
Distance modulus
Encyclopedia
Definition
The distance modulus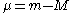 is the difference between the apparent magnitude
is the difference between the apparent magnitudeApparent magnitude
The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere...
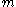 (ideally, corrected from the effects of interstellar absorption) and the absolute magnitude
(ideally, corrected from the effects of interstellar absorption) and the absolute magnitudeAbsolute magnitude
Absolute magnitude is the measure of a celestial object's intrinsic brightness. it is also the apparent magnitude a star would have if it were 32.6 light years away from Earth...
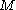 of an astronomical object
of an astronomical objectAstronomical object
Astronomical objects or celestial objects are naturally occurring physical entities, associations or structures that current science has demonstrated to exist in the observable universe. The term astronomical object is sometimes used interchangeably with astronomical body...
. It is related to the distance
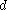 in parsecs by:
in parsecs by: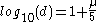
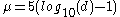
This definition is convenient because the observed brightness of a light source is related to its distance by the inverse square law (a source twice as far away appears one quarter as bright) and because brightnesses are usually expressed not directly, but in magnitudes
Apparent magnitude
The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere...
.
Absolute magnitude
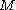 is defined as the apparent magnitude of an object when seen at a distance of 10 parsec
is defined as the apparent magnitude of an object when seen at a distance of 10 parsecParsec
The parsec is a unit of length used in astronomy. It is about 3.26 light-years, or just under 31 trillion kilometres ....
s. Suppose a light source has luminosity L(d) when observed from a distance of
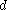 parsecs, and luminosity L(10) when observed from a distance of 10 parsecs. The inverse-square law is then written like:
parsecs, and luminosity L(10) when observed from a distance of 10 parsecs. The inverse-square law is then written like:
The magnitudes and luminosities are related by:
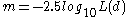
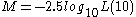
Substituting and rearranging, we get:

which means that the apparent magnitude is the absolute magnitude plus the distance modulus.
Isolating
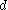 from the equation
from the equation 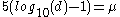 , we find that the distance in parsecs is given by
, we find that the distance in parsecs is given by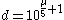
The uncertainty in the distance in parsecs (δd) can be computed from the uncertainty in the distance modulus (δμ) using
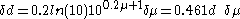
which is derived using standard error analysis.
Different kinds of distance moduli
Distance is not the only quantity relevant in determining the difference between absolute and apparent magnitude. Absorption is another important factor and it may even be a dominant one in particular cases (e. g. in the direction of the galactic center).Thus a distinction is made between distance moduli uncorrected for interstellar absorption (whose values would overestimate the distance if used naively) and absorption-corrected moduli.
The first ones are termed visual distance moduli and are denoted by
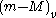 while the second ones are called true distance moduli and denoted by
while the second ones are called true distance moduli and denoted by  .
.Visual distance moduli are computed by calculating the difference between the observed apparent magnitude and some theoretical estimate of the absolute magnitude. True distance moduli require a further theoretical step, that is the estimation of the interstellar absorption coefficient.
Usage
Distance moduli are most commonly used when expressing the distance to other galaxies in the relatively nearby universe. For example, the Large Magellanic CloudLarge Magellanic Cloud
The Large Magellanic Cloud is a nearby irregular galaxy, and is a satellite of the Milky Way. At a distance of slightly less than 50 kiloparsecs , the LMC is the third closest galaxy to the Milky Way, with the Sagittarius Dwarf Spheroidal and Canis Major Dwarf Galaxy lying closer to the center...
is at a distance modulus of 18.5, the Andromeda Galaxy
Andromeda Galaxy
The Andromeda Galaxy is a spiral galaxy approximately 2.5 million light-years from Earth in the constellation Andromeda. It is also known as Messier 31, M31, or NGC 224, and is often referred to as the Great Andromeda Nebula in older texts. Andromeda is the nearest spiral galaxy to the...
's distance modulus is 24.4, and the galaxy NGC 4548 in the Virgo Cluster
Virgo Cluster
The Virgo Cluster is a cluster of galaxies whose center is 53.8 ± 0.3 Mly away in the constellation Virgo. Comprising approximately 1300 member galaxies, the cluster forms the heart of the larger Local Supercluster, of which the Local Group is an outlying member...
has a DM of 31.0. In the case of the LMC, this means that the supernova
Supernova
A supernova is a stellar explosion that is more energetic than a nova. It is pronounced with the plural supernovae or supernovas. Supernovae are extremely luminous and cause a burst of radiation that often briefly outshines an entire galaxy, before fading from view over several weeks or months...
SN1987A, with a peak apparent magnitude of 2.8, had an absolute magnitude of -15.7, which is low by supernova standards.
Using distance moduli makes computing magnitudes easy. As for instance, a solar type star (M=5) in Andromeda galaxy (DM=24.4) would have an apparent magnitude (m) of 5 + 24.4 = 29.4, so it would be barely visible in the HST
Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope is a space telescope that was carried into orbit by a Space Shuttle in 1990 and remains in operation. A 2.4 meter aperture telescope in low Earth orbit, Hubble's four main instruments observe in the near ultraviolet, visible, and near infrared...
, which has a limiting magnitude of about 30 http://www.astro.uu.nl/~strous/AA/en/antwoorden/magnituden.html. This calculation can be done quickly in one's head. Since it is apparent magnitudes which are actually measured at a telescope, this way of looking at things serves to highlight the fact that many discussions about distances in astronomy are really discussions about the putative or derived absolute magnitudes of the distant objects being observed.

