
Economy of Latvia
Encyclopedia
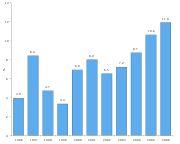
Until the middle of 2008, Latvia
had the fastest developing economy in Europe. In 2003, GDP growth was 7.5% and inflation was 2.9%. Unemployment was 9% in 2003 - 2005; however, in 2009 it rose to 23% and is the highest in the European Union. Privatization is mostly complete, except for some of the large state-owned utilities. On May 1, 2004, Latvia joined the European Union
.
The Financial Crisis of 2008 is still affecting the Latvian economy, primarily as a result of the easy credit bubble that began building up during 2004. The bubble burst lead to a rapidly weakening economy, resulting in a budget, wage and unemployment crisis. Latvia had the worst economic performance in 2009, with annual growth rate averaging -18%.
 For centuries under Hanseatic and German influence and then during its inter-war independence, Latvia used its geographic location as an important East-West commercial and trading center. Industry served local markets, while timber, paper and agricultural products were Latvia's main exports. Conversely, the years of Russian and Soviet occupation tended to integrate Latvia's economy to serve those empires' large internal industrial needs.
For centuries under Hanseatic and German influence and then during its inter-war independence, Latvia used its geographic location as an important East-West commercial and trading center. Industry served local markets, while timber, paper and agricultural products were Latvia's main exports. Conversely, the years of Russian and Soviet occupation tended to integrate Latvia's economy to serve those empires' large internal industrial needs.
After reestablishing its independence, Latvia proceeded with market-oriented reforms, albeit at a measured pace. Its freely traded currency, the lat, was introduced in 1993 and held steady, or appreciated, against major world currencies. Inflation
was reduced from 958.6% in 1992 to 25% by 1995 and 1.4% by 2002. However by 2007, inflation was 16% – the highest inflation rate in the European Union.
After contracting substantially between 1991–93, the economy steadied in late 1994, led by recovery in light industry and a boom in commerce and finance. This recovery was interrupted twice, first by a banking crisis and the bankruptcy of Banka Baltija, Latvia's largest bank, in 1995 and second by a severe crisis in the financial system of neighbouring Russia in 1998. After 2000, Latvian GDP grew by 6–8% a year for 4 consecutive years. Latvia's state budget was balanced in 1997 but the 1998 Russian financial crisis resulted in large deficits, which were reduced from 4% of GDP in 1999 to 1.8% in 2003. These deficits were smaller than in most of the other countries joining the European Union in 2004.
The centrally planned system of the Soviet period was replaced with a structure based on free-market principles. Two-thirds of employment and 60% of GDP is now in the private sector. Recovery in light industry and Riga's emergence as a regional financial and commercial center offset shrinkage of the state-owned industrial sector and agriculture. The official unemployment figure held steady in the 7%-10% range.
is almost complete. Virtually all of the previously state-owned small and medium companies have been privatized, leaving only a small number of politically sensitive large state companies. In particular, the country's main energy company, Latvenergo remains state-owned and there are no plans to privatize it. The government also holds minority shares in Ventspils Nafta oil transit company and the country's main telecom company Lattelecom
but it plans to sell those.
Foreign investment in Latvia is still modest compared with the levels in north-central Europe. A law expanding the scope for selling land, including land sales to foreigners, was passed in 1997. Representing 10.2% of Latvia's total foreign direct investment, American companies invested $127 million in 1999. In the same year, the United States exported $58.2 million of goods and services to Latvia and imported $87.9 million. Eager to join Western economic institutions like the World Trade Organization
, OECD, and the European Union
, Latvia signed a Europe Agreement with the EU in 1995 with a 4-year transition period. Latvia and the United States
have signed treaties on investment, trade, and intellectual property protection and avoidance of double taxation.
in Lithuania to replace the Ignalina Nuclear Power Plant
.
Latvia faces a potential energy famine because in 2009 Lithuania will shut down Ignalina. Without any other policy, Latvia will have to rely more heavily on Russia
n gas and other sources of electricity.
was running at 10%.
By August 2009, Latvia's GDP had fallen by 20% year on year, with S&P predicting a further 16% contraction to come. The International Monetary Fund
suggested a devaluation
of Latvia's currency, but the European Union objected to this, on the grounds that the majority of Latvia's debt was denominated in foreign currencies. Financial economist Michael Hudson
has advocated for redominating foreign currency liabilities in Latvian lats before devaluing, with possible some loss sharing with foreign creditors.
Paul Krugman
, the Nobel Laureate in economics for 2008, wrote in his New York Times Op-Ed column for December 15, 2008:
"The most acute problems are on Europe’s periphery, where many smaller economies are experiencing crises strongly reminiscent of past crises in Latin America and Asia: Latvia is the new Argentina "
lowest 10%:
2.9%
highest 10%:
25.9% (1998)
Industries:
synthetic fibers, agricultural machinery, fertilizers, radios, electronics, pharmaceuticals, processed foods, textiles, timber; note – dependent on imports for energy and raw materials
Industrial production growth rate:
8.5% (2004 est.)
