
Digital room correction
Encyclopedia
Acoustics
Acoustics is the interdisciplinary science that deals with the study of all mechanical waves in gases, liquids, and solids including vibration, sound, ultrasound and infrasound. A scientist who works in the field of acoustics is an acoustician while someone working in the field of acoustics...
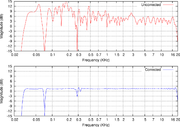
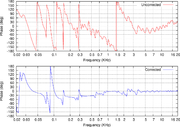
where digital filters designed to ameliorate unfavorable effects of a room's acoustics are applied to the input of a sound reproduction system. Modern room correction systems produce substantial improvements in the time domain
Time
Time is a part of the measuring system used to sequence events, to compare the durations of events and the intervals between them, and to quantify rates of change such as the motions of objects....
and frequency domain
Frequency domain
In electronics, control systems engineering, and statistics, frequency domain is a term used to describe the domain for analysis of mathematical functions or signals with respect to frequency, rather than time....
response of the sound reproduction system.
History
Equalization (audio)
Equalization is the process commonly used in sound recording and reproduction to alter the frequency response of an audio system using linear filters. Most hi-fi equipment uses relatively simple filters to make bass and treble adjustments. Graphic and parametric equalizers have much more...
, to normalize the frequency response of a playback system has a long history; however, analog filters are very limited in their ability to correct the distortion found in many rooms. Although digital implementations of the equalizers have been available for some time, digital room correction is usually used to refer to the construction of filters which attempt to invert the impulse response
Impulse response
In signal processing, the impulse response, or impulse response function , of a dynamic system is its output when presented with a brief input signal, called an impulse. More generally, an impulse response refers to the reaction of any dynamic system in response to some external change...
of the room and playback system, at least in part. Digital correction systems are able to use acausal filters
Anticausal system
An anticausal system is a hypothetical system with outputs and internal states that depend solely on future input values. Some textbooks and published research literature might define an anticausal system to be one that does not depend on past input values An anticausal system is a hypothetical...
, and are able to operate with optimal time resolution, optimal frequency resolution, or any desired compromise along the Gabor limit. Digital room correction is a fairly new area of study which has only recently been made possible by the computational power of modern CPUs
Central processing unit
The central processing unit is the portion of a computer system that carries out the instructions of a computer program, to perform the basic arithmetical, logical, and input/output operations of the system. The CPU plays a role somewhat analogous to the brain in the computer. The term has been in...
and DSPs
Digital signal processor
A digital signal processor is a specialized microprocessor with an architecture optimized for the fast operational needs of digital signal processing.-Typical characteristics:...
.
Operation
The configuration of a digital room correction system begins with measuring the impulse responseImpulse response
In signal processing, the impulse response, or impulse response function , of a dynamic system is its output when presented with a brief input signal, called an impulse. More generally, an impulse response refers to the reaction of any dynamic system in response to some external change...
of the room at the listening location for each of the loudspeakers. Then, computer software is used to compute a FIR filter
Finite impulse response
A finite impulse response filter is a type of a signal processing filter whose impulse response is of finite duration, because it settles to zero in finite time. This is in contrast to infinite impulse response filters, which have internal feedback and may continue to respond indefinitely...
, which reverses the effects of the room and linear distortion in the loudspeakers. Finally, the calculated filter is loaded into a computer or other room correction device which applies the filter in real time. Because most room correction filters are acausal, there is some delay. Most DRC systems allow the operator to control the added delay through configurable parameters.
Challenges
DRC systems are not normally used to create a perfect inversion of the room's response because a perfect correction would only be valid at the location where it was measured: a few millimeters away the arrival times from various reflections will differ and the inversion will be imperfect. The imperfectly corrected signal may end up sounding worse than the uncorrected signal because the acausal filters used in digital room correction may cause pre-echoPre-echo
Pre-echo is a digital audio compression artifact where a sound is heard before it occurs . It is most noticeable in impulsive sounds from percussion instruments such as castanets or cymbals....
. Room correction filter calculation systems instead favor a robust approach, and employ sophisticated processing to attempt to produce an inverse filter which will work over a usably large area, and which avoid producing bad-sounding artifacts outside of that area, at the expense of peak accuracy at the measurement location.
See also
- DeconvolutionDeconvolutionIn mathematics, deconvolution is an algorithm-based process used to reverse the effects of convolution on recorded data. The concept of deconvolution is widely used in the techniques of signal processing and image processing...
- Digital filterDigital filterIn electronics, computer science and mathematics, a digital filter is a system that performs mathematical operations on a sampled, discrete-time signal to reduce or enhance certain aspects of that signal. This is in contrast to the other major type of electronic filter, the analog filter, which is...
- Filter (signal processing)Filter (signal processing)In signal processing, a filter is a device or process that removes from a signal some unwanted component or feature. Filtering is a class of signal processing, the defining feature of filters being the complete or partial suppression of some aspect of the signal...
- Filter designFilter designFilter design is the process of designing a filter , often a linear shift-invariant filter, that satisfies a set of requirements, some of which are contradictory...
- LARESLARESLARES is an electronic sound enhancement system that uses microprocessors to control multiple loudspeakers and microphones placed around a performance space for the purpose of providing active acoustic treatment. LARES was invented in Massachusetts in 1988, by engineers working at Lexicon,...
- Minimum phaseMinimum phaseIn control theory and signal processing, a linear, time-invariant system is said to be minimum-phase if the system and its inverse are causal and stable....
- Stereophonic soundStereophonic soundThe term Stereophonic, commonly called stereo, sound refers to any method of sound reproduction in which an attempt is made to create an illusion of directionality and audible perspective...
- Surround soundSurround soundSurround sound encompasses a range of techniques such as for enriching the sound reproduction quality of an audio source with audio channels reproduced via additional, discrete speakers. Surround sound is characterized by a listener location or sweet spot where the audio effects work best, and...
Presentations
- Duff Room Correction, a wiki on digital room correction.
Papers
- On Room Correction and Equalization of Sound Systems, by Dr. Mathias Johansson
- Digital Room Equalization, by Michael Gerzon
Articles
- Room Correction: A Primer, by Nyal Mellor of Acoustic Frontiers
- Sound Correction in the Frequency and Time Domain, by Bernt Ronningsbak of Audiolense
- The Three Acoustical Issues a Room Correction Product Can't Actually Correct, by Nyal Mellor of Acoustic Frontiers

