
Densitometry
Encyclopedia
Measurement
Measurement is the process or the result of determining the ratio of a physical quantity, such as a length, time, temperature etc., to a unit of measurement, such as the metre, second or degree Celsius...
of optical density in light-sensitive materials, such as photographic paper
Photographic paper
Photographic paper is paper coated with light-sensitive chemicals, used for making photographic prints.Photographic paper is exposed to light in a controlled manner, either by placing a negative in contact with the paper directly to produce a contact print, by using an enlarger in order to create a...
or film
Photographic film
Photographic film is a sheet of plastic coated with an emulsion containing light-sensitive silver halide salts with variable crystal sizes that determine the sensitivity, contrast and resolution of the film...
, due to exposure to light
Light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye, and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light has wavelength in a range from about 380 nanometres to about 740 nm, with a frequency range of about 405 THz to 790 THz...
. Optical density is a result of the darkness of a developed picture and can be expressed absolutely as the number of dark spots (i.e., silver
Silver
Silver is a metallic chemical element with the chemical symbol Ag and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it has the highest electrical conductivity of any element and the highest thermal conductivity of any metal...
grains in developed films) in a given area, but usually it is a relative value, expressed in a scale
Scale (ratio)
The scale ratio of some sort of model which represents an original proportionally is the ratio of a linear dimension of the model to the same dimension of the original. Examples include a 3-dimensional scale model of a building or the scale drawings of the elevations or plans of a building. In such...
.
Since density is usually measured by the decrease in the amount of light which shines through a transparent film, it is also called absorptiometry, the measure of light absorption
Absorption (electromagnetic radiation)
In physics, absorption of electromagnetic radiation is the way by which the energy of a photon is taken up by matter, typically the electrons of an atom. Thus, the electromagnetic energy is transformed to other forms of energy for example, to heat. The absorption of light during wave propagation is...
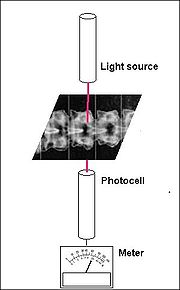
through the medium. The corresponding measuring device is called a densitometer
Densitometer
A densitometer is a device that measures the degree of darkness of a photographic or semitransparent material or of a reflecting surface. The densitometer is basically a light source aimed at a photoelectric cell. It determines the density of a sample placed between the light source and the...
(absorptiometer). The logarithm
Logarithm
The logarithm of a number is the exponent by which another fixed value, the base, has to be raised to produce that number. For example, the logarithm of 1000 to base 10 is 3, because 1000 is 10 to the power 3: More generally, if x = by, then y is the logarithm of x to base b, and is written...
of the reciprocal of the transmittance
Transmittance
In optics and spectroscopy, transmittance is the fraction of incident light at a specified wavelength that passes through a sample. A related term is absorptance, or absorption factor, which is the fraction of radiation absorbed by a sample at a specified wavelength...
is called the absorbance or density.
DMax and DMin refer to the maximum and minimum density that can be recorded on the material. The difference between the two is the density range. The density range is related to the exposure range (dynamic range), which is the range of light intensity that is represented by the recording, via the Hurter–Driffield curve. The dynamic range can be measured in "stops", which is the binary logarithm
Binary logarithm
In mathematics, the binary logarithm is the logarithm to the base 2. It is the inverse function of n ↦ 2n. The binary logarithm of n is the power to which the number 2 must be raised to obtain the value n. This makes the binary logarithm useful for anything involving powers of 2,...
of the ratio of highest and lowest distinguishable exposures.
Uses
According to the principle of operation of the densitometer, one can have:- spot densitometry: the value of light absorption is measured at a single spot
- line densitometry: the values of successive spots along a dimension are expressed as a graph
- bidimensional densitometry: the values of light absorption are expressed as a 2D synthetic image, usually using false-colorFalse-colorA false-color image is an image that depicts a subject in colors that differ from those a full-color photograph would show.-True- and false-color:...
shading
Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry
Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry
Dual-emission X-ray absorptiometry is a means of measuring bone mineral density . Two X-ray beams with differing energy levels are aimed at the patient's bones. When soft tissue absorption is subtracted out, the BMD can be determined from the absorption of each beam by bone...
is used in medicine
Medicine
Medicine is the science and art of healing. It encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness....
to evaluate calcium
Calcium
Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust...
bone
Bone
Bones are rigid organs that constitute part of the endoskeleton of vertebrates. They support, and protect the various organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells and store minerals. Bone tissue is a type of dense connective tissue...
density, which is altered in several diseases such as osteopenia
Osteopenia
Osteopenia is a condition where bone mineral density is lower than normal. It is considered by many doctors to be a precursor to osteoporosis. However, not every person diagnosed with osteopenia will develop osteoporosis...
and osteoporosis
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a disease of bones that leads to an increased risk of fracture. In osteoporosis the bone mineral density is reduced, bone microarchitecture is deteriorating, and the amount and variety of proteins in bone is altered...
. Special devices have been developed and are in current use for clinical diagnosis
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is the identification of the nature and cause of anything. Diagnosis is used in many different disciplines with variations in the use of logics, analytics, and experience to determine the cause and effect relationships...
, called bone densitometers.
External links
- Fundamentals of Densitometry, by Mark Vivino.