Electricity – production:
4,547 GWh (2002)
Electricity – production by source:
fossil fuel:
29.1%
hydro:
70.9%
nuclear:
0%
other:
0% (2001)
Electricity – consumption:
5,829 GWh (2002)
Electricity – exports:
1,100 GWh (2002)
Electricity – imports:
2,700 GWh (2002)
Agriculture – products:
grain, potatoes, vegetables; beef, milk, eggs; fish
Foreign direct investments in Latvia:
Lursoft statistics on remaining amount of investments at the end of each year. http://www.lursoft.lv/stat/ur_stat_153.html
Exchange rates:
lati per US dollar – 0.44 (2008) 0.5402 (2004), 0.57 (2003), 0.62 (2002), 0.63 (2001), 0.61 (2000), 0.59 (1999), 0.590 (1998), 0.581 (1997), 0.551 (1996), 0.528 (1995)
Packet of 20 cigarettes: 0.70 – 2.00 LVL. Most Western brands (Marlboro, etc.) are about 1.50 LVL.
Latvia
Latvia , officially the Republic of Latvia , is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by Estonia , to the south by Lithuania , to the east by the Russian Federation , to the southeast by Belarus and shares maritime borders to the west with Sweden...
had the fastest developing economy in Europe. In 2003, GDP growth was 7.5% and inflation was 2.9%. Unemployment was 9% in 2003 - 2005; however, in 2009 it rose to 23% and is the highest in the European Union. Privatization is mostly complete, except for some of the large state-owned utilities. On May 1, 2004, Latvia joined the European Union
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
.
The Financial Crisis of 2008 is still affecting the Latvian economy, primarily as a result of the easy credit bubble that began building up during 2004. The bubble burst lead to a rapidly weakening economy, resulting in a budget, wage and unemployment crisis. Latvia had the worst economic performance in 2009, with annual growth rate averaging -18%.
Economic history

After reestablishing its independence, Latvia proceeded with market-oriented reforms, albeit at a measured pace. Its freely traded currency, the lat, was introduced in 1993 and held steady, or appreciated, against major world currencies. Inflation
Inflation
In economics, inflation is a rise in the general level of prices of goods and services in an economy over a period of time.When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services. Consequently, inflation also reflects an erosion in the purchasing power of money – a...
was reduced from 958.6% in 1992 to 25% by 1995 and 1.4% by 2002. However by 2007, inflation was 16% – the highest inflation rate in the European Union.
After contracting substantially between 1991–93, the economy steadied in late 1994, led by recovery in light industry and a boom in commerce and finance. This recovery was interrupted twice, first by a banking crisis and the bankruptcy of Banka Baltija, Latvia's largest bank, in 1995 and second by a severe crisis in the financial system of neighbouring Russia in 1998. After 2000, Latvian GDP grew by 6–8% a year for 4 consecutive years. Latvia's state budget was balanced in 1997 but the 1998 Russian financial crisis resulted in large deficits, which were reduced from 4% of GDP in 1999 to 1.8% in 2003. These deficits were smaller than in most of the other countries joining the European Union in 2004.
The centrally planned system of the Soviet period was replaced with a structure based on free-market principles. Two-thirds of employment and 60% of GDP is now in the private sector. Recovery in light industry and Riga's emergence as a regional financial and commercial center offset shrinkage of the state-owned industrial sector and agriculture. The official unemployment figure held steady in the 7%-10% range.
Privatisation
Privatisation in LatviaLatvia
Latvia , officially the Republic of Latvia , is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by Estonia , to the south by Lithuania , to the east by the Russian Federation , to the southeast by Belarus and shares maritime borders to the west with Sweden...
is almost complete. Virtually all of the previously state-owned small and medium companies have been privatized, leaving only a small number of politically sensitive large state companies. In particular, the country's main energy company, Latvenergo remains state-owned and there are no plans to privatize it. The government also holds minority shares in Ventspils Nafta oil transit company and the country's main telecom company Lattelecom
Lattelecom
Lattelecom is a Latvian internet service provider and telecommunications company.The Lattelecom group provides IT, telecommunication and outsourced business process solutions that are provided by all of the companies of the group...
but it plans to sell those.
Foreign investment in Latvia is still modest compared with the levels in north-central Europe. A law expanding the scope for selling land, including land sales to foreigners, was passed in 1997. Representing 10.2% of Latvia's total foreign direct investment, American companies invested $127 million in 1999. In the same year, the United States exported $58.2 million of goods and services to Latvia and imported $87.9 million. Eager to join Western economic institutions like the World Trade Organization
World Trade Organization
The World Trade Organization is an organization that intends to supervise and liberalize international trade. The organization officially commenced on January 1, 1995 under the Marrakech Agreement, replacing the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade , which commenced in 1948...
