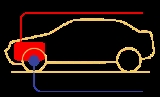
FF layout
Encyclopedia
In automotive design
, an FF, or Front-engine
, Front-wheel drive
layout
places both the internal combustion engine
and driven roadwheels at the front of the vehicle.
(FR), the FF layout eliminates the need for a central tunnel or a higher chassis clearance to accommodate a driveshaft
providing power to the rear wheels. Like the rear-engine, rear-wheel drive layout (RR) and rear mid-engine, rear-wheel drive layout (RMR) layouts, it places the engine over the drive wheels, improving traction in many applications. As the steered wheels are also the driven wheels, FF cars are generally considered superior to FR cars in conditions where there is low traction
such as snow, mud, gravel or wet tarmac. When hill climbing in low traction conditions RR is considered the best two-wheel drive layout, primarily due to the shift of weight to the rear wheels when climbing. The cornering ability of a FF vehicle is generally better, because the engine is placed over the steered wheels. However, as the driven wheels have the additional demands of steering, if a vehicle accelerates quickly, less grip is available for cornering, which can result in understeer
. High-performance vehicles rarely use the FF layout because weight is transferred to the rear wheels under acceleration, while unloading the front wheels and sharply reducing their grip, effectively putting a cap on the amount of power which could realistically be utilized; in addition, the high horsepower of high-performance cars can result in the sensation of torque steer. Electronic traction control can avoid wheel-spin but largely negates the benefit of extra power. This was a reason for the adoption of the four-wheel drive quattro system by front wheel drive specialist Audi
with the 1980 Audi Quattro
for road cars.
, the 1948 Citroën 2CV
, 1949 Saab 92
and the 1959 Mini
. In the 1980s, the traction and packaging advantages of this layout caused many compact and mid-sized vehicles to adopt it.
There are four different arrangements for this basic layout, depending on the location of the engine, which is the heaviest component of the drivetrain.
solved the weight distribution issue by placing the transmission at the front of the car with the differential between it and the engine. Combined with the car's low slung unibody design, this resulted in handling which was remarkable for the era. Citroën and Renault used this layout in some models into the 1980s.
, designed by Jean-Albert Grégoire
, had the engine longitudinally in front of the front wheels, with the transmission behind the engine and the differential at the rear of the assembly. This arrangement, used by Panhard until 1967, potentially had a weight distribution problem analogous to that of the Cord L29 mentioned above. However, the Panhard's engine was very light, reducing the effect. The engine of the Citroën 2CV was in front of the front wheels, with the transmission behind the axle and the differential between the two. This became quite popular; cars using this layout included the German Ford Taunus 12M
and the Lancia Flavia
and Fulvia
. This is the standard configuration of Audi and Subaru front wheel drive vehicles. The first generation Oldsmobile Toronado
and the Saab 99
and “classic” Saab 900
had their engines mounted approximately on the front axle center line, with power being taken by chains or a gear train to a transmission and differential mounted below and beside the engine.
's Mini
of 1959 and related cars such as the Maxi
, Austin 1100/1300
and Allegro
had the engine transversely mounted. The transmission was located in the sump below the crankshaft, with power transmitted by transfer gears.
Dante Giacosa
's Autobianchi Primula
of 1964, Fiat 128
and Fiat 127
, put the transmission on one side of the transversely mounted engine, and doubled back the drivetrain to put the differential just behind the transmission, but offset to one side. Hence the driveshafts to the wheels are longer on one side than the other. This located the weight just a bit in front of the wheels. It is this system which dominates worldwide at present.
Vehicles with the Giacosa arrangement tend to suffer from torque steer under heavy acceleration. The shorter drive shaft, being stiffer than the longer drive shaft, transmits the motion to the wheels immediately instead of 'winding' up due to the drive torque. The net result is more tractive force at the wheel with the shorter drive shaft and the car tends to pull to the opposite side.
