
Debian build toolchain
Encyclopedia
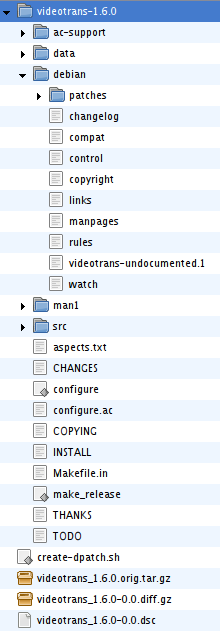
Debian
Debian is a computer operating system composed of software packages released as free and open source software primarily under the GNU General Public License along with other free software licenses. Debian GNU/Linux, which includes the GNU OS tools and Linux kernel, is a popular and influential...
source packages (
.dsc) and Debian binary packagesDeb (file format)
deb is the extension of the Debian software package format and the most often used name for such binary packages. Like the "Deb" part of the term Debian, it originates from the name of Debra, erstwhile girlfriend and now ex-wife of Debian's founder Ian Murdock.Debian packages are also used in...
(
.deb files) from upstream source tarballTarball
Tarball can refer to:* Tar , a computer file format that can combine multiple files into a single "tarball" file* Tarball , a blob of semi-solid oil found on or near the ocean...
s.
These tools are used in the Debian project and also in Debian-based distributions such as Ubuntu
Ubuntu (operating system)
Ubuntu is a computer operating system based on the Debian Linux distribution and distributed as free and open source software. It is named after the Southern African philosophy of Ubuntu...
.
Overview
Source code for free softwareFree software
Free software, software libre or libre software is software that can be used, studied, and modified without restriction, and which can be copied and redistributed in modified or unmodified form either without restriction, or with restrictions that only ensure that further recipients can also do...
is typically distributed in compressed tar
Tar (file format)
In computing, tar is both a file format and the name of a program used to handle such files...
archives called tarballs. Debian is a binary-oriented distribution, meaning that its
deb packages include precompiled binaries and data files arranged into a file system hierarchy that the software expects. The Debian build toolchain thus needs instructions on how to use the upstream build system to build correct deb packages.These instructions are stored in the
debian subdirectory, which is added to the source tree for the software being packaged by the package maintainerSoftware maintainer
In free and open source software, a software maintainer is usually one or more people who build source code into a binary package for distribution, commit patches, or organize code in a source repository....
. While it is possible to build the package directly from the modified source tree, it is standard practice to create source packages, which contain the changes the maintainer made to the upstream sources in redistributable form.
Source packages
A typical Debian source package consists of three files:- The original tarball — a mere copy of the upstream source tarball if it is in
tar.gzformat and no changes are necessary, or a repacked tarball. The latter can happen if it contains a snapshot from a version control system that was never released in tarball form, or if the maintainer needs to remove files not compatible with the Debian Free Software GuidelinesDebian Free Software GuidelinesThe Debian Free Software Guidelines is a set of guidelines that the Debian Project uses to determine whether a software license is a free software license, which in turn is used to determine whether a piece of software can be included in Debian...
. - The
diff.gzfile, which contains changes to the upstream source made by the package maintainer. This includes the entiredebiandirectory and any modified files outside it (although such changes are usually aggregated into patch files that are automatically applied before building). It is a file in the unified diffDiffIn computing, diff is a file comparison utility that outputs the differences between two files. It is typically used to show the changes between one version of a file and a former version of the same file. Diff displays the changes made per line for text files. Modern implementations also...
format, compressed with gzipGzipGzip is any of several software applications used for file compression and decompression. The term usually refers to the GNU Project's implementation, "gzip" standing for GNU zip. It is based on the DEFLATE algorithm, which is a combination of Lempel-Ziv and Huffman coding...
. - The
dscfile, which is a text file with metadataMetadataThe term metadata is an ambiguous term which is used for two fundamentally different concepts . Although the expression "data about data" is often used, it does not apply to both in the same way. Structural metadata, the design and specification of data structures, cannot be about data, because at...
, such as the names of all files constituting the source package and their MD5MD5The MD5 Message-Digest Algorithm is a widely used cryptographic hash function that produces a 128-bit hash value. Specified in RFC 1321, MD5 has been employed in a wide variety of security applications, and is also commonly used to check data integrity...
checksums. It also contains the signature of the creator of the source package.
