
Extragalactic cosmic ray
Encyclopedia
Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that contains the Solar System. This name derives from its appearance as a dim un-resolved "milky" glowing band arching across the night sky...
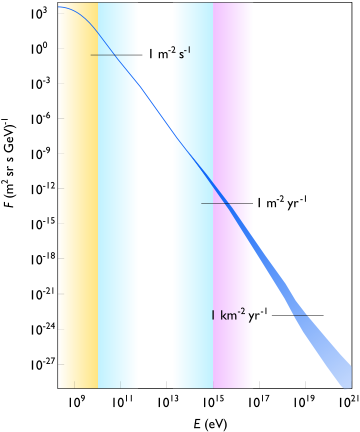
. The energies these particles possess are in excess of 1015 eV
Electronvolt
In physics, the electron volt is a unit of energy equal to approximately joule . By definition, it is equal to the amount of kinetic energy gained by a single unbound electron when it accelerates through an electric potential difference of one volt...
.
Origin
Unlike solar or galactic cosmic rayGalactic cosmic ray
Galactic cosmic rays are cosmic rays that have their origin inside our Galaxy. GCRs are high-energy charged particles, and are usually protons, electrons, and fully ionized nuclei of light elements...
s, little is known about the origins of extragalactic cosmic rays. This is largely due to a lack of statistics: only about 1 extragalactic cosmic ray particle per square meter per year reaches the Earth's surface (see figure).

Shock wave
A shock wave is a type of propagating disturbance. Like an ordinary wave, it carries energy and can propagate through a medium or in some cases in the absence of a material medium, through a field such as the electromagnetic field...
s of some violent object allows some of the particles to gain energy. Eventually they may build up enough speed that the object can no longer contain them, and they escape. Proposed sites for this type of acceleration include gamma ray burst
Gamma ray burst
Gamma-ray bursts are flashes of gamma rays associated with extremely energetic explosions that have been observed in distant galaxies. They are the most luminous electromagnetic events known to occur in the universe. Bursts can last from ten milliseconds to several minutes, although a typical...
s and active galactic nuclei. Indeed, recent analysis of cosmic ray measurements with the Pierre Auger Observatory
Pierre Auger Observatory
The Pierre Auger Observatory is an international cosmic ray observatory designed to detect ultra-high-energy cosmic rays: single sub-atomic particles with energies beyond 1020 eV...
suggests a correlation between the arrival directions of cosmic rays of the highest energies of more than 5×1019 eV
Electronvolt
In physics, the electron volt is a unit of energy equal to approximately joule . By definition, it is equal to the amount of kinetic energy gained by a single unbound electron when it accelerates through an electric potential difference of one volt...
and the positions of nearby active galaxies.
There are many more possible sources scientists are considering. These include colliding galaxy systems, accretion flow shocks to clusters of galaxies, and more exotic processes from the very early universe, such as the decay of superheavy particles trapped in the galactic halo
Galactic halo
The term galactic halo is used to denote an extended, roughly spherical component of a galaxy, which extends beyond the main, visible component. It can refer to any of several distinct components which share these properties:* the galactic spheroid...
, or topological defect
Topological defect
In mathematics and physics, a topological soliton or a topological defect is a solution of a system of partial differential equations or of a quantum field theory homotopically distinct from the vacuum solution; it can be proven to exist because the boundary conditions entail the existence of...
s.
Composition
Due to the very low flux of extragalactic cosmic particles received on Earth, little is known about their composition. Most estimates, based on theoretical and numerical models, predict that light atomic nuclei such as protonProton
The proton is a subatomic particle with the symbol or and a positive electric charge of 1 elementary charge. One or more protons are present in the nucleus of each atom, along with neutrons. The number of protons in each atom is its atomic number....
s are the dominant particle type.