Automotive design
Automotive design is the profession involved in the development of the appearance, and to some extent the ergonomics, of motor vehicles or more specifically road vehicles. This most commonly refers to automobiles but also refers to motorcycles, trucks, buses, coaches, and vans...
, an FF, or Front-engine
Front-engine design
A front-mounted engine describes the placement of an automobile engine in front of the vehicle passenger compartment.Historically, this designation was used regardless of whether or not the entire engine was behind the front axle line...
, Front-wheel drive
Front-wheel drive
Front-wheel drive is a form of engine/transmission layout used in motor vehicles, where the engine drives the front wheels only. Most modern front-wheel drive vehicles feature a transverse engine, rather than the conventional longitudinal engine arrangement generally found in rear-wheel drive and...
layout
Automobile layout
In automotive design, the automobile layout describes where on the vehicle the engine and drive wheels are found. Many different combinations of engine location and driven wheels are found in practice, and the location of each is dependent on the application the vehicle will be used for...
places both the internal combustion engine
Internal combustion engine
The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer in a combustion chamber. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high -pressure gases produced by combustion apply direct force to some component of the engine...
and driven roadwheels at the front of the vehicle.
Usage implications
In contrast with the front-engine, rear-wheel drive layoutFront-engine, rear-wheel drive layout
In automotive design, an FR, or Front-engine, Rear-wheel drive layout is one where the engine is located at the front of the vehicle and driven wheels are located at the rear. This was the traditional automobile layout for most of the 20th century....
(FR), the FF layout eliminates the need for a central tunnel or a higher chassis clearance to accommodate a driveshaft
Driveshaft
A drive shaft, driveshaft, driving shaft, propeller shaft, or Cardan shaft is a mechanical component for transmitting torque and rotation, usually used to connect other components of a drive train that cannot be connected directly because of distance or the need to allow for relative movement...
providing power to the rear wheels. Like the rear-engine, rear-wheel drive layout (RR) and rear mid-engine, rear-wheel drive layout (RMR) layouts, it places the engine over the drive wheels, improving traction in many applications. As the steered wheels are also the driven wheels, FF cars are generally considered superior to FR cars in conditions where there is low traction
Traction (engineering)
Traction refers to the maximum frictional force that can be produced between surfaces without slipping.The units of traction are those of force, or if expressed as a coefficient of traction a ratio.-Traction:...
such as snow, mud, gravel or wet tarmac. When hill climbing in low traction conditions RR is considered the best two-wheel drive layout, primarily due to the shift of weight to the rear wheels when climbing. The cornering ability of a FF vehicle is generally better, because the engine is placed over the steered wheels. However, as the driven wheels have the additional demands of steering, if a vehicle accelerates quickly, less grip is available for cornering, which can result in understeer
Understeer
Understeer and oversteer are vehicle dynamics terms used to describe the sensitivity of a vehicle to steering. Simply put, oversteer is what occurs when a car turns by more than the amount commanded by the driver...
. High-performance vehicles rarely use the FF layout because weight is transferred to the rear wheels under acceleration, while unloading the front wheels and sharply reducing their grip, effectively putting a cap on the amount of power which could realistically be utilized; in addition, the high horsepower of high-performance cars can result in the sensation of torque steer. Electronic traction control can avoid wheel-spin but largely negates the benefit of extra power. This was a reason for the adoption of the four-wheel drive quattro system by front wheel drive specialist Audi
Audi
Audi AG is a German automobile manufacturer, from supermini to crossover SUVs in various body styles and price ranges that are marketed under the Audi brand , positioned as the premium brand within the Volkswagen Group....
with the 1980 Audi Quattro
Audi Quattro
The Audi Quattro is a road and rally car, produced by the German automobile manufacturer Audi, now part of the Volkswagen Group. It was first shown at the 1980 Geneva Motor Show on 3 March.The word quattro is derived from the Italian word for "four"...
for road cars.
