
Cyclic nucleotide
Encyclopedia
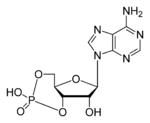
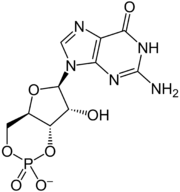
Nucleotide
Nucleotides are molecules that, when joined together, make up the structural units of RNA and DNA. In addition, nucleotides participate in cellular signaling , and are incorporated into important cofactors of enzymatic reactions...
in which the phosphate
Phosphate
A phosphate, an inorganic chemical, is a salt of phosphoric acid. In organic chemistry, a phosphate, or organophosphate, is an ester of phosphoric acid. Organic phosphates are important in biochemistry and biogeochemistry or ecology. Inorganic phosphates are mined to obtain phosphorus for use in...
group is bonded to two of the sugar
Sugar
Sugar is a class of edible crystalline carbohydrates, mainly sucrose, lactose, and fructose, characterized by a sweet flavor.Sucrose in its refined form primarily comes from sugar cane and sugar beet...
's hydroxyl groups, forming a cyclical or ring structure.
These include:
- cyclic AMP
- cyclic GMP
- cyclic ADP-riboseCyclic ADP-riboseCyclic ADP Ribose, frequently abbreviated as cADPR, is a cyclic adenine nucleotide with two phosphate groups present on 5' OH of the adenosine , further connected to another ribose at the 5' position, which, in turn, closes the cycle by glycosidic bonding to the nitrogen 1 of the same adenine...
These function as second messengers associated with G protein
G protein
G proteins are a family of proteins involved in transmitting chemical signals outside the cell, and causing changes inside the cell. They communicate signals from many hormones, neurotransmitters, and other signaling factors. G protein-coupled receptors are transmembrane receptors...
s and calcium signaling
Calcium signaling
Calcium is a common signaling mechanism, as once it enters the cytoplasm it exerts allosteric regulatory effects on many enzymes and proteins...
.

