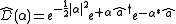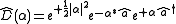Displacement operator
Encyclopedia
The displacement operator for one mode in quantum optics
is the operator
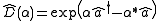 ,
,
where is the amount of displacement in optical phase space
is the amount of displacement in optical phase space
,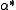 is the complex conjugate of that displacement, and
is the complex conjugate of that displacement, and 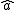 and
and 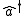 are the lowering and raising operators
are the lowering and raising operators
, respectively.
The name of this operator is derived from its ability to displace a localized state in phase space by a magnitude . It may also act on the vacuum state by displacing it into a coherent state
. It may also act on the vacuum state by displacing it into a coherent state
. Specifically,
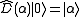 where
where 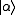 is a coherent state.
is a coherent state.
Displaced states are eigenfunctions of the annihilation (lowering) operator.
, and therefore obeys
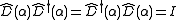 ,
,
where I is the identity matrix. Since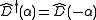 , the hermitian conjugate of the displacement operator can also be interpreted as a displacement of opposite magnitude (
, the hermitian conjugate of the displacement operator can also be interpreted as a displacement of opposite magnitude (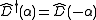 ). The effect of applying this operator in a similarity transformation of the ladder operators results in their displacement.
). The effect of applying this operator in a similarity transformation of the ladder operators results in their displacement.
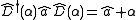
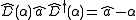
The product of two displacement operators is another displacement operator , apart from a phase factor, has the total displacement as the sum of the two individual displacements. This can be seen by utilizing the Baker-Campbell-Hausdorff formula.
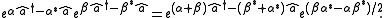
which shows us that:
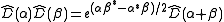
When acting on an eigenket, the phase factor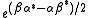 appears in each term of the resulting state, which makes it physically irrelevant.
appears in each term of the resulting state, which makes it physically irrelevant.
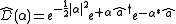
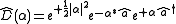
Quantum optics
Quantum optics is a field of research in physics, dealing with the application of quantum mechanics to phenomena involving light and its interactions with matter.- History of quantum optics :...
is the operator
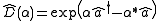 ,
,where
 is the amount of displacement in optical phase space
is the amount of displacement in optical phase spaceOptical phase space
In quantum optics, an optical phase space is a phase space in which all quantum states of an optical system are described. Each point in the optical phase space corresponds to a unique state of an optical system. For any such system, a plot of the quadratures against each other, possibly as...
,
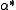 is the complex conjugate of that displacement, and
is the complex conjugate of that displacement, and 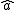 and
and 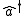 are the lowering and raising operators
are the lowering and raising operatorsCreation and annihilation operators
Creation and annihilation operators are mathematical operators that have widespread applications in quantum mechanics, notably in the study of quantum harmonic oscillators and many-particle systems. An annihilation operator lowers the number of particles in a given state by one...
, respectively.
The name of this operator is derived from its ability to displace a localized state in phase space by a magnitude
 . It may also act on the vacuum state by displacing it into a coherent state
. It may also act on the vacuum state by displacing it into a coherent stateCoherent state
In quantum mechanics a coherent state is a specific kind of quantum state of the quantum harmonic oscillator whose dynamics most closely resembles the oscillating behaviour of a classical harmonic oscillator...
. Specifically,
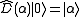 where
where 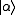 is a coherent state.
is a coherent state.Displaced states are eigenfunctions of the annihilation (lowering) operator.
Properties
The displacement operator is a unitary operatorUnitary operator
In functional analysis, a branch of mathematics, a unitary operator is a bounded linear operator U : H → H on a Hilbert space H satisfyingU^*U=UU^*=I...
, and therefore obeys
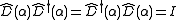 ,
,where I is the identity matrix. Since
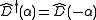 , the hermitian conjugate of the displacement operator can also be interpreted as a displacement of opposite magnitude (
, the hermitian conjugate of the displacement operator can also be interpreted as a displacement of opposite magnitude (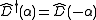 ). The effect of applying this operator in a similarity transformation of the ladder operators results in their displacement.
). The effect of applying this operator in a similarity transformation of the ladder operators results in their displacement.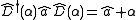
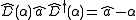
The product of two displacement operators is another displacement operator , apart from a phase factor, has the total displacement as the sum of the two individual displacements. This can be seen by utilizing the Baker-Campbell-Hausdorff formula.
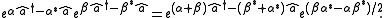
which shows us that:
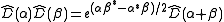
When acting on an eigenket, the phase factor
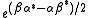 appears in each term of the resulting state, which makes it physically irrelevant.
appears in each term of the resulting state, which makes it physically irrelevant.Alternative expressions
Two alternative ways to express the displacement operator are: