
Desorption atmospheric pressure photoionization
Encyclopedia
Mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique that measures the mass-to-charge ratio of charged particles.It is used for determining masses of particles, for determining the elemental composition of a sample or molecule, and for elucidating the chemical structures of molecules, such as peptides and...
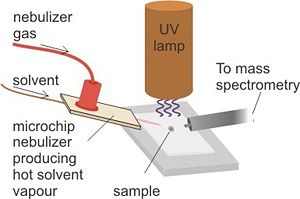
. DAPPI enables direct analysis of solid samples without pretreatment and analysis of samples deposited on surfaces by means of a jet of hot solvent vapour and vacuum ultraviolet light. The hot jet thermally desorbs the sample from a surface and the vaporized sample is ionized by the vacuum ultraviolet light and consequently sampled into a mass spectrometer.
Desorption and ionization mechanisms
The main desorption mechanism in DAPPI is thermal desorption due to rapid heating of the surface. Therefore DAPPI only works well for surfaces of low thermal conductivity. The ionization mechanism depends on the analyteAnalyte
An analyte, or component , is a substance or chemical constituent that is of interest in an analytical procedure. Grammatically, it is important to note that experiments always seek to measure properties of analytes—and that analytes themselves can never be measured. For instance, one cannot...
and solvent
Solvent
A solvent is a liquid, solid, or gas that dissolves another solid, liquid, or gaseous solute, resulting in a solution that is soluble in a certain volume of solvent at a specified temperature...
used and for example the following analyte (M) ions may be formed: [M + H]+, [M - H]-, M+•, M-•.
Applications
DAPPI has the potential to analyze both polarChemical polarity
In chemistry, polarity refers to a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole or multipole moment. Polar molecules interact through dipole–dipole intermolecular forces and hydrogen bonds. Molecular polarity is dependent on the difference in...
(e.g. verapamil
Verapamil
Verapamil is an L-type calcium channel blocker of the phenylalkylamine class. It has been used in the treatment of hypertension, angina pectoris, cardiac arrhythmia, and most recently, cluster headaches. It is also an effective preventive medication for migraine...
) and nonpolar (e.g. anthracene
Anthracene
Anthracene is a solid polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon consisting of three fused benzene rings. It is a component of coal-tar. Anthracene is used in the production of the red dye alizarin and other dyes...
) compounds. Performance of DAPPI has also been demonstrated on direct analysis of illicit drugs.