Historical arrangements
Early cars using the FF layout include the 1929 Cord L-29, 1931 DKW F1DKW
DKW is a historic German car and motorcycle marque. The name derives from Dampf-Kraft-Wagen .In 1916, the Danish engineer Jørgen Skafte Rasmussen founded a factory in Zschopau, Saxony, Germany, to produce steam fittings. In the same year, he attempted to produce a steam-driven car, called the DKW...
, the 1948 Citroën 2CV
Citroën 2CV
The Citroën 2CV |tax horsepower]]”) was an economy car produced by the French automaker Citroën between 1948 and 1990. It was technologically advanced and innovative, but with uncompromisingly utilitarian unconventional looks, and deceptively simple Bauhaus inspired bodywork, that belied the sheer...
, 1949 Saab 92
Saab 92
Saab 92 is an automobile from Saab. The design was very aerodynamic for its time, and the cW value was 0.30 . The entire body was stamped out of one piece of sheet metal and then cut to accommodate doors and windows. Full-scale production started December 12, 1949, based on the prototype Saab 92001...
and the 1959 Mini
Mini
The Mini is a small car that was made by the British Motor Corporation and its successors from 1959 until 2000. The original is considered a British icon of the 1960s, and its space-saving front-wheel-drive layout influenced a generation of car-makers...
. In the 1980s, the traction and packaging advantages of this layout caused many compact and mid-sized vehicles to adopt it.
There are four different arrangements for this basic layout, depending on the location of the engine, which is the heaviest component of the drivetrain.
Mid-engine / Front-wheel drive
The earliest such arrangement was not technically FF, but rather mid-engine, front-wheel drive layout (MF). The engine was mounted longitudinally (fore-and-aft, or north-south) behind the wheels, with the transmission ahead of the engine and differential at the very front of the car. With the engine so far back, the weight distribution of such cars as the Cord L-29 was not ideal; the driven wheels did not carry a large enough proportion of weight for good traction and handling. The 1934 Citroën Traction AvantCitroën Traction Avant
The Citroën Traction Avant is an automobile which was produced by the French manufacturer Citroën from 1934 to 1957. About 760,000 units were produced.-Impact on the world:...
solved the weight distribution issue by placing the transmission at the front of the car with the differential between it and the engine. Combined with the car's low slung unibody design, this resulted in handling which was remarkable for the era. Citroën and Renault used this layout in some models into the 1980s.
Front-engine longitudinally mounted / Front-wheel drive
The 1946 Panhard Dyna XPanhard Dyna X
The Panhard Dyna X was a lightweight compact saloon car designed by the visionary engineer Jean Albert Grégoire and first exhibited as the AFG Dyna at the Paris Motor Show in 1946....
, designed by Jean-Albert Grégoire
Jean-Albert Grégoire
Jean-Albert Grégoire was one of the great pioneers of the front-wheel drive car. He contributed to the development of front wheel drive vehicles in two ways...
, had the engine longitudinally in front of the front wheels, with the transmission behind the engine and the differential at the rear of the assembly. This arrangement, used by Panhard until 1967, potentially had a weight distribution problem analogous to that of the Cord L29 mentioned above. However, the Panhard's engine was very light, reducing the effect. The engine of the Citroën 2CV was in front of the front wheels, with the transmission behind the axle and the differential between the two. This became quite popular; cars using this layout included the German Ford Taunus 12M
Ford Taunus
The Ford Taunus is a family car sold by Ford in Germany and other countries. Models from 1970 onward were similar to the Ford Cortina in the United Kingdom...
and the Lancia Flavia
Lancia Flavia
The Lancia Flavia is a medium sized luxury saloon, launched with a 1500 cc engine at the 1960 Turin Motor Show by Lancia and introduced in major European markets during the next twelve months. Coupe and cabriolet versions developed by Pininfarina quickly followed, together with one or two low...
and Fulvia
Lancia Fulvia
The Lancia Fulvia is an Italian car introduced at the Geneva Motor Show in 1963 by Lancia. It was produced by that company through 1976. Fulvias are notable for their role in automobile racing history, including winning the International Rally Championship in 1972...
