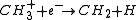Dissociative recombination
Encyclopedia
Dissociative recombination is a process where a positive molecular ion recombines with an electron, and as a result, the neutral molecule dissociates. This reaction is important for extraterrestrial and atmospheric chemistry. On Earth
, dissociative recombination is practically non-existent, as free electrons would react with any molecule
(even neutral molecules) they encounter. Even in the best laboratory conditions, dissociative recombination is hard to observe.
In astrophysics
, dissociative recombination is one of the main paths via which molecules are broken down, and other molecules are formed. The existence of dissociative recombination is possible due to the vacuum
of the interstellar medium
. A typical example of dissociative recombination in astrophysics is:
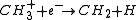
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
, dissociative recombination is practically non-existent, as free electrons would react with any molecule
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
(even neutral molecules) they encounter. Even in the best laboratory conditions, dissociative recombination is hard to observe.
In astrophysics
Astrophysics
Astrophysics is the branch of astronomy that deals with the physics of the universe, including the physical properties of celestial objects, as well as their interactions and behavior...
, dissociative recombination is one of the main paths via which molecules are broken down, and other molecules are formed. The existence of dissociative recombination is possible due to the vacuum
Vacuum
In everyday usage, vacuum is a volume of space that is essentially empty of matter, such that its gaseous pressure is much less than atmospheric pressure. The word comes from the Latin term for "empty". A perfect vacuum would be one with no particles in it at all, which is impossible to achieve in...
of the interstellar medium
Interstellar medium
In astronomy, the interstellar medium is the matter that exists in the space between the star systems in a galaxy. This matter includes gas in ionic, atomic, and molecular form, dust, and cosmic rays. It fills interstellar space and blends smoothly into the surrounding intergalactic space...
. A typical example of dissociative recombination in astrophysics is: