
Dupuit assumption
Encyclopedia
The Dupuit assumption holds that groundwater
moves horizontally in an unconfined aquifer, and that the groundwater discharge is proportional to the saturated aquifer
thickness. It was first designed by Jules Dupuit
in 1863 to simplify the groundwater flow equation
for analytical solutions.
The Dupuit assumption requires that the water table
is relatively flat, and that the groundwater is hydrostatic (i.e., the equipotential
lines are vertical):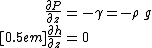
where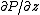 is the vertical pressure gradient,
is the vertical pressure gradient,  is the specific weight
is the specific weight
,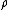 is the density of water,
is the density of water,  is the standard gravity
is the standard gravity
, and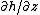 is the vertical hydraulic gradient.
is the vertical hydraulic gradient.
Groundwater
Groundwater is water located beneath the ground surface in soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. A unit of rock or an unconsolidated deposit is called an aquifer when it can yield a usable quantity of water. The depth at which soil pore spaces or fractures and voids in rock...
moves horizontally in an unconfined aquifer, and that the groundwater discharge is proportional to the saturated aquifer
Aquifer
An aquifer is a wet underground layer of water-bearing permeable rock or unconsolidated materials from which groundwater can be usefully extracted using a water well. The study of water flow in aquifers and the characterization of aquifers is called hydrogeology...
thickness. It was first designed by Jules Dupuit
Jules Dupuit
Jules Dupuit was an Italian-born French civil engineer and economist.He was born in Fossano, Italy then under the rule of Napoleon Bonaparte. At the age of ten he emigrated to France with his family where he studied in Versailles — winning a Physics prize at graduation. He then studied in the...
in 1863 to simplify the groundwater flow equation
Groundwater flow equation
Used in hydrogeology, the groundwater flow equation is the mathematical relationship which is used to describe the flow of groundwater through an aquifer. The transient flow of groundwater is described by a form of the diffusion equation, similar to that used in heat transfer to describe the flow...
for analytical solutions.
The Dupuit assumption requires that the water table
Water table
The water table is the level at which the submarine pressure is far from atmospheric pressure. It may be conveniently visualized as the 'surface' of the subsurface materials that are saturated with groundwater in a given vicinity. However, saturated conditions may extend above the water table as...
is relatively flat, and that the groundwater is hydrostatic (i.e., the equipotential
Equipotential
Equipotential or isopotential in mathematics and physics refers to a region in space where every point in it is at the same potential. This usually refers to a scalar potential , although it can also be applied to vector potentials...
lines are vertical):
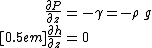
where
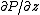 is the vertical pressure gradient,
is the vertical pressure gradient,  is the specific weight
is the specific weightSpecific weight
The specific weight is the weight per unit volume of a material. The symbol of specific weight is γ ....
,
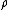 is the density of water,
is the density of water,  is the standard gravity
is the standard gravityStandard gravity
Standard gravity, or standard acceleration due to free fall, usually denoted by g0 or gn, is the nominal acceleration of an object in a vacuum near the surface of the Earth. It is defined as precisely , or about...
, and
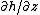 is the vertical hydraulic gradient.
is the vertical hydraulic gradient.

