
Equivalent isotropically radiated power
Encyclopedia
In radio
communication systems, Equivalent isotropically radiated power (EIRP) or, alternatively, Effective isotropically radiated power is the amount of power that a theoretical isotropic antenna (which evenly distributes power in all directions) would emit to produce the peak power density observed in the direction of maximum antenna gain
. EIRP can take into account the losses in transmission line
and connectors and includes the gain of the antenna. The EIRP is often stated in terms of decibel
s over a reference power emitted by an isotropic radiator with an equivalent signal strength. The EIRP allows comparisons between different emitters regardless of type, size or form. From the EIRP, and with knowledge of a real antenna's gain, it is possible to calculate real power and field strength values.
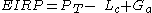
where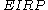 and
and 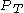 (power of transmitter) are in dBm
(power of transmitter) are in dBm
, cable losses (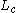 ) is in dB
) is in dB
, and antenna gain (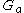 ) is expressed in dBi
) is expressed in dBi
, relative to a (theoretical) isotropic reference antenna.
This example uses dBm, although it is also common to see dBW.
Decibel
s are a convenient way to express the ratio between two quantities. dBm uses a reference of 1 mW and dBW uses a reference of 1 W.
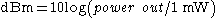
and
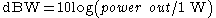
A transmitter with a 50W output can be expressed as a 17 dBW output or 47 dBm.
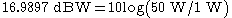
The EIRP is used to estimate the service area of the transmitter, and to coordinate transmitters on the same frequency so that their coverage areas do not overlap.
In built-up areas, regulations may restrict the EIRP of a transmitter to prevent exposure of personnel to high power electromagnetic
fields, however EIRP is normally restricted to minimise interference to services on similar frequencies.
Radio
Radio is the transmission of signals through free space by modulation of electromagnetic waves with frequencies below those of visible light. Electromagnetic radiation travels by means of oscillating electromagnetic fields that pass through the air and the vacuum of space...
communication systems, Equivalent isotropically radiated power (EIRP) or, alternatively, Effective isotropically radiated power is the amount of power that a theoretical isotropic antenna (which evenly distributes power in all directions) would emit to produce the peak power density observed in the direction of maximum antenna gain
Antenna gain
In electromagnetics, an antenna's power gain or simply gain is a key performance figure which combines the antenna's directivity and electrical efficiency. As a transmitting antenna, the figure describes how well the antenna converts input power into radio waves headed in a specified direction...
. EIRP can take into account the losses in transmission line
Transmission line
In communications and electronic engineering, a transmission line is a specialized cable designed to carry alternating current of radio frequency, that is, currents with a frequency high enough that its wave nature must be taken into account...
and connectors and includes the gain of the antenna. The EIRP is often stated in terms of decibel
Decibel
The decibel is a logarithmic unit that indicates the ratio of a physical quantity relative to a specified or implied reference level. A ratio in decibels is ten times the logarithm to base 10 of the ratio of two power quantities...
s over a reference power emitted by an isotropic radiator with an equivalent signal strength. The EIRP allows comparisons between different emitters regardless of type, size or form. From the EIRP, and with knowledge of a real antenna's gain, it is possible to calculate real power and field strength values.
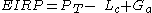
where
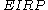 and
and 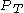 (power of transmitter) are in dBm
(power of transmitter) are in dBmDBm
dBm is an abbreviation for the power ratio in decibels of the measured power referenced to one milliwatt . It is used in radio, microwave and fiber optic networks as a convenient measure of absolute power because of its capability to express both very large and very small values in a short form...
, cable losses (
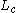 ) is in dB
) is in dBDB
DB may refer to:In science and technology:*Decibel , a logarithmic unit of measurement in acoustics and electronics*Dubnium , a chemical element*DB connector, a size of D-subminiature electrical connector...
, and antenna gain (
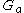 ) is expressed in dBi
) is expressed in dBiDBI
DBI may refer to:*dBi, decibel isotropic*Perl DBI, a database interface for Perl*Diazepam binding inhibitor*DBi Technologies Inc., a provider of text mining, scheduling and UI design component software, services and computer programs...
, relative to a (theoretical) isotropic reference antenna.
This example uses dBm, although it is also common to see dBW.
Decibel
Decibel
The decibel is a logarithmic unit that indicates the ratio of a physical quantity relative to a specified or implied reference level. A ratio in decibels is ten times the logarithm to base 10 of the ratio of two power quantities...
s are a convenient way to express the ratio between two quantities. dBm uses a reference of 1 mW and dBW uses a reference of 1 W.
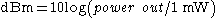
and
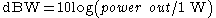
A transmitter with a 50W output can be expressed as a 17 dBW output or 47 dBm.
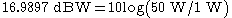
The EIRP is used to estimate the service area of the transmitter, and to coordinate transmitters on the same frequency so that their coverage areas do not overlap.
In built-up areas, regulations may restrict the EIRP of a transmitter to prevent exposure of personnel to high power electromagnetic
Electromagnetism
Electromagnetism is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three are the strong interaction, the weak interaction and gravitation...
fields, however EIRP is normally restricted to minimise interference to services on similar frequencies.
See also
- Effective radiated powerEffective radiated powerIn radio telecommunications, effective radiated power or equivalent radiated power is a standardized theoretical measurement of radio frequency energy using the SI unit watts, and is determined by subtracting system losses and adding system gains...
, which is similar to EIRP but may use some other reference antennaReference antennaA reference antenna is an antenna with known performance. It is normally used to calibrate other systems.Reference antennas are built with particular care taken to make them simple, robust and repeatable. In a common usage scenario a reference antenna would be used as a transfer standard. First...
than an isotropic antenna, e.g. a half-wave dipole - Effective monopole-radiated power, which is similar to EIRP but with a reference antenna of an electrically short monopole

