of Constraints
Theory of Constraints
The theory of constraints adopts the common idiom "A chain is no stronger than its weakest link" as a new management paradigm. This means that processes, organizations, etc., are vulnerable because the weakest person or part can always damage or break them or at least adversely affect the...
. In addition, the PRM was informed by what agencies are currently measuring through PART assessments, GPRA, enterprise architecture
Enterprise architecture
An enterprise architecture is a rigorous description of the structure of an enterprise, which comprises enterprise components , the externally visible properties of those components, and the relationships between them...
, and Capital Planning and Investment Control. The PRM is currently composed of four measurement areas:
- Mission and Business Results
- Customer Results
- Processes and Activities
- Technology
Business Reference Model (BRM)

Business reference model
Business reference model is a reference model, concentrating on the functional and organizational aspects of the core business of an enterprise, service organization or government agency....
, a function-driven framework for describing the business operations of the Federal Government independent of the agencies that perform them. This business reference model provides an organized, hierarchical construct for describing the day-to-day business operations of the Federal government using a functionally driven approach. The BRM is the first layer of the Federal Enterprise Architecture and it is the main viewpoint for the analysis of data, service components and technology.
The BRM is broken down into four areas:
- Services For Citizens
- Mode of Delivery
- Support Delivery of Services
- Management of Government Resources
The Business Reference Model provides a framework that facilitates a functional (as opposed to organizational) view of the federal government’s LoBs, including its internal operations and its services for the citizens, independent of the agencies, bureaus and offices that perform them. By describing the federal government around common business areas instead of by a stovepiped, agency-by-agency view, the BRM promotes agency collaboration and serves as the underlying foundation for the FEA and E-Gov strategies.
While the BRM does provide an improved way of thinking about government operations, it is only a model; its true utility can only be realized when it is effectively used. The functional approach promoted by the BRM will do little to help accomplish the goals of E-Government if it is not incorporated into EA business architectures and the management processes of all Federal agencies and OMB.
Service Component Reference Model (SRM)

The SRM establishes the following domains:
- Customer Services
- Process Automation Services
- Business Management Services
- Digital Asset Services
- Business Analytical Services
- Back Office Services
- Support Services
Each Service Domain is decomposed into Service Types. For example, the three Service Types associated with the Customer Services Domain are: Customer Preferences; Customer Relationship Management; and Customer Initiated Assistance. And each Service Type is decomposed further into components. For example, the four components within the Customer Preferences Service Type include: Personalization; Subscriptions; Alerts and Notifications; and Profile Management.
Data Reference Model (DRM)

Data Reference Model
The Data Reference Model is one of the five reference models of the Federal Enterprise Architecture .- Overview :The DRM is a framework whose primary purpose is to enable information sharing and reuse across the United States federal government via the standard description and discovery of common...
(DRM) describes, at an aggregate level, the data and information that support government program and business line operations. This model enables agencies to describe the types of interaction and exchanges that occur between the Federal Government and citizens. The DRM categorizes government information into greater levels of detail. It also establishes a classification for Federal data and identifies duplicative data resources. A common data model will streamline information exchange processes within the Federal government and between government and external stakeholders.
Volume One of the DRM provides a high-level overview of the structure, usage, and data-identification constructs. This document:
- Provides an introduction and high-level overview of the contents that will be detailed in Volumes 2–4 of the model;
- Encourages community of interest development of the remaining volumes; and
- Provides the basic concepts, strategy, and structure to be used in future development.
The DRM is the starting point from which data architects should develop modeling standards and concepts. The combined volumes of the DRM support data classification and enable horizontal and vertical information sharing.
Technical Reference Model (TRM)