For example, a source package named
foo with upstream version 1.2.3 and Debian revision 4 can consist of the following files:
-
foo_1.2.3.orig.tar.gz -
foo_1.2.3-4.diff.gz -
foo_1.2.3-4.dsc
A source package is created using the
dpkg-buildpackage tool or its wrapper debuild. When invoked to create a source package, dpkg-buildpackage calls the maintainer's rules to clean the source tree of any intermediate files, does various sanity checks, executes diff to produce the difference between the original tarball and the unpacked source tree, and finally, signs the dsc file with the packager's key using the debsign utility.The reverse process — producing the unpacked source tree from a source package — is accomplished using the
dpkg-source utility, which extracts the original tarball to a subdirectory and then applies the changes from the diff.gz file. This is the first step that a build system does when building binary packages from a source package.The debian directory
The debian directory contains files used by dpkg-buildpackage to create both binary and source packages. Unlike RPMRPM Package Manager
RPM Package Manager is a package management system. The name RPM variously refers to the .rpm file format, files in this format, software packaged in such files, and the package manager itself...
, which uses a single
spec file for instructions, the Debian tools use an entire subdirectory with multiple files. Three files are required at minimum to correctly build a package — changelog, control and rules. A fourth file, copyright, is mandated by the Debian policy, but is a legal requirement rather than a technical one.By design, since they must be representable in a diff, all files in the
debian directory are text files, most of which are human-readable and edited with a simple text editor.debian/changelog
This file contains information about all versions of the package since it was created. The build tools only process the top entry, which is used to determine the package version, urgency (which is only of relevance to Debian itself), and bugs in the distribution that this release fixes.For example, for a package named
foo, an example debian/changelog entry can read like this:foo (1.2.3-1) unstable; urgency=low
* New upstream release.
* Dropped 02_manpage_hyphens.dpatch, fixed upstream.
* Added 04_edit_button_crash.dpatch: fix a crash after pressing the edit button. (Closes: #654321)
* debian/control: foo should conflict with libbar. (Closes: #987654)
-- John Doe
Debian provides two main utilities for manipulating the
debian/changelog file:
-
dchis used to add new entries to the changelog or modify existing ones. -
dpkg-parsechangelogparses the most recent entry and extracts data from it in aKey: valueformat similar todebian/control. It is primarily used in scripts.
debian/control
This file contains information about the source package and all binary packages it builds (there can be more than one; for example, the source package libbar can serve as the source for binary packages libbar0, which contains just the shared library, and libbar-dev, which contains a static version of the library and header files).It lists (among others) such things as the package name, maintainer, target architectures (for binary packages), build dependencies (packages that must be installed for the package to successfully build) and dependencies (packages that must be installed for the package to function properly when installed).
debian/rules
This file is a script that is invoked by dpkg-buildpackage with a single argument that specifies the action to take (clean, build, install, binary). Although it can technically be any kind of script, it is typically implemented as a makefile.Apart from invoking the upstream build system, most instructions in
debian/rules are highly repetitive and ubiquitous, and thus, virtually all debian/rules files wrap this functionality in debhelperDebhelper
debhelper is a suite of programs originally written by Joey Hess that help a Debian packager write rules files. A rules file is a makefile that contains instructions for building and creating a Debian package.- Overview :...
scripts. For example, automatically determining the dependencies based on shared libraries used is a very common action, and thus, instead of including the code necessary to do it, the
debian/rules file simply calls dh_shlibdeps. Other examples of debhelper scripts include dh_installdocs, which installs stock documentation files such as debian/copyright into their appropriate locations, or dh_fixperms, which ensures that files in the package have correct access rights (for example, executables in /usr/bin have the "executable" bit set, but are only writable by the superuser).Since sequences of
debhelper scripts are themselves repetitive, some packages simplify debian/rules files directly by using CDBSCDBS
CDBS is a system that greatly aids in the creation of Debian packages, which are software packages that make the installation of software much easier on Debian GNU/Linux and its derivatives. CDBS is an acronym for Common Debian Build System...
