
Deutsche Wertungszahl
Encyclopedia
The Deutsche Wertungszahl (abbreviation: DWZ, ger. German Evaluation Number) is an evaluation number in chess
to compare the playing performance of individual players. It is a chess rating system used in Germany. A higher rating number corresponds to a stronger player. A beginner is rated around 500 and a world champion
about 2800.
in 1990. On January 1, 1993 the DWZ was introduced nationwide and replaced the Ingo-System of the DSB in the Federal Republic of Germany and the NWZ-System of the German Chess Association in East Germany. The DWZ is similar to the Elo rating system of the FIDE, but was enhanced further over the years. In development, the experiences of the Ingo-System and the NWZ-System were respected. The scale goes from about 500 (beginners) to over 2800 (world champions), but is in theory open at the top and bottom. The evaluation of the tournaments is done by DWZ-abstractors who transfer the tournament results to the headquarters of the DOSB (Deutscher Olympischer Sportbund, ger. German Olympic Sports Confederation), where the ZDB (Zentrale Wertungsdatenbank, ger. Central Evaluation Database) is administrated. There, a chronological subsequent billing is accomplished according to the finish date of the tournament.
In contrast to the Ingo System, a higher DWZ represents a better playing ability. The DWZ consists of a evaluation number as a measurement of the playing ability and an index number which is separated from that by a "-" sign. For players who do not have a DWZ, but have a FIDE-ELO, the FIDE-ELO ist used, marked with the index 6 and resumed as DWZ. For players who neither have a DWZ nor a FIDE-ELO, but have a national evaluation number, this number is used and translated if necessary. In this case the index is set to zero.
is necessary to determine the expectation of winnings. Only chess results against competitors with a DWZ are taken into account.
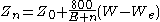
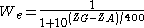
The expected points are calculated for each game of chess and then added. The exact values of the expected points can be looked at in the table of the DSB. The formula provides good approximations.

with
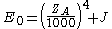
The component J depends on the age of the player.
teenagers up to 20 years: J = 5,
junior adults (21 – 25 years): J = 10,
over-25-year-olds: J = 15
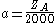
For the acceleration factor a it is claimed: It can't be higher than 1 or lower than 0.5. Furthermore it is only calculated if the player is less than 20 years old and has achieved more points than expected. The acceleration factor a is 1 if that is not the case. The acceleration factor helps young players to improve their DWZs more quickly.
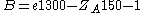
The braking value B is only calculated for players with a DWZ of under 1300 points and only if the achieved points are less or equal to the expected ones, else the braking value is zero. The braking value makes the DWZ of poor players decrease not so rapidly.
Besides, E depends on the number of the previously evaluated tournaments. The index i is 1 in the first DWZ and is increased by 1 after every tournament evaluation.
Also consider that:
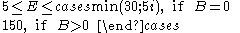
This formula is only considered when a DWZ already exists, viz. i is not only zero. So E is normally increased to 5, if the coefficient is less than five, or decreased to thirty if E is higher than 30. If a braking factor is present (B>0), E can also go beyond 30.
The next step is to round E to the nearest integer
.
Chess
Chess is a two-player board game played on a chessboard, a square-checkered board with 64 squares arranged in an eight-by-eight grid. It is one of the world's most popular games, played by millions of people worldwide at home, in clubs, online, by correspondence, and in tournaments.Each player...
to compare the playing performance of individual players. It is a chess rating system used in Germany. A higher rating number corresponds to a stronger player. A beginner is rated around 500 and a world champion
World Chess Championship
The World Chess Championship is played to determine the World Champion in the board game chess. Men and women of any age are eligible to contest this title....
about 2800.
Preface
The DWZ was introduced by the DSB (Deutscher Schachbund, ger. German Chess Association) after the German reunificationGerman reunification
German reunification was the process in 1990 in which the German Democratic Republic joined the Federal Republic of Germany , and when Berlin reunited into a single city, as provided by its then Grundgesetz constitution Article 23. The start of this process is commonly referred by Germans as die...
in 1990. On January 1, 1993 the DWZ was introduced nationwide and replaced the Ingo-System of the DSB in the Federal Republic of Germany and the NWZ-System of the German Chess Association in East Germany. The DWZ is similar to the Elo rating system of the FIDE, but was enhanced further over the years. In development, the experiences of the Ingo-System and the NWZ-System were respected. The scale goes from about 500 (beginners) to over 2800 (world champions), but is in theory open at the top and bottom. The evaluation of the tournaments is done by DWZ-abstractors who transfer the tournament results to the headquarters of the DOSB (Deutscher Olympischer Sportbund, ger. German Olympic Sports Confederation), where the ZDB (Zentrale Wertungsdatenbank, ger. Central Evaluation Database) is administrated. There, a chronological subsequent billing is accomplished according to the finish date of the tournament.
In contrast to the Ingo System, a higher DWZ represents a better playing ability. The DWZ consists of a evaluation number as a measurement of the playing ability and an index number which is separated from that by a "-" sign. For players who do not have a DWZ, but have a FIDE-ELO, the FIDE-ELO ist used, marked with the index 6 and resumed as DWZ. For players who neither have a DWZ nor a FIDE-ELO, but have a national evaluation number, this number is used and translated if necessary. In this case the index is set to zero.
Calculating the DWZ
The basic curve for calculation is the Gauss error distribution curve. For calculation, an integralIntegral
Integration is an important concept in mathematics and, together with its inverse, differentiation, is one of the two main operations in calculus...
is necessary to determine the expectation of winnings. Only chess results against competitors with a DWZ are taken into account.
Basic formula
The DWZ is calculated in the following way: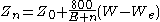
-
- Z0: present DWZ
- Zn: new DWZ
- W: achieved points
- We: expected points
- n: number of finished games
- E: development coefficient
Expected and archived points
The achieved points W are the sum of the game results in which a win counts 1 point, a draw counts ½ point, and a defeat 0 points. The expected points We are calculated with the following approximation: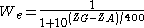
-
- ZA: present DWZ
- ZG: present DWZ of the competitor
The expected points are calculated for each game of chess and then added. The exact values of the expected points can be looked at in the table of the DSB. The formula provides good approximations.
The development coefficient
Another constituent is the development coefficient E. It consists of the fundamental value E0, the acceleration factor a and the braking value B:
with
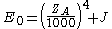
The component J depends on the age of the player.
teenagers up to 20 years: J = 5,
junior adults (21 – 25 years): J = 10,
over-25-year-olds: J = 15
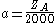
For the acceleration factor a it is claimed: It can't be higher than 1 or lower than 0.5. Furthermore it is only calculated if the player is less than 20 years old and has achieved more points than expected. The acceleration factor a is 1 if that is not the case. The acceleration factor helps young players to improve their DWZs more quickly.
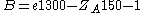
The braking value B is only calculated for players with a DWZ of under 1300 points and only if the achieved points are less or equal to the expected ones, else the braking value is zero. The braking value makes the DWZ of poor players decrease not so rapidly.
Besides, E depends on the number of the previously evaluated tournaments. The index i is 1 in the first DWZ and is increased by 1 after every tournament evaluation.
Also consider that:
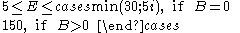
This formula is only considered when a DWZ already exists, viz. i is not only zero. So E is normally increased to 5, if the coefficient is less than five, or decreased to thirty if E is higher than 30. If a braking factor is present (B>0), E can also go beyond 30.
The next step is to round E to the nearest integer
Integer
The integers are formed by the natural numbers together with the negatives of the non-zero natural numbers .They are known as Positive and Negative Integers respectively...
.

