
ENOB
Encyclopedia
Effective number of bits (ENOB) is a measure of the quality of a digitised signal. The resolution of a digital-to-analog
or analog-to-digital
converter (DAC or ADC) is commonly specified by the number of bit
s used to represent the analog value, in principle giving 2N signal levels for an N-bit signal. However, all real signals contain a certain amount of noise
. If the converter is able to represent signal levels below the system noise floor
, the lower bits of the digitised signal only represent system noise and do not contain useful information. ENOB specifies the number of bits in the digitised signal above the noise floor. Often ENOB is used as a quality measure also for other blocks like sample-and-hold amplifiers
. This way also analog blocks can be easily included to signal-chain calculations as the total ENOB of a chain of blocks is usually below the ENOB of the worst block.
 ,
,
where all values are given in dB, and
This definition compares the SINAD of an ideal ADC or DAC with a word length of ENOB bits with the SINAD of the ADC or DAC being tested.
The offset error in this case is -0.01 V or -0.01 LSB as 1 V = 1 LSB
in this example. The gain error is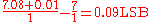 .
.
Correcting the offset and gain error, we obtain the following list of measurements:
This allows the INL
and DNL
to be calculated:
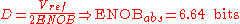
The absolute and relative accuracy can now be calculated. In this case, the ENOB absolute accuracy is calculated using the largest absolute deviation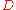 , in this case 0.08 V:
, in this case 0.08 V:
The effective number of bits relative accuracy is calculated using the largest relative (INL) deviation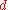 , in this case 0.09 V.
, in this case 0.09 V.

For this kind of ENOB calculation, note that the effective number of bits can be larger or smaller than the actual number of bits. When the ENOB is smaller than the ANOB, this means that some of the least significant bits of the result are inaccurate.
However, one can also argue that the ENOB can never be larger than the ANOB, because you always have to add the quantization error of an ideal converter which is +-0.5 LSB. Different designers may use different definitions of ENOB!
Digital-to-analog converter
In electronics, a digital-to-analog converter is a device that converts a digital code to an analog signal . An analog-to-digital converter performs the reverse operation...
or analog-to-digital
Analog-to-digital converter
An analog-to-digital converter is a device that converts a continuous quantity to a discrete time digital representation. An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement...
converter (DAC or ADC) is commonly specified by the number of bit
Bit
A bit is the basic unit of information in computing and telecommunications; it is the amount of information stored by a digital device or other physical system that exists in one of two possible distinct states...
s used to represent the analog value, in principle giving 2N signal levels for an N-bit signal. However, all real signals contain a certain amount of noise
Noise (electronics)
Electronic noise is a random fluctuation in an electrical signal, a characteristic of all electronic circuits. Noise generated by electronic devices varies greatly, as it can be produced by several different effects...
. If the converter is able to represent signal levels below the system noise floor
Noise floor
In signal theory, the noise floor is the measure of the signal created from the sum of all the noise sources and unwanted signals within a measurement system, where the noise is defined as any signal other than the one being monitored....
, the lower bits of the digitised signal only represent system noise and do not contain useful information. ENOB specifies the number of bits in the digitised signal above the noise floor. Often ENOB is used as a quality measure also for other blocks like sample-and-hold amplifiers
Sample and hold
In electronics, a sample and hold circuit is an analog device that samples the voltage of a continuously varying analog signal and holds its value at a constant level for a specified minimal period of time. Sample and hold circuits and related peak detectors are the elementary analog memory...
. This way also analog blocks can be easily included to signal-chain calculations as the total ENOB of a chain of blocks is usually below the ENOB of the worst block.
Definition
An often used definition for ENOB is ,
,where all values are given in dB, and
- SINADSINADSINAD stands for Signal-to-noise and distortion ratio. It is a measure of the quality of a signal from a communications device, often defined as:...
is the ratio of the total signal including distortion and noise to the wanted signal. - The 6.02 term in the divisor converts decibels (a log10 representation) to bits (a log2 representation).

- The 1.76 term comes from quantization error in an ideal ADC.
This definition compares the SINAD of an ideal ADC or DAC with a word length of ENOB bits with the SINAD of the ADC or DAC being tested.
Example
The following are measurements of a 3-bit unipolar D/A converter with reference voltage Vref = 8 V:| Digital Input | 000 | 001 | 010 | 011 | 100 | 101 | 110 | 111 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analog Output (V) | -0.01 | 1.03 | 2.02 | 2.96 | 3.95 | 5.02 | 6.00 | 7.08 |
The offset error in this case is -0.01 V or -0.01 LSB as 1 V = 1 LSB
Least significant bit
In computing, the least significant bit is the bit position in a binary integer giving the units value, that is, determining whether the number is even or odd. The lsb is sometimes referred to as the right-most bit, due to the convention in positional notation of writing less significant digits...
in this example. The gain error is
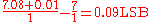 .
.Correcting the offset and gain error, we obtain the following list of measurements:
- (0, 1.03, 2.00, 2.93, 3.91, 4.96, 5.93, 7) LSB
This allows the INL
Integral nonlinearity
Integral nonlinearity is a term describing the maximum deviation between the ideal output of a DAC and the actual output level...
and DNL
Differential nonlinearity
Differential nonlinearity is a term describing the deviation between two analog values corresponding to adjacent input digital values. It is an important specification for measuring error in a digital-to-analog converter ; the accuracy of a DAC is mainly determined by this specification...
to be calculated:
- INL = (0, 0.03, 0, -0.07, -0.09, -0.04, -0.07, 0) LSB
- DNL = (0.03, -0.03, -0.07, -0.02, 0.05, -0.03, 0.07, 0) LSB
The absolute and relative accuracy can now be calculated. In this case, the ENOB absolute accuracy is calculated using the largest absolute deviation
 , in this case 0.08 V:
, in this case 0.08 V:
The effective number of bits relative accuracy is calculated using the largest relative (INL) deviation
 , in this case 0.09 V.
, in this case 0.09 V.
For this kind of ENOB calculation, note that the effective number of bits can be larger or smaller than the actual number of bits. When the ENOB is smaller than the ANOB, this means that some of the least significant bits of the result are inaccurate.
However, one can also argue that the ENOB can never be larger than the ANOB, because you always have to add the quantization error of an ideal converter which is +-0.5 LSB. Different designers may use different definitions of ENOB!
External links
- Video tutorial on ENOB from Texas Instruments
- The Effective Number of Bits (ENOB) - This application note explains how to measure the oscilloscope ENOB.