instead of using
debhelper directly.Patch systems
Sometimes, a maintainer needs to modify the original source. While this can be done simply by editing the files in place and including the changes in thediff.gz, this can make maintenance difficult when new upstream versions are released, because all the changes have to be examined and merged when necessary.Therefore, the Debian build toolchain includes several patch systems that allow applying and reverting groups of logically separated patches, each of which deals with one change and can be sent upstream as is. The canonical location for these files is
debian/patches.The two most popular patch systems are
dpatch and quilt. The former generates and executes shell scripts that are non-standard unified diff files with a header, which nevertheless are compatible with the standard diff utility. The debian/rules file is modified to call dpatch apply-all before building the binary package and dpatch deapply-all before building the source package (and cleaning up any build byproducts).quilt and certain other patch systems eliminate the need for special headers and use standard diff files.Tracking changes in source packages: debdiff and interdiff
Sometimes a user may want to look at differences between two source packages — for example, to generate a proposed patch against the version currently in the repository for inclusion in the distribution's bug tracking systemBug tracking system
A bug tracking system is a software application that is designed to help quality assurance and programmers keep track of reported software bugs in their work. It may be regarded as a type of issue tracking system....
. If both packages use the same upstream version, this can done using the
debdiff tool, which produces differences between two source trees with packaging changes included.If the upstream tarballs for the two versions are different, such a naive comparison cannot be used. Instead, the
interdiff utility can be used to produce a diff between two diff files (in this case, between two diff.gz files). A drawback is that an interdiff output requires more effort to apply, and the one applying the changes must also find and download the newer upstream tarball, which is typically done using the get-orig-source rule in debian/rules.Sanity checks with lintian
This tool provides automated checks for common packaging mistakes in both binary and source packages, including Debian policy violations and potential compatibility problems.While a maintainer typically aims to correct all issues pointed out by
lintian, different distributions can have different policies regarding them. For example, UbuntuUbuntu (operating system)
Ubuntu is a computer operating system based on the Debian Linux distribution and distributed as free and open source software. It is named after the Southern African philosophy of Ubuntu...
requires all packages originating in Ubuntu to be clean, but for a package merged into Ubuntu from Debian, there is no such requirement: new changes should simply not introduce any warnings in addition to existing ones. This is done to minimize the divergence between Debian and Ubuntu packages.
Here are example
lintian outputs:W: foo source: source-contains-CVS-dir config/CVS
N:
N: Package contains a CVS directory. It was most likely included by
N: accident, since transient CVS data usually doesn't belong in packages.
N: Export from CVS rather than use a checkout.
N:
W: libfoo-dev: debian-changelog-line-too-long line 2
N:
N: The given line of the latest changelog entry is over 80 columns. Such
N: changelog entries may look poor in terminal windows and mail messages
N: and be annoying to read. Please wrap changelog entries at 80 columns
N: or less where possible.
N:
I: foo: arch-dep-package-has-big-usr-share 3399kB 77%
N:
N: The package has a significant amount of architecture-independent data
N: in /usr/share, while it is an architecture-dependent package. This is
N: wasteful of mirror space and bandwidth, as we then end up with
N: multiple copies of this data, one for each architecture.
N:
N: If the data in /usr/share is not architecture-independent, it is a
N: policy violation, and in this case, you should move that data
N: elsewhere.
N:
N: See also:
N: http://www.debian.org/doc/developers-reference/ch-best-pkging-practice
N: s#s-bpp-archindepdata
Isolated build environments
Source packages are intended to be buildable on any installation of the target distribution version, provided that build dependencies are met. In addition, builds can be affected by packages already present in the system.To verify that a package builds on any system, and to exclude any external factors, tools to create isolated build environments are used. These are
pbuilder (Personal Builder) and sbuild.These tools maintain minimal working systems in chroot
Chroot
A chroot on Unix operating systems is an operation that changes the apparent root directory for the current running process and its children. A program that is run in such a modified environment cannot name files outside the designated directory tree. The term "chroot" may refer to the chroot...
, install only the necessary build dependencies listed in
debian/control, and remove them when the build is finished. Therefore, using pbuilder, a package maintainer can detect if some build dependencies were not specified in debian/control. Also, pbuilder makes it possible to test-build for distributions other than the one the maintainer is running: for example, for the development version, while actually running the stable version.sbuild is designed for integration with automated build daemons (buildd). It is used by Debian build servers, which automatically build binary packages for every supported architecture. The LaunchpadLaunchpad (website)
Launchpad is a web application and website that allow users to develop and maintain software, particularly free software. Launchpad is developed and maintained by Canonical Ltd....
service provides similar build daemons for Ubuntu, both the official distribution and personal package archives (PPAs).

