
Direct insolation
Encyclopedia
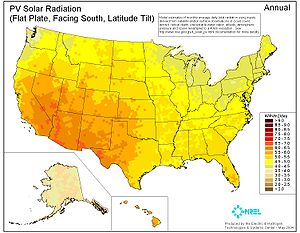
Irradiance
Irradiance is the power of electromagnetic radiation per unit area incident on a surface. Radiant emittance or radiant exitance is the power per unit area radiated by a surface. The SI units for all of these quantities are watts per square meter , while the cgs units are ergs per square centimeter...
measured at a given location on Earth with a surface element perpendicular to the Sun's rays, excluding diffuse insolation (the solar radiation that is scattered or reflected by atmospheric components in the sky). Direct insolation is equal to the solar constant
Solar constant
The solar constant, a measure of flux density, is the amount of incoming solar electromagnetic radiation per unit area that would be incident on a plane perpendicular to the rays, at a distance of one astronomical unit...
minus the atmospheric losses due to absorption
Absorption (electromagnetic radiation)
In physics, absorption of electromagnetic radiation is the way by which the energy of a photon is taken up by matter, typically the electrons of an atom. Thus, the electromagnetic energy is transformed to other forms of energy for example, to heat. The absorption of light during wave propagation is...
and scattering
Light scattering
Light scattering is a form of scattering in which light is the form of propagating energy which is scattered. Light scattering can be thought of as the deflection of a ray from a straight path, for example by irregularities in the propagation medium, particles, or in the interface between two media...
. While the solar constant varies with the Earth-Sun distance
Earth's orbit
In astronomy, the Earth's orbit is the motion of the Earth around the Sun, at an average distance of about 150 million kilometers, every 365.256363 mean solar days .A solar day is on average 24 hours; it takes 365.256363 of these to orbit the sun once in the sense of returning...
and solar cycle
Solar cycle
The solar cycle, or the solar magnetic activity cycle, is a periodic change in the amount of irradiation from the Sun that is experienced on Earth. It has a period of about 11 years, and is one component of solar variation, the other being aperiodic fluctuations. Solar variation causes changes in...
s, the losses depend on the time of day (length of light's path through the atmosphere depending on the Solar elevation angle
Solar elevation angle
The solar elevation angle is the elevation angle of the sun. That is, the angle between the directionof the geometric center of the sun's apparent disk and the horizon...
), cloud cover
Cloud cover
Cloud cover refers to the fraction of the sky obscured by clouds when observed from a particular location...
, moisture
Moisture
Humidity is the amount of moisture the air can hold before it rains. Moisture refers to the presence of a liquid, especially water, often in trace amounts...
content, and other impurities.
Average direct insolation
For practical purposes, a time-average of the direct insolation over the course of the year is commonly used. This averaging takes into account the absence of sunlight during the night, increased scatter in the morning and evening hours, average effects of cloud cover and smogSmog
Smog is a type of air pollution; the word "smog" is a portmanteau of smoke and fog. Modern smog is a type of air pollution derived from vehicular emission from internal combustion engines and industrial fumes that react in the atmosphere with sunlight to form secondary pollutants that also combine...
, as well as seasonal variations of the mid-day solar elevation.
Units of measurement
Direct insolation is measured in (W/m²) or kilowatt-hours per square meter per day (kW·h/(m²·day)).- 1 kW·h/(m²·day) = 1,000 W · 1 hour / ( 1 m² · 24 hours) = 41.67 W/m²
In the case of photovoltaics, average direct insolation is commonly measured in terms of peak direct insolation as kWh/(kWp·y)
(kilowatt hours per year per kilowatt peak rating)

