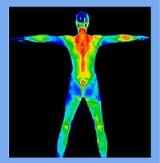
Digital infrared thermal imaging in health care
Encyclopedia
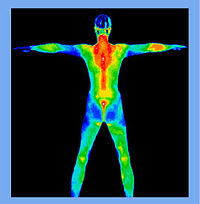
Thermology
Thermography or Thermology is the medical science that derives diagnostic indications from highly detailed and sensitive infrared images of the human body. Thermology is sometimes referred to as medical infrared imaging or tele-thermology and utilizes highly resolute and sensitive infrared cameras...
) who interpret the images for the patient to submit to their health profession
Health profession
The health care industry, or medical industry, is the sector of the economic system that provides goods and services to treat patients with curative, preventive, rehabilitative, palliative, or, at times, unnecessary care...
al for further evaluation.
History
"In 1986, a joint meeting was held in Austin, Texas to discuss the lawsuit against Medicare in an attempt to stop them from removing thermography from the official Medicare fee guidelines. Asked to testify before the State organization were Mr. Victor Yannacome, a trial attorney from New York City who is famous for his defeat of the U.S. Military and Dow Chemical for the use of Agent Orange, and Dr William Cockburn, a clinical thermographer from Los Angeles, CA."Mr. Yannacome and Dr. Cockburn had a meeting afterwards whereas the future of medical thermal imaging was discussed. It was during this meeting that Mr. Yannacome came to the conclusion the word "thermography" was now associated with fraud and would need to be changed in order for it to survive. It was at this meeting that Mr. Yannacome came up with the new name DITI, or Digital Infrared Thermal Imaging.
While some groups try to claim the term DITI as their own construct, the term DITI was coined by a nationally renowned lawyer in 1986 in Austin, TX.
Common clinical uses
- Early detection of breast cancer
- Monitoring changes in overall health
- Monitoring healing processes
- Disease and Virus Monitoring
- Fever Screening (i.e. H1N1, SARS)
Types of screening
- Breast ScreeningMammographyMammography is the process of using low-energy-X-rays to examine the human breast and is used as a diagnostic and a screening tool....
to detect breast cancerBreast cancerBreast cancer is cancer originating from breast tissue, most commonly from the inner lining of milk ducts or the lobules that supply the ducts with milk. Cancers originating from ducts are known as ductal carcinomas; those originating from lobules are known as lobular carcinomas...
and other disorders at their earliest stages - Full Body Screening to detect areas of inflammation and origins of unexplained pain
- Region of InterestRegion of interestA Region of Interest, often abbreviated ROI, is a selected subset of samples within a dataset identified for a particular purpose.For example:* on a waveform , a time or frequency interval...
Screening to identify and monitor localized conditions such as thyroid conditions, TMJ, carpal tunnel syndromeCarpal tunnel syndromeCarpal Tunnel Syndrome is an entrapment idiopathic median neuropathy, causing paresthesia, pain, and other symptoms in the distribution of the median nerve due to its compression at the wrist in the carpal tunnel. The pathophysiology is not completely understood but can be considered compression...
, etc. - Mass Screening, in areas such as airports, to monitor the potential spread of viruses such as H1N1H1N1'Influenza A virus is a subtype of influenza A virus and was the most common cause of human influenza in 2009. Some strains of H1N1 are endemic in humans and cause a small fraction of all influenza-like illness and a small fraction of all seasonal influenza. H1N1 strains caused a few percent of...
(Swine Flu) by identifying fever symptoms in specific individuals
External links
DITI:- Picture Your Health
- Meditherm
- Digital Infrared Thermal Imaging In Medical Therapy by Brenda Witt
- Pain Free Breast Imaging (http://painfreebreastimaging.com/what.html)
- Medical Infrared Imaging (http://www.MedicalIR.com)
- FDA Cleared DITI Cameras (http://www.infraredcamerasinc.com/Thermal-Cameras/FDA-Medical-Thermal-Cameras/FDA_Cleared_Medical_Thermal_Imagers.html)
- Core Health Thermography

