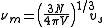Debye frequency
Encyclopedia
The Debye frequency of a crystal
is a theoretical maximum frequency
of vibration
for the atom
s that make up the crystal http://scienceworld.wolfram.com/physics/DebyeFrequency.html. It was proposed by Peter Debye
as part of the Debye model
. It is generally not the same as the actual maximum oscillation frequency for the crystal, due to approximations in the model, however it is still a useful quantity http://farside.ph.utexas.edu/teaching/sm1/lectures/node71.html. It plays a role in the computation of the specific heat capacity of solids and in theoretical estimates of rates of diffusion
. It is related to the speed of sound
(vs) in the crystal and the number density of the crystal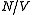 as follows http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/HBASE/thermo/debye.html:
as follows http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/HBASE/thermo/debye.html:
Crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituent atoms, molecules, or ions are arranged in an orderly repeating pattern extending in all three spatial dimensions. The scientific study of crystals and crystal formation is known as crystallography...
is a theoretical maximum frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
of vibration
Oscillation
Oscillation is the repetitive variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value or between two or more different states. Familiar examples include a swinging pendulum and AC power. The term vibration is sometimes used more narrowly to mean a mechanical oscillation but sometimes...
for the atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
s that make up the crystal http://scienceworld.wolfram.com/physics/DebyeFrequency.html. It was proposed by Peter Debye
Peter Debye
Peter Joseph William Debye FRS was a Dutch physicist and physical chemist, and Nobel laureate in Chemistry.-Early life:...
as part of the Debye model
Debye model
In thermodynamics and solid state physics, the Debye model is a method developed by Peter Debye in 1912 for estimating the phonon contribution to the specific heat in a solid. It treats the vibrations of the atomic lattice as phonons in a box, in contrast to the Einstein model, which treats the...
. It is generally not the same as the actual maximum oscillation frequency for the crystal, due to approximations in the model, however it is still a useful quantity http://farside.ph.utexas.edu/teaching/sm1/lectures/node71.html. It plays a role in the computation of the specific heat capacity of solids and in theoretical estimates of rates of diffusion
Diffusion
Molecular diffusion, often called simply diffusion, is the thermal motion of all particles at temperatures above absolute zero. The rate of this movement is a function of temperature, viscosity of the fluid and the size of the particles...
. It is related to the speed of sound
Speed of sound
The speed of sound is the distance travelled during a unit of time by a sound wave propagating through an elastic medium. In dry air at , the speed of sound is . This is , or about one kilometer in three seconds or approximately one mile in five seconds....
(vs) in the crystal and the number density of the crystal
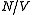 as follows http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/HBASE/thermo/debye.html:
as follows http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/HBASE/thermo/debye.html: