
Effective rate of protection
Encyclopedia
In economics
, the effective rate of protection is a measure of the total effect of the entire tariff structure on the value added
per unit of output in each industry, when both intermediate and final goods are imported. This statistic is used by economist
s to measure the real amount of protection
afforded to a particular industry by import duties, tariffs or other trade restriction
s.
good (shoes) that uses one tradable input to produce (leather). Both shoes and leather are imported into the home country. Suppose that in the absence of any tariffs, shoes use $100 worth of leather to make, and shoes sell for $150 in the international markets. Shoemakers around the world add $50 of value. If the home country imposes a 20% tariff on shoes, but no tariff on leather, shoes would sell for $180 in the home country, and the value added for the domestic shoe maker would increase by $30, from $50 to $80. The domestic shoe maker is afforded a 60% effective rate of protection per dollar of value added.
This equals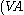 d/
d/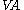 int) -
int) - 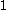 , where:
, where:
An alternative that yields an identical answer is that the effective rate of protection equals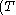 f
f 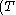 i)
i)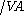 int, where:
int, where:
The effective rate of protection is used to estimate the protection really afforded to domestic producers at each stage of production, i.e., how much extra they can charge and still be competitive with imported goods. If the total value of the tariffs on importable inputs exceeds that on the output, the effective rate of protection is negative, i.e., the industry is discriminated against in comparison with the imported product.
In this context, it does not matter whether the final product or the inputs used to make it were actually imported or not. What is important is that they are importable. If so, the implied tariffs should be included in the above formulas because, even if the item was not actually imported, the existence of the tariff should have raised its price in the local market by an equivalent value.
The effective rate of protection reveals the extremely adverse effect of tariffs that escalate from low rates on raw materials to high rates on intermediate inputs and yet higher rates on the final product as, in fact, most countries' tariff schedules do. Less developed countries complain that such tariff schedules gravely impede their access to developed countries' markets.
Economics
Economics is the social science that analyzes the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. The term economics comes from the Ancient Greek from + , hence "rules of the house"...
, the effective rate of protection is a measure of the total effect of the entire tariff structure on the value added
Value added
In economics, the difference between the sale price and the production cost of a product is the value added per unit. Summing value added per unit over all units sold is total value added. Total value added is equivalent to Revenue less Outside Purchases...
per unit of output in each industry, when both intermediate and final goods are imported. This statistic is used by economist
Economist
An economist is a professional in the social science discipline of economics. The individual may also study, develop, and apply theories and concepts from economics and write about economic policy...
s to measure the real amount of protection
Protectionism
Protectionism is the economic policy of restraining trade between states through methods such as tariffs on imported goods, restrictive quotas, and a variety of other government regulations designed to allow "fair competition" between imports and goods and services produced domestically.This...
afforded to a particular industry by import duties, tariffs or other trade restriction
Trade restriction
A trade restriction is an artificial restriction on the trade of goods between two countries. It is the result of protectionism. However, the term is not uncontroversial since what one part may see as a trade restriction another may see as a way to protect consumers from inferior, harmful or...
s.
Explanation
Consider a simple case, there is a tradableTradable
Tradability is the property of a good or service that can be sold in another location distant from where it was produced. A good that is not tradable is called non-tradable. Different goods have differing levels of tradability: the higher the cost of transportation and the shorter the shelf life,...
good (shoes) that uses one tradable input to produce (leather). Both shoes and leather are imported into the home country. Suppose that in the absence of any tariffs, shoes use $100 worth of leather to make, and shoes sell for $150 in the international markets. Shoemakers around the world add $50 of value. If the home country imposes a 20% tariff on shoes, but no tariff on leather, shoes would sell for $180 in the home country, and the value added for the domestic shoe maker would increase by $30, from $50 to $80. The domestic shoe maker is afforded a 60% effective rate of protection per dollar of value added.
This equals
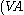 d/
d/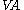 int) -
int) - 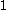 , where:
, where:- VAd = domestic value added
- VAint = international value added
An alternative that yields an identical answer is that the effective rate of protection equals
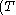 f
f 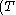 i)
i)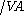 int, where:
int, where:- Tf = the total tariffTariffA tariff may be either tax on imports or exports , or a list or schedule of prices for such things as rail service, bus routes, and electrical usage ....
theoretically or actually paid on the final product - Ti = the total tariffs paid, theoretically or actually, on the importable inputs used to make that product.
The effective rate of protection is used to estimate the protection really afforded to domestic producers at each stage of production, i.e., how much extra they can charge and still be competitive with imported goods. If the total value of the tariffs on importable inputs exceeds that on the output, the effective rate of protection is negative, i.e., the industry is discriminated against in comparison with the imported product.
In this context, it does not matter whether the final product or the inputs used to make it were actually imported or not. What is important is that they are importable. If so, the implied tariffs should be included in the above formulas because, even if the item was not actually imported, the existence of the tariff should have raised its price in the local market by an equivalent value.
The effective rate of protection reveals the extremely adverse effect of tariffs that escalate from low rates on raw materials to high rates on intermediate inputs and yet higher rates on the final product as, in fact, most countries' tariff schedules do. Less developed countries complain that such tariff schedules gravely impede their access to developed countries' markets.

