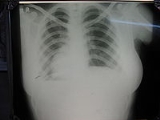
Dextrocardia
Encyclopedia
Dextrocardia is a congenital defect in which the heart
is situated on the right side of the body. There are two main types of dextrocardia: dextrocardia of embryonic arrest (also known as isolated dextrocardia) and dextrocardia situs inversus. Dextrocardia situs inversus is further divided.
.
to be mirrored, the correct term is dextrocardia situs inversus totalis
.
Dextrocardia is believed to occur in approximately 1 in 12,000 people,
Kartagener’s syndrome
occurs in approximately 1 in 25 of totalis. This disorder affects the sinus
and bronchial
cilia
causing constant sinus and bronchial symptoms that medication cannot rectify. With Kartagener’s both are usually present all year rather than being seasonal.
Although statistically people with dextrocardia situs inversus do not have any medical problems from the disorder, some are prone to a number of bowel, esophagus, bronchial and cardiac problems. Some of these conditions can be life threatening if left unchecked.
of the two forms of congenital dextrocardia can be made by ECG or imaging.
leads must be placed in reversed positions on a person with dextrocardia. In addition, when defibrillating
someone with dextrocardia, the pads should be placed in reverse positions. That is, instead of upper right and lower left, pads should be placed upper left and lower right.
Heart
The heart is a myogenic muscular organ found in all animals with a circulatory system , that is responsible for pumping blood throughout the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions...
is situated on the right side of the body. There are two main types of dextrocardia: dextrocardia of embryonic arrest (also known as isolated dextrocardia) and dextrocardia situs inversus. Dextrocardia situs inversus is further divided.
Dextrocardia of embryonic arrest
In this form of dextrocardia, the heart is simply placed farther right in the thorax than is normal. It is commonly associated with severe defects of the heart and related abnormalities including pulmonary hypoplasiaPulmonary hypoplasia
Pulmonary hypoplasia is incomplete development of the lungs, resulting in an abnormally low number or size of bronchopulmonary segments or alveoli. A congenital malformation, it most often occurs secondary to other fetal abnormalities that interfere with normal development of the lungs...
.
Dextrocardia situs inversus
Dextrocardia situs inversus refers to the heart being a mirror image situated on the right side. For all visceral organsOrgan (anatomy)
In biology, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in structural unit to serve a common function. Usually there is a main tissue and sporadic tissues . The main tissue is the one that is unique for the specific organ. For example, main tissue in the heart is the myocardium, while sporadic are...
to be mirrored, the correct term is dextrocardia situs inversus totalis
Situs inversus
Situs inversus is a congenital condition in which the major visceral organs are reversed or mirrored from their normal positions. The normal arrangement is known as situs solitus...
.
Dextrocardia is believed to occur in approximately 1 in 12,000 people,
Kartagener’s syndrome
Primary ciliary dyskinesia
Primary ciliary dyskinesia , also known as immotile ciliary syndrome or Kartagener Syndrome ', is a rare, ciliopathic, autosomal recessive genetic disorder that causes a defect in the action of the cilia lining the respiratory tract and fallopian tube, and also of the flagella of sperm in...
occurs in approximately 1 in 25 of totalis. This disorder affects the sinus
Sinus (anatomy)
Sinus is Latin for "bay", "pocket", "curve", or "bosom". In anatomy, the term is used in various contexts.A sinus is a sack or cavity in any organ or tissue, or an abnormal cavity or passage caused by the destruction of tissue...
and bronchial
Bronchiole
The bronchioles or bronchioli are the first airway branches that no longer contain cartilage or glands in their submucosa. They are branches of the bronchi.The bronchioles terminate by entering the circular sacs called alveoli.- Structure :...
cilia
Cilium
A cilium is an organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Cilia are slender protuberances that project from the much larger cell body....
causing constant sinus and bronchial symptoms that medication cannot rectify. With Kartagener’s both are usually present all year rather than being seasonal.
Although statistically people with dextrocardia situs inversus do not have any medical problems from the disorder, some are prone to a number of bowel, esophagus, bronchial and cardiac problems. Some of these conditions can be life threatening if left unchecked.
Diagnosis
Medical diagnosisMedical diagnosis
Medical diagnosis refers both to the process of attempting to determine or identify a possible disease or disorder , and to the opinion reached by this process...
of the two forms of congenital dextrocardia can be made by ECG or imaging.
Technical dextrocardia
Technical dextrocardia refers to an ECG reading that has no basis in the patient's anatomy. This apparent presentation of dextrocardia is caused usually by the technician inadvertently swapping the limb leads on a 12 lead ECG. Usually this would show as an extreme axis deviation.Management
ECGElectrocardiogram
Electrocardiography is a transthoracic interpretation of the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time, as detected by electrodes attached to the outer surface of the skin and recorded by a device external to the body...
leads must be placed in reversed positions on a person with dextrocardia. In addition, when defibrillating
Defibrillation
Defibrillation is a common treatment for life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias, ventricular fibrillation and pulseless ventricular tachycardia. Defibrillation consists of delivering a therapeutic dose of electrical energy to the affected heart with a device called a defibrillator...
someone with dextrocardia, the pads should be placed in reverse positions. That is, instead of upper right and lower left, pads should be placed upper left and lower right.