. This is the standard configuration of Audi and Subaru front wheel drive vehicles. The first generation Oldsmobile Toronado
Oldsmobile Toronado
The original Toronado began as a design painting by Oldsmobile stylist David North in 1962. His design, dubbed the "Flame Red Car," was for a compact sports/personal car never intended for production...
and the Saab 99
Saab 99
- Development :On April 2, 1965, Gudmund's day in Sweden, after several years of planning, the Saab board started Project Gudmund. This was a project to develop a new and larger car to take the manufacturer beyond the market for the smaller Saab 96...
and “classic” Saab 900
900
Year 900 was a leap year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar.- Asia :* April 21 – Namwaran and his children, Lady Angkatan and Bukah, are granted pardon by the Datu of Tondo, as represented Jayadewa, Lord Minister of Pila, which released them of all their debts as inscribed in the...
had their engines mounted approximately on the front axle center line, with power being taken by chains or a gear train to a transmission and differential mounted below and beside the engine.
Front-engine transversely mounted / Front-wheel drive
IssigonisAlec Issigonis
Sir Alexander Arnold Constantine Issigonis, CBE, FRS was a Greek-British designer of cars, now remembered chiefly for the groundbreaking and influential development of the Mini, launched by the British Motor Corporation in 1959.- Early life:Issigonis was born into the Greek community of Smyrna ...
's Mini
Mini
The Mini is a small car that was made by the British Motor Corporation and its successors from 1959 until 2000. The original is considered a British icon of the 1960s, and its space-saving front-wheel-drive layout influenced a generation of car-makers...
of 1959 and related cars such as the Maxi
Austin Maxi
The Austin Maxi was a medium sized 5-door hatchback car from British Leyland for the 1970s. It was the first British five speed five-door hatchback.-History:...
, Austin 1100/1300
BMC ADO16
ADO16 is the codename for the development of what became the Morris 1100, a small family car built by the British Motor Corporation and, later, British Leyland...
and Allegro
Austin Allegro
The Austin Allegro is a small family car manufactured by British Leyland under the Austin name from 1973 until 1983. The same vehicle was built in Italy by Innocenti between 1974 and 1975 and sold as the Innocenti Regent...
had the engine transversely mounted. The transmission was located in the sump below the crankshaft, with power transmitted by transfer gears.
Dante Giacosa
Dante Giacosa
Dante Giacosa was an Italian car designer. His work covered a large range from minicars to sports cars, using all the different layouts as and when they were the best solution at the time to meet the design parameters....
's Autobianchi Primula
Autobianchi Primula
The Autobianchi Primula is a small car from the Italian automaker, Autobianchi , built between 1964 and 1970. It was Fiat's first automobile with the front-wheel drive, transverse engine setup, as well as the first Fiat group car with rack and pinion steering...
of 1964, Fiat 128
Fiat 128
The Fiat 128 is a small family car manufactured by the Italian manufacturer Fiat from 1969 to 1985. The engine was designed by the famous Ferrari racing engine designer Aurelio Lampredi.-History:...
and Fiat 127
Fiat 127
The Fiat 127 is a supermini produced by the Italian automaker Fiat between 1971 and 1983. It was introduced in 1971 as the replacement for the Fiat 850...
, put the transmission on one side of the transversely mounted engine, and doubled back the drivetrain to put the differential just behind the transmission, but offset to one side. Hence the driveshafts to the wheels are longer on one side than the other. This located the weight just a bit in front of the wheels. It is this system which dominates worldwide at present.
Vehicles with the Giacosa arrangement tend to suffer from torque steer under heavy acceleration. The shorter drive shaft, being stiffer than the longer drive shaft, transmits the motion to the wheels immediately instead of 'winding' up due to the drive torque. The net result is more tractive force at the wheel with the shorter drive shaft and the car tends to pull to the opposite side.
Further reading
- Sedgwick, Michael Cars of the 50s and 60s. Gothenburg, Sweden: A B Nordbok, 1983. (Includes pictures of the engine layouts of the Traction Avant and other designs).

