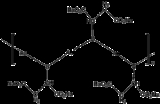
Disodium aurothiomalate
Encyclopedia
Disodium aurothiomalate is a chemical compound
with the formula AuSCH(CO2Na)CH2CO2Na. In conjunction with its monoprotonated derivative, this coordination complex or closely related species are used to treat rheumatoid arthritis
, under the tradename Myochrysine. The thiomalate is racemic
in most formulation.
Na2Au2T(TH) salt (T = thiomalate3-, TH = monoprotonated thiomalate2-) is related to disodium aurothiomalate but is easier to crystallise and characterise by X-ray crystallography
. The compound is polymeric with Au-S-Au-S... chains with succinoyl groups attached to the sulfur atoms. The structure of the related drug Aurothioglucose is also polymeric with two-coordinate gold(I) centers. In such compounds, the efficacy results from the compound in solution, the structures of such solution species are often poorly understood. Medical texts sometimes suggest that free Au+ ions exist in this and related gold(I) compounds, but the Au-thiolate bonding is highly covalent and free gold ions do not exist in solution. Whereas simple gold thiolates are lipophilic
, the carboxylate substituents render disodium aurothiomalate soluble in water.
Disodium aurothiomalate contains no Au-C bonds, so it is not an organometallic compound in the formal sense.
Gold salts can decrease the inflammation of the joint lining. This effect can prevent destruction of bone and cartilage. In former times gold salts were used as second-line drugs (used when the arthritis progressed in spite of antiinflammatory drugs). Nowadays such former "second-line" drugs are used from the beginning of therapy to inhibit joint erosion if possible.
Chemical compound
A chemical compound is a pure chemical substance consisting of two or more different chemical elements that can be separated into simpler substances by chemical reactions. Chemical compounds have a unique and defined chemical structure; they consist of a fixed ratio of atoms that are held together...
with the formula AuSCH(CO2Na)CH2CO2Na. In conjunction with its monoprotonated derivative, this coordination complex or closely related species are used to treat rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic, systemic inflammatory disorder that may affect many tissues and organs, but principally attacks synovial joints. The process produces an inflammatory response of the synovium secondary to hyperplasia of synovial cells, excess synovial fluid, and the development...
, under the tradename Myochrysine. The thiomalate is racemic
Racemic
In chemistry, a racemic mixture, or racemate , is one that has equal amounts of left- and right-handed enantiomers of a chiral molecule. The first known racemic mixture was "racemic acid", which Louis Pasteur found to be a mixture of the two enantiomeric isomers of tartaric acid.- Nomenclature :A...
in most formulation.
Structure
Disodium aurothiomalate is a coordination polymer. The salt CsCaesium
Caesium or cesium is the chemical element with the symbol Cs and atomic number 55. It is a soft, silvery-gold alkali metal with a melting point of 28 °C , which makes it one of only five elemental metals that are liquid at room temperature...
Na2Au2T(TH) salt (T = thiomalate3-, TH = monoprotonated thiomalate2-) is related to disodium aurothiomalate but is easier to crystallise and characterise by X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography is a method of determining the arrangement of atoms within a crystal, in which a beam of X-rays strikes a crystal and causes the beam of light to spread into many specific directions. From the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, a crystallographer can produce a...
. The compound is polymeric with Au-S-Au-S... chains with succinoyl groups attached to the sulfur atoms. The structure of the related drug Aurothioglucose is also polymeric with two-coordinate gold(I) centers. In such compounds, the efficacy results from the compound in solution, the structures of such solution species are often poorly understood. Medical texts sometimes suggest that free Au+ ions exist in this and related gold(I) compounds, but the Au-thiolate bonding is highly covalent and free gold ions do not exist in solution. Whereas simple gold thiolates are lipophilic
Lipophilic
Lipophilicity, , refers to the ability of a chemical compound to dissolve in fats, oils, lipids, and non-polar solvents such as hexane or toluene. These non-polar solvents are themselves lipophilic — the axiom that like dissolves like generally holds true...
, the carboxylate substituents render disodium aurothiomalate soluble in water.
Disodium aurothiomalate contains no Au-C bonds, so it is not an organometallic compound in the formal sense.
Mechanism of action
Unknown. In vitro experiments have shown that Au(I) can inhibit lymphocyte proliferation, lysosomal enzyme release, the release of reactive oxygen species from macrophages, and IL-1 production.Gold salts can decrease the inflammation of the joint lining. This effect can prevent destruction of bone and cartilage. In former times gold salts were used as second-line drugs (used when the arthritis progressed in spite of antiinflammatory drugs). Nowadays such former "second-line" drugs are used from the beginning of therapy to inhibit joint erosion if possible.

