Dimethoxyamphetamine
Encyclopedia
DMA, or dimethoxy
amphetamine
, is a series of lesser-known psychedelic drugs
similar in structure to amphetamine and to trimethoxyamphetamine
(TMA). They were first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin
and written up in his book PiHKAL (Phenethylamines i Have Known And Loved)
. Very little data is known about their dangers or toxicity.
Dosage: 60 mg or greater
Duration: short
Effects: stimulative
, amphetamine-like effects
The DO analogue of 2C-H
(DOH)
CAS Number: 2801-68-5
Dosage: 80–160 mg
Duration: 6–8 hours
Effects: Mydriasis
, increase in heart rate
Dosage: unknown
Duration: unknown
Effects: Mescaline
-like visuals
Note that two other positional isomers of dimethoxyamphetamine, 2,6-DMA and 3,5-DMA, have also been made, but these drugs have not been tested in humans and their effects are unknown. However, it is likely that these compounds would also produce amphetamine-like stimulation or possibly hallucinogenic effects.
Methoxy
In chemistry , methoxy refers to the functional group consisting of a methyl group bound to oxygen. This alkoxy group has the formula O–CH3.The word is used in organic nomenclature usually to describe an ether...
amphetamine
Amphetamine
Amphetamine or amfetamine is a psychostimulant drug of the phenethylamine class which produces increased wakefulness and focus in association with decreased fatigue and appetite.Brand names of medications that contain, or metabolize into, amphetamine include Adderall, Dexedrine, Dextrostat,...
, is a series of lesser-known psychedelic drugs
Psychedelics, dissociatives and deliriants
This general group of pharmacological agents can be divided into three broad categories: psychedelics, dissociatives, and deliriants. These classes of psychoactive drugs have in common that they can cause subjective changes in perception, thought, emotion and consciousness...
similar in structure to amphetamine and to trimethoxyamphetamine
Trimethoxyamphetamine
TMAs, also known as trimethoxyamphetamines, are a family of isomeric psychedelic hallucinogenic drugs. There exist six different TMAs that differ only in the position of the three methoxy groups: TMA, TMA-2, TMA-3, TMA-4, TMA-5, and TMA-6. The TMAs are analogs of the phenethylamine cactus alkaloid...
(TMA). They were first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin
Alexander Shulgin
Alexander "Sasha" Theodore Shulgin is an American pharmacologist, chemist, artist, and drug developer.Shulgin is credited with the popularization of MDMA, commonly known as ecstasy, in the late 1970s and early 1980s, especially for psychopharmaceutical use and the treatment of depression and...
and written up in his book PiHKAL (Phenethylamines i Have Known And Loved)
PiHKAL
PiHKAL: A Chemical Love Story is a book by Dr. Alexander Shulgin and Ann Shulgin which was published in 1991. The subject of the work is psychoactive phenethylamine chemical derivatives, notably those that act as psychedelics and/or empathogen-entactogens...
. Very little data is known about their dangers or toxicity.
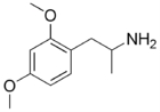
2,4-DMA

Dosage: 60 mg or greater
Duration: short
Effects: stimulative
Stimulant
Stimulants are psychoactive drugs which induce temporary improvements in either mental or physical function or both. Examples of these kinds of effects may include enhanced alertness, wakefulness, and locomotion, among others...
, amphetamine-like effects
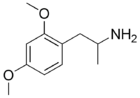
2,5-DMA

The DO analogue of 2C-H
2C-H
2C-H, or 2,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine, is a lesser-known chemical of the 2C family. 2C-H was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL , the dosage and duration are both unknown...
(DOH)
CAS Number: 2801-68-5
Dosage: 80–160 mg
Duration: 6–8 hours
Effects: Mydriasis
Mydriasis
Mydriasis is a dilation of the pupil due to disease, trauma or the use of drugs. Normally, the pupil dilates in the dark and constricts in the light to respectively improve vividity at night and to protect the retina from sunlight damage during the day...
, increase in heart rate
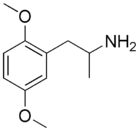
3,4-DMA

Dosage: unknown
Duration: unknown
Effects: Mescaline
Mescaline
Mescaline or 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenethylamine is a naturally occurring psychedelic alkaloid of the phenethylamine class used mainly as an entheogen....
-like visuals
Note that two other positional isomers of dimethoxyamphetamine, 2,6-DMA and 3,5-DMA, have also been made, but these drugs have not been tested in humans and their effects are unknown. However, it is likely that these compounds would also produce amphetamine-like stimulation or possibly hallucinogenic effects.

