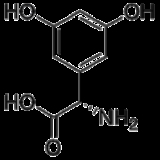
Dihydroxyphenylglycine
Encyclopedia
-3,5-Dihydroxyphenylglycine or DHPG is a potent agonist
of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) mGluR1
and mGluR5
.
DHPG was the first agonist shown to be selective for group I mGluRs. Agonist activity is found in only the S isomer
, and (S)-DHPG may be a partial agonist
of group I mGluRs.
(S)-DHPG has been investigated for therapeutic effects in the treatment of neuron
al injury (such as those associated with ischemia
or hypoxia
), cognitive enhancement, and Alzheimer's disease
.
Agonist
An agonist is a chemical that binds to a receptor of a cell and triggers a response by that cell. Agonists often mimic the action of a naturally occurring substance...
of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) mGluR1
Metabotropic glutamate receptor 1
The glutamate receptor, metabotropic 1, also known as GRM1, is a human gene which encodes the metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 protein.-Function:...
and mGluR5
Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5
Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GRM5 gene.- Function :The amino acid L-glutamate is the major excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system and activates both ionotropic and metabotropic glutamate receptors...
.
DHPG was the first agonist shown to be selective for group I mGluRs. Agonist activity is found in only the S isomer
Isomer
In chemistry, isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formulas. Isomers do not necessarily share similar properties, unless they also have the same functional groups. There are many different classes of isomers, like stereoisomers, enantiomers, geometrical...
, and (S)-DHPG may be a partial agonist
Partial agonist
Partial agonists bind and activate a given receptor, but have only partial efficacy at the receptor relative to a full agonist...
of group I mGluRs.
(S)-DHPG has been investigated for therapeutic effects in the treatment of neuron
Neuron
A neuron is an electrically excitable cell that processes and transmits information by electrical and chemical signaling. Chemical signaling occurs via synapses, specialized connections with other cells. Neurons connect to each other to form networks. Neurons are the core components of the nervous...
al injury (such as those associated with ischemia
Ischemia
In medicine, ischemia is a restriction in blood supply, generally due to factors in the blood vessels, with resultant damage or dysfunction of tissue. It may also be spelled ischaemia or ischæmia...
or hypoxia
Hypoxia (medical)
Hypoxia, or hypoxiation, is a pathological condition in which the body as a whole or a region of the body is deprived of adequate oxygen supply. Variations in arterial oxygen concentrations can be part of the normal physiology, for example, during strenuous physical exercise...
), cognitive enhancement, and Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease also known in medical literature as Alzheimer disease is the most common form of dementia. There is no cure for the disease, which worsens as it progresses, and eventually leads to death...
.

