Epstein-Zin preferences
Encyclopedia
In economics
, Epstein-Zin/Weil preferences is a specification of recursive utility.
A recursive utility function can be constructed from two components: a time aggregator that characterizes preferences in the absence of uncertainty and a risk aggregator that defines the certainty equivalent function that characterizes preferences over static gambles and is used to aggregate the risk associated with future utility. With Epstein-Zin preferences, the time aggregator is a CES aggregate of current consumption and the certainty equivalent of all future utility, measured in units of current consumption. The certainty-equivalent function is a CES aggregate of future utility. Specifically,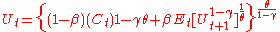
Economics
Economics is the social science that analyzes the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. The term economics comes from the Ancient Greek from + , hence "rules of the house"...
, Epstein-Zin/Weil preferences is a specification of recursive utility.
A recursive utility function can be constructed from two components: a time aggregator that characterizes preferences in the absence of uncertainty and a risk aggregator that defines the certainty equivalent function that characterizes preferences over static gambles and is used to aggregate the risk associated with future utility. With Epstein-Zin preferences, the time aggregator is a CES aggregate of current consumption and the certainty equivalent of all future utility, measured in units of current consumption. The certainty-equivalent function is a CES aggregate of future utility. Specifically,