
Deformation (meteorology)
Encyclopedia
Deformation is the rate of change of shape of fluid bodies. Meteorologically, this quantity is very important in the formation of atmospheric fronts, in the explanation of cloud
shapes, and in the diffusion of materials and properties.
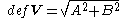 , where
, where 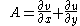 and
and 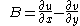 , representing the derivatives of wind component. Because these derivatives vary greatly with the rotation of the coordinate system, so do
, representing the derivatives of wind component. Because these derivatives vary greatly with the rotation of the coordinate system, so do  and
and 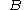 .
.
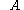 and
and  (above) can be used to find the direction of the dilatation axis, the line along which the material elements stretch (also known as the stretching direction). Several flow patterns are characteristic of large deformation: confluence, diffluence, and shear flow. , also known as stretching, is the elongating of a fluid body along the flow (streamline convergence). , also known as shearing, is the elongating of a fluid body normal to the flow (streamline divergence).
(above) can be used to find the direction of the dilatation axis, the line along which the material elements stretch (also known as the stretching direction). Several flow patterns are characteristic of large deformation: confluence, diffluence, and shear flow. , also known as stretching, is the elongating of a fluid body along the flow (streamline convergence). , also known as shearing, is the elongating of a fluid body normal to the flow (streamline divergence).
Cloud
A cloud is a visible mass of liquid droplets or frozen crystals made of water and/or various chemicals suspended in the atmosphere above the surface of a planetary body. They are also known as aerosols. Clouds in Earth's atmosphere are studied in the cloud physics branch of meteorology...
shapes, and in the diffusion of materials and properties.
Equations
The deformation of horizontal wind is defined as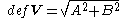 , where
, where 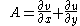 and
and 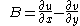 , representing the derivatives of wind component. Because these derivatives vary greatly with the rotation of the coordinate system, so do
, representing the derivatives of wind component. Because these derivatives vary greatly with the rotation of the coordinate system, so do  and
and 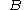 .
.Stretching direction
The deformation elements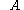 and
and  (above) can be used to find the direction of the dilatation axis, the line along which the material elements stretch (also known as the stretching direction). Several flow patterns are characteristic of large deformation: confluence, diffluence, and shear flow. , also known as stretching, is the elongating of a fluid body along the flow (streamline convergence). , also known as shearing, is the elongating of a fluid body normal to the flow (streamline divergence).
(above) can be used to find the direction of the dilatation axis, the line along which the material elements stretch (also known as the stretching direction). Several flow patterns are characteristic of large deformation: confluence, diffluence, and shear flow. , also known as stretching, is the elongating of a fluid body along the flow (streamline convergence). , also known as shearing, is the elongating of a fluid body normal to the flow (streamline divergence).

