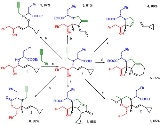
Divergent synthesis
Overview
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
a divergent synthesis is a strategy with the aim to improve the efficiency of chemical synthesis
Chemical synthesis
In chemistry, chemical synthesis is purposeful execution of chemical reactions to get a product, or several products. This happens by physical and chemical manipulations usually involving one or more reactions...
. It is often an alternative to convergent synthesis
Convergent synthesis
In chemistry a convergent synthesis is a strategy that aims to improve the efficiency of multi-step chemical synthesis, most often in organic synthesis...
or linear synthesis.
In one strategy divergent synthesis aims to generate a library
Library (biology)
In molecular biology, a library is a collection of DNA fragments that is stored and propagated in a population of micro-organisms through the process of molecular cloning...
of chemical compound
Chemical compound
A chemical compound is a pure chemical substance consisting of two or more different chemical elements that can be separated into simpler substances by chemical reactions. Chemical compounds have a unique and defined chemical structure; they consist of a fixed ratio of atoms that are held together...
s by first reacting a molecule with a set of reactants. The next generation of compounds is generated by further reactions with each compound in generation 1. This methodology quickly diverges to large numbers of new compounds
- A generates A1, A2, A3, A4, A5 in generation 1
- A1 generates A11, A12, A13 in generation 2 and so on.
An entire library of new chemical compounds for instance sugar
Carbohydrate
A carbohydrate is an organic compound with the empirical formula ; that is, consists only of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, with a hydrogen:oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 . However, there are exceptions to this. One common example would be deoxyribose, a component of DNA, which has the empirical...
s can be screened for desirable properties.
Discussions

