Dibenzylideneacetone
Encyclopedia
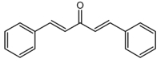
Dibenzylideneacetone or dibenzalacetone, often abbreviated dba, is an organic compound
with the formula C17H14O. It is a bright-yellow solid insoluble in water, but soluble in ethanol. Dibenzylideneacetone is used as a sunscreen
component and as a ligand
in organometallic chemistry
, for instance in tris(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium(0)
. In this case, it is a labile ligand that is easily displaced by stronger ligands like triphenylphosphine
, hence it serves a useful entry point into palladium
(0) chemistry.
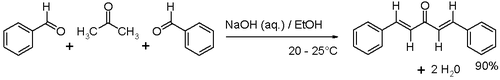
of benzaldehyde
and acetone
with sodium hydroxide in a water/ethanol medium with the exclusive formation of the trans,trans isomer (melting point
110–111 °C).
This reaction is frequently encountered in organic chemistry
education as a laboratory procedure. The conversion proceeds via the intermediacy of benzylideneacetone
.
Prolonged exposure to sunlight converts the compound in a [2+2] cycloaddition
to a mixture of four cyclobutane
isomers.
Organic compound
An organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon. For historical reasons discussed below, a few types of carbon-containing compounds such as carbides, carbonates, simple oxides of carbon, and cyanides, as well as the...
with the formula C17H14O. It is a bright-yellow solid insoluble in water, but soluble in ethanol. Dibenzylideneacetone is used as a sunscreen
Sunscreen
Sunblock is a lotion, spray, gel or other topical product that absorbs or reflects some of the sun's ultraviolet radiation on the skin exposed to sunlight and thus helps protect against sunburn...
component and as a ligand
Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding between metal and ligand generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs. The nature of metal-ligand bonding can range from...
in organometallic chemistry
Organometallic chemistry
Organometallic chemistry is the study of chemical compounds containing bonds between carbon and a metal. Since many compounds without such bonds are chemically similar, an alternative may be compounds containing metal-element bonds of a largely covalent character...
, for instance in tris(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium(0)
Tris(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium(0)
Trisdipalladium or Pd23 is an organometallic complex based on palladium and dibenzylideneacetone used in organic chemistry. It was discovered in 1970.-Preparation and structure:...
. In this case, it is a labile ligand that is easily displaced by stronger ligands like triphenylphosphine
Triphenylphosphine
Triphenylphosphine is a common organophosphorus compound with the formula P3 - often abbreviated to PPh3 or Ph3P. It is widely used in the synthesis of organic and organometallic compounds. PPh3 exists as relatively air stable, colorless crystals at room temperature...
, hence it serves a useful entry point into palladium
Palladium
Palladium is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Pd and an atomic number of 46. It is a rare and lustrous silvery-white metal discovered in 1803 by William Hyde Wollaston. He named it after the asteroid Pallas, which was itself named after the epithet of the Greek goddess Athena, acquired...
(0) chemistry.
Preparation
The compound can be prepared in the laboratory by an aldol condensationAldol condensation
An aldol condensation is an organic reaction in which an enol or an enolate ion reacts with a carbonyl compound to form a β-hydroxyaldehyde or β-hydroxyketone, followed by a dehydration to give a conjugated enone....
of benzaldehyde
Benzaldehyde
Benzaldehyde is an organic compound consisting of a benzene ring with a formyl substituent. It is the simplest aromatic aldehyde and one of the most industrially useful. This colorless liquid has a characteristic pleasant almond-like odor...
and acetone
Acetone
Acetone is the organic compound with the formula 2CO, a colorless, mobile, flammable liquid, the simplest example of the ketones.Acetone is miscible with water and serves as an important solvent in its own right, typically as the solvent of choice for cleaning purposes in the laboratory...
with sodium hydroxide in a water/ethanol medium with the exclusive formation of the trans,trans isomer (melting point
Melting point
The melting point of a solid is the temperature at which it changes state from solid to liquid. At the melting point the solid and liquid phase exist in equilibrium. The melting point of a substance depends on pressure and is usually specified at standard atmospheric pressure...
110–111 °C).
This reaction is frequently encountered in organic chemistry
Organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation of carbon-based compounds, hydrocarbons, and their derivatives...
education as a laboratory procedure. The conversion proceeds via the intermediacy of benzylideneacetone
Benzylideneacetone
Benzylideneacetone is the organic compound described by the formula C6H5CH=CHCCH3. Although both cis- and trans-isomers are possible for the α,β-unsaturated ketone, only the trans isomer is observed...
.
Prolonged exposure to sunlight converts the compound in a [2+2] cycloaddition
Cycloaddition
A cycloaddition is a pericyclic chemical reaction, in which "two or more unsaturated molecules combine with the formation of a cyclic adduct in which there is a net reduction of the bond multiplicity." The resulting reaction is a cyclization reaction.Cycloadditions are usually described by the...
to a mixture of four cyclobutane
Cyclobutane
Cyclobutane is an organic compound with the formula 4. Cyclobutane is a colourless gas and commercially available as a liquefied gas. Derivatives of cyclobutane are called cyclobutanes...
isomers.