Depolarization ratio
Encyclopedia
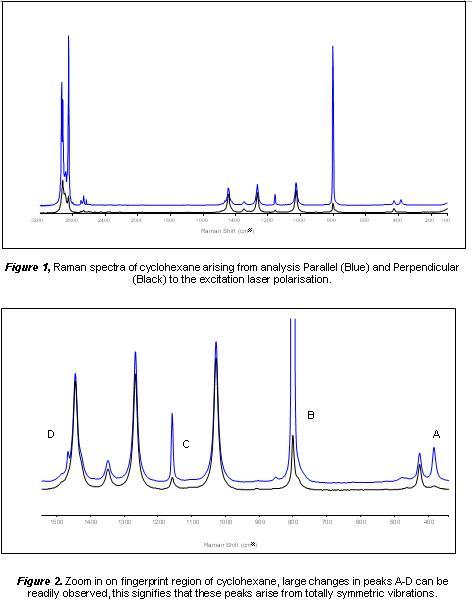
In Raman spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy is a spectroscopic technique used to study vibrational, rotational, and other low-frequency modes in a system.It relies on inelastic scattering, or Raman scattering, of monochromatic light, usually from a laser in the visible, near infrared, or near ultraviolet range...
, the depolarization ratio is the intensity
Intensity (physics)
In physics, intensity is a measure of the energy flux, averaged over the period of the wave. The word "intensity" here is not synonymous with "strength", "amplitude", or "level", as it sometimes is in colloquial speech...
ratio between the perpendicular component and the parallel component of the Raman scattered light.
Early work in this field was carried out by George Placzek
George Placzek
Georg Placzek was a Czech physicist.Born in Brno, Moravia, Placzek studied physics in Prague and Vienna. He worked with Hans Bethe, Edward Teller, Rudolf Peierls, Werner Heisenberg, Victor Weisskopf, Enrico Fermi, Niels Bohr, Lev Landau, Edoardo Amaldi, Emilio Segrè, Leon van Hove and many other...
, who developed the theoretical treatment of bond polarizability
The Raman scattered light is emitted by the stimulation of the electric field
Electric field
In physics, an electric field surrounds electrically charged particles and time-varying magnetic fields. The electric field depicts the force exerted on other electrically charged objects by the electrically charged particle the field is surrounding...
of the incident light. Therefore, the direction of the vibration of the electric field, or polarization direction, of the scattered light might be expected to be the same as that of the incident light. In reality, however, some fraction of the Raman scattered light has a polarization direction that is perpendicular to that of the incident light. This component is called the perpendicular component. Naturally, the component of the Raman scattered light whose polarization direction is parallel to that of the incident light is called the parallel component, and the Raman scattered light consists of the parallel component and the perpendicular component. The ratio between these two components is expressed as the depolarization ratio.
The value of the depolarization ratio of a Raman band depends on the symmetry
Symmetry
Symmetry generally conveys two primary meanings. The first is an imprecise sense of harmonious or aesthetically pleasing proportionality and balance; such that it reflects beauty or perfection...
of the molecule and the normal vibrational mode, in other words, the point group
Point group
In geometry, a point group is a group of geometric symmetries that keep at least one point fixed. Point groups can exist in a Euclidean space with any dimension, and every point group in dimension d is a subgroup of the orthogonal group O...
of the molecule and its irreducible representation to which the normal mode
Normal mode
A normal mode of an oscillating system is a pattern of motion in which all parts of the system move sinusoidally with the same frequency and with a fixed phase relation. The frequencies of the normal modes of a system are known as its natural frequencies or resonant frequencies...
belongs. Under Placzek’s polarizability approximation, it is known that the depolarization ratio of a totally symmetric vibrational mode is less than 0.75, and that of the other modes equals 0.75. A Raman band whose depolarization ratio is less than 0.75 is called a polarized band, and a band with a 0.75 depolarization ratio is called a depolarized band.
The ratio of the peak intensity of the parallel and perpendicular component is known as the depolarisation ratio. And can be obtained as shown in equation 1.
Equation 1. Raman depolarisation ratio. Where 'Iperpendicular' signifies the peak intensity with excitation and Raman analysis polarisers orientated perpendicular to one another.
For example if you have a species with a peak which had an intensity 10 units, when the polarisers were parallel, and an intensity of 1 unit when the polarisers were perpendicular, then the depolarisation ratio would be 1/10 = 0.1, this peak would be highly polarised band.
Spectral Images shown here are taken, with permission from PerkinElmer Raman Division.

