
Dark Energy Dominated Era
Encyclopedia
The dark-energy-dominated era refers to one of the three phases of the known universe, the other two being the matter-dominated era
and the radiation-dominated era
. The dark-energy-dominated era began after the matter-dominated era, i.e. when the Universe was about 5 billion years old. As other forms of the matter – dust and radiation – dropped to very low concentrations, the cosmological constant
term started to dominate the energy density of the Universe.
For a dark-energy-dominated universe, the evolution of the scale factor in the Friedmann-Lemaitre-Robertson-Walker metric is easily obtained solving the Friedmann equations
: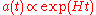
Here, the coefficient H in the exponential, the Hubble constant, is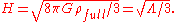
This exponential dependence on time makes the spacetime geometry identical to the de Sitter Universe
, and only holds for a positive sign of the cosmological constant, the sign that was observed to be realized in Nature anyway.
As the current density of the observable universe
is of the order of 9.44 x 10−27kg m−3, and the age of the universe is of the order of 13.7 billion years, or 4.32339 x 1017s, the present scale factor a(t) is ~2.699738. The Hubble parameter, H, is ~70.88 km s−1Mpc−1. (The Hubble time is 13.79 billion years.) The value of the cosmological constant, Λ, is ~2 x 10−35s−2.
Matter-Dominated Era
The matter-dominated era was the epoch in the evolution of the Universe that began after the radiation-dominated era ended, when the Universe was about 70,000 years old. Although it was often said that we still live in the matter-dominated era, it is more correct to say that when the Universe was...
and the radiation-dominated era
Radiation-Dominated Era
The radiation-dominated era refers to one of the three phases of the known universe, the other two being the matter-dominated era and the dark-energy-dominated era. During this era, the dynamics of the universe were set by radiation, which refers generally to the constituents of the universe which...
. The dark-energy-dominated era began after the matter-dominated era, i.e. when the Universe was about 5 billion years old. As other forms of the matter – dust and radiation – dropped to very low concentrations, the cosmological constant
Cosmological constant
In physical cosmology, the cosmological constant was proposed by Albert Einstein as a modification of his original theory of general relativity to achieve a stationary universe...
term started to dominate the energy density of the Universe.
For a dark-energy-dominated universe, the evolution of the scale factor in the Friedmann-Lemaitre-Robertson-Walker metric is easily obtained solving the Friedmann equations
Friedmann equations
The Friedmann equations are a set of equations in physical cosmology that govern the expansion of space in homogeneous and isotropic models of the universe within the context of general relativity...
:
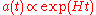
Here, the coefficient H in the exponential, the Hubble constant, is
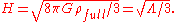
This exponential dependence on time makes the spacetime geometry identical to the de Sitter Universe
De Sitter universe
A de Sitter universe is a cosmological solution to Einstein's field equations of General Relativity which is named after Willem de Sitter. It models the universe as spatially flat and neglects ordinary matter, so the dynamics of the universe are dominated by the cosmological constant, thought to...
, and only holds for a positive sign of the cosmological constant, the sign that was observed to be realized in Nature anyway.
As the current density of the observable universe
Observable universe
In Big Bang cosmology, the observable universe consists of the galaxies and other matter that we can in principle observe from Earth in the present day, because light from those objects has had time to reach us since the beginning of the cosmological expansion...
is of the order of 9.44 x 10−27kg m−3, and the age of the universe is of the order of 13.7 billion years, or 4.32339 x 1017s, the present scale factor a(t) is ~2.699738. The Hubble parameter, H, is ~70.88 km s−1Mpc−1. (The Hubble time is 13.79 billion years.) The value of the cosmological constant, Λ, is ~2 x 10−35s−2.