, OECD, and the European Union
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
, Latvia signed a Europe Agreement with the EU in 1995 with a 4-year transition period. Latvia and the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
have signed treaties on investment, trade, and intellectual property protection and avoidance of double taxation.
Energy
With Lithuania, Poland, and Estonia, Latvia is considering participating in the Visaginas Nuclear Power PlantVisaginas nuclear power plant
Visaginas nuclear power plant is a planned nuclear power plant project in Lithuania. It is proposed to be built at the site of the closed Ignalina Nuclear Power Plant which was shut-down on 31 December 2009 in accordance with Lithuania's accession agreement to the European Union...
in Lithuania to replace the Ignalina Nuclear Power Plant
Ignalina Nuclear Power Plant
The Ignalina Nuclear Power Plant is a closed two-unit RBMK-1500 nuclear power station in Visaginas, Lithuania. It was named after the nearby city of Ignalina...
.
Latvia faces a potential energy famine because in 2009 Lithuania will shut down Ignalina. Without any other policy, Latvia will have to rely more heavily on Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
n gas and other sources of electricity.
Economic contraction 2008
The Latvian economy entered a phase of fiscal contraction during the second half of 2008 after an extended period of credit-based speculation and unrealistic inflation of real estate values. The national account deficit for 2007, for example, represented more than 22% of the GDP for the year while inflationInflation
In economics, inflation is a rise in the general level of prices of goods and services in an economy over a period of time.When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services. Consequently, inflation also reflects an erosion in the purchasing power of money – a...
was running at 10%.
By August 2009, Latvia's GDP had fallen by 20% year on year, with S&P predicting a further 16% contraction to come. The International Monetary Fund
International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund is an organization of 187 countries, working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world...
suggested a devaluation
Devaluation
Devaluation is a reduction in the value of a currency with respect to those goods, services or other monetary units with which that currency can be exchanged....
of Latvia's currency, but the European Union objected to this, on the grounds that the majority of Latvia's debt was denominated in foreign currencies. Financial economist Michael Hudson
Michael Hudson (economist)
Michael Hudson is research professor of economics at University of Missouri, Kansas City and a research associate at the Levy Economics Institute of Bard College...
has advocated for redominating foreign currency liabilities in Latvian lats before devaluing, with possible some loss sharing with foreign creditors.
Paul Krugman
Paul Krugman
Paul Robin Krugman is an American economist, professor of Economics and International Affairs at the Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs at Princeton University, Centenary Professor at the London School of Economics, and an op-ed columnist for The New York Times...
, the Nobel Laureate in economics for 2008, wrote in his New York Times Op-Ed column for December 15, 2008:
"The most acute problems are on Europe’s periphery, where many smaller economies are experiencing crises strongly reminiscent of past crises in Latin America and Asia: Latvia is the new Argentina "
Statistics
Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%:
2.9%
highest 10%:
25.9% (1998)
Industries:
synthetic fibers, agricultural machinery, fertilizers, radios, electronics, pharmaceuticals, processed foods, textiles, timber; note – dependent on imports for energy and raw materials
Industrial production growth rate:
8.5% (2004 est.)
Electricity – production:
4,547 GWh (2002)
Electricity – production by source:
fossil fuel:
29.1%
hydro:
70.9%
nuclear:
0%
other:
0% (2001)
Electricity – consumption:
5,829 GWh (2002)
Electricity – exports:
1,100 GWh (2002)
Electricity – imports:
2,700 GWh (2002)
Agriculture – products:
grain, potatoes, vegetables; beef, milk, eggs; fish
Foreign direct investments in Latvia:
Lursoft statistics on remaining amount of investments at the end of each year. http://www.lursoft.lv/stat/ur_stat_153.html
Exchange rates:
lati per US dollar – 0.44 (2008) 0.5402 (2004), 0.57 (2003), 0.62 (2002), 0.63 (2001), 0.61 (2000), 0.59 (1999), 0.590 (1998), 0.581 (1997), 0.551 (1996), 0.528 (1995)
Packet of 20 cigarettes: 0.70 – 2.00 LVL. Most Western brands (Marlboro, etc.) are about 1.50 LVL.
External links
- Latvia's Tiger Economy Loses Its Bite by Kristina Rizga, The NationThe NationThe Nation is the oldest continuously published weekly magazine in the United States. The periodical, devoted to politics and culture, is self-described as "the flagship of the left." Founded on July 6, 1865, It is published by The Nation Company, L.P., at 33 Irving Place, New York City.The Nation...
, October 28, 2009