The TRM consists of:
- Service Areas : represent a technical tier supporting the secure construction, exchange, and delivery of Service Components. Each Service Area aggregates the standards and technologies into lower-level functional areas. Each Service Area consists of multiple Service Categories and Service Standards. This hierarchy provides the framework to group standards and technologies that directly support the Service Area. (Purple headings)
- Service Categories : classify lower levels of technologies and standards with respect to the business or technology function they serve. In turn, each Service Category comprises one or more Service Standards. (Bold-face groupings)
- Service Standards : define the standards and technologies that support a Service Category. To support agency mapping into the TRM, many of the Service Standards provide illustrative specifications or technologies as examples.(Plain text)
The figure on the right provides a high-level depiction of the TRM.
Aligning agency capital investments to the TRM leverages a common, standardized vocabulary, allowing interagency discovery, collaboration, and interoperability. Agencies and the federal government will benefit from economies of scale by identifying and reusing the best solutions and technologies to support their business functions, mission, and target architecture. Organized in a hierarchy, the TRM categorizes the standards and technologies that collectively
support the secure delivery, exchange, and construction of business and application Service Components that may be used and leveraged in a component-based
Component-based software engineering
Component-based software engineering is a branch of software engineering that emphasizes the separation of concerns in respect of the wide-ranging functionality available throughout a given software system...
or service-oriented architecture
Service-oriented architecture
In software engineering, a Service-Oriented Architecture is a set of principles and methodologies for designing and developing software in the form of interoperable services. These services are well-defined business functionalities that are built as software components that can be reused for...
.
FEA Architecture levels
In the FEA enterprise, segment, and solution architecture provide different business perspectives by varying the level of detail and addressing related but distinct concerns. Just as enterprises are themselves hierarchically organized, so are the different views provided by each type of architecture. The Federal Enterprise Architecture Practice Guidance (2006) has defined three types of architecture:
- Enterprise architecture,
- Segment architecture, and
- Solution architecture.
By definition, Enterprise Architecture
Enterprise architecture
An enterprise architecture is a rigorous description of the structure of an enterprise, which comprises enterprise components , the externally visible properties of those components, and the relationships between them...
(EA) is fundamentally concerned with identifying common or shared assets – whether they are strategies, business processes, investments, data, systems, or technologies. EA is driven by strategy; it helps an agency identify whether its resources are properly aligned to the agency mission and strategic goals and objectives. From an investment perspective, EA is used to drive decisions about the IT investment portfolio as a whole. Consequently, the primary stakeholders of the EA are the senior managers and executives tasked with ensuring the agency fulfills its mission as effectively and efficiently as possible.
By contrast, "segment architecture
Segment architecture
Segment architecture defines a simple roadmap for a core mission area, business service, or enterprise service. Segment architecture is driven by business management and delivers products that improve the delivery of services to citizens and agency staff...
" defines a simple roadmap for a core mission area, business service, or enterprise service. Segment architecture is driven by business management and delivers products that improve the delivery of services to citizens and agency staff. From an investment perspective, segment architecture drives decisions for a business case or group of business cases supporting a core mission area or common or shared service. The primary stakeholders for segment architecture are business owners and managers. Segment architecture is related to EA through three principles:
- structure: segment architecture inherits the framework used by the EA, although it may be extended and specialized to meet the specific needs of a core mission area or common or shared service.
- reuse : segment architecture reuses important assets defined at the enterprise level including: data; common business processes and investments; and applications and technologies.
- alignment : segment architecture aligns with elements defined at the enterprise level, such as business strategies, mandates, standards, and performance measures.
"Solution architecture
Solution architecture
Solution architecture in enterprise architecture is a kind of architecture domain, that aims to address specific problems and requirements, usually through the design of specific information systems or applications.Solution architecture is either:...
" defines agency IT assets such as applications or components used to automate and improve individual agency business functions. The scope of a solution architecture is typically limited to a single project and is used to implement all or part of a system or business solution. The primary stakeholders for solution architecture are system users and developers. Solution architecture is commonly related to segment architecture and enterprise architecture through definitions and constraints. For example, segment architecture provides definitions of data or service interfaces used within a core mission area or service, which are accessed by individual solutions. Equally, a solution may be constrained to specific technologies and standards that are defined at the enterprise level.
FEA tools
A number of modeling tools enable you to capture the Federal Enterprise Architect reference models and align your enterprise architecture against them; some of these are listed below.- Adaptive Inc.
- Future Tech Systems, Inc.
- IBM (formerly Telelogic) System Architect (software)System Architect (software)IBM Rational System Architect is an enterprise architecture tool that is used by the business and technology departments of corporations and government agencies to model their business operations and the systems, applications, and databases that support them...
- Troux TechnologiesTroux TechnologiesTroux Technologies is a software vendor that provides tools and services in the areas of Enterprise Architecture and Strategic Planning for large enterprises. Troux is based in Austin, Texas with offices in Washington D.C. & London. Troux was founded by Gerald H...
Architect - Iteraplan – Open Source EA Tool
- Opentext Metastorm Provision
The CIO Council's ET.gov site can be used to identify technical specifications (standards) that are not yet included in the TRM but should be. Those that have been identified thus far can be discovered using the advanced ET.gov search service hosted by IntelligenX.
See also
- Business reference modelBusiness reference modelBusiness reference model is a reference model, concentrating on the functional and organizational aspects of the core business of an enterprise, service organization or government agency....
- Department of Defense Architecture FrameworkDepartment of Defense Architecture FrameworkThe Department of Defense Architecture Framework is an architecture framework for the United States Department of Defense, that provides structure for a specific stakeholder concern through viewpoints organized by various views....
- FDIC Enterprise Architecture FrameworkFDIC Enterprise Architecture FrameworkFDIC Enterprise Architecture Framework is the Enterprise Architecture framework of the United States Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation...
- Reference modelReference ModelA reference model in systems, enterprise, and software engineering is a model of something that embodies the basic goal or idea of something and can then be looked at as a reference for various purposes.- Overview :...
- Treasury Enterprise Architecture FrameworkTreasury Enterprise Architecture FrameworkTreasury Enterprise Architecture Framework is an Enterprise architecture framework for treasury, based on the Zachman Framework.It was developed by the US Department of the Treasury and published in July 2000.- Overview :...
- FEA with ADOit
- Baldrige Performance Excellence Program

