Destrin
Encyclopedia
Destrin or DSTN is a protein
which in humans is encoded by the DSTN gene
. Destrin is a component protein in microfilament
s.
The product of this gene belongs to the actin
-binding proteins ADF (Actin-Depolymerizing Factor)/cofilin
family. This family of proteins is responsible for enhancing the turnover rate of actin in vivo. This gene encodes the actin depolymerizing protein that severs actin filaments (F-actin) and binds to actin monomers (G-actin). Two transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been identified for this gene.
. The secondary and tertiary structures of destrin are similar to the gelsolin
family which is another actin-regulating protein family.
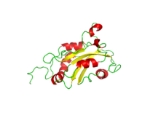
There are three ordered layers to destrin which is a globular protein. There is a central β sheet that is composed of one parallel strand and three antiparallel strands. This β sheet is between a long α helix along with a shorter one and two shorter helices on the opposite side. The four helices are parallel to the β strands.
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
which in humans is encoded by the DSTN gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
. Destrin is a component protein in microfilament
Microfilament
Microfilaments are the thinnest filaments of the cytoskeleton, a structure found in the cytoplasm of all eukaryotic cells. These linear polymers of actin subunits are flexible and relatively strong, resisting buckling by multi-piconewton compressive forces and filament fracture by nanonewton...
s.
The product of this gene belongs to the actin
Actin
Actin is a globular, roughly 42-kDa moonlighting protein found in all eukaryotic cells where it may be present at concentrations of over 100 μM. It is also one of the most highly-conserved proteins, differing by no more than 20% in species as diverse as algae and humans...
-binding proteins ADF (Actin-Depolymerizing Factor)/cofilin
Cofilin
ADF/cofilin is a family of actin-binding proteins which disassembles actin filaments.Three highly conserved and highly identical genes belonging to this family have been described in human and mice:...
family. This family of proteins is responsible for enhancing the turnover rate of actin in vivo. This gene encodes the actin depolymerizing protein that severs actin filaments (F-actin) and binds to actin monomers (G-actin). Two transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been identified for this gene.
Structure
The tertiary structure of destrin was determined by the use of triple-resonance multidimensional nuclear magnetic resonance, NMRProtein nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins is a field of structural biology in which NMR spectroscopy is used to obtain information about the structure and dynamics of proteins. The field was pioneered by Richard R. Ernst and Kurt Wüthrich, among others...
. The secondary and tertiary structures of destrin are similar to the gelsolin
Gelsolin
Gelsolin is an actin-binding protein that is a key regulator of actin filament assembly and disassembly. Gelsolin is one of the most potent members of the actin-severing gelsolin/villin superfamily, as it severs with nearly 100% efficiency...
family which is another actin-regulating protein family.
There are three ordered layers to destrin which is a globular protein. There is a central β sheet that is composed of one parallel strand and three antiparallel strands. This β sheet is between a long α helix along with a shorter one and two shorter helices on the opposite side. The four helices are parallel to the β strands.
Function
In a variety of eukaryotes, destrin regulates actin in the cytoskeleton. Destrin binds actin and is thought to connect it as gelsolin segment-1 does. Furthermore, the binding of actin by destrin and cofilin is regulated negatively by phosphorylation. Destrin can also sever actin filaments.External links
- Ramachandran PlotRamachandran plot-Introduction and early history:A Ramachandran plot , originally developed in 1963 by G. N. Ramachandran C. Ramakrishnan and V...
for destrin:

