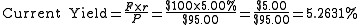Current yield
Encyclopedia
The current yield, interest yield, income yield, flat yield or running yield is a financial
term used in reference to bond
s and other fixed-interest securities such as gilts
. It is the ratio of the annual interest payment and the bond's current clean price
:
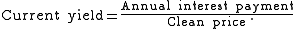
The current yield only therefore refers to the yield of the bond at the current moment. It does not reflect the total return over the life of the bond. In particular, it takes no account of reinvestment risk (the uncertainty about the rate at which future cashflows can be reinvested) or the fact that bonds usually mature at par value, which can be an important component of a bond's return.
, and coupon yield. When a bond sells at;
Current Yield = Total Yield - Capital Gains Yield
The current yield is the annual payment divided by the price.
Algebraically expressed as Y = R/P, where Y is yield, R is the annual payment, and P represents price. This creation shows the fine line between high and low returns over more than one period. A high yield will produce a relative payment and a low yield will do the same. When the yields of several periods are compared a higher yield will show a higher payment with less risk associated. This equates to investors expecting a higher yield over a length of investing. The possibility of market risks are ignored.
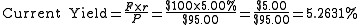
Finance
"Finance" is often defined simply as the management of money or “funds” management Modern finance, however, is a family of business activity that includes the origination, marketing, and management of cash and money surrogates through a variety of capital accounts, instruments, and markets created...
term used in reference to bond
Bond (finance)
In finance, a bond is a debt security, in which the authorized issuer owes the holders a debt and, depending on the terms of the bond, is obliged to pay interest to use and/or to repay the principal at a later date, termed maturity...
s and other fixed-interest securities such as gilts
Gilts
Gilts are bonds issued by certain national governments. The term is of British origin, and originally referred to the debt securities issued by the Bank of England, which had a gilt edge. Hence, they are called gilt-edged securities, or gilts for short. The term is also sometimes used in Ireland...
. It is the ratio of the annual interest payment and the bond's current clean price
Clean price
In finance, the clean price is the price of a bond excluding any interest that has accrued since issue or the most recent coupon payment. This is to be compared with the dirty price, which is the price of a bond including the accrued interest....
:
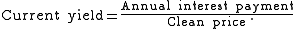
The current yield only therefore refers to the yield of the bond at the current moment. It does not reflect the total return over the life of the bond. In particular, it takes no account of reinvestment risk (the uncertainty about the rate at which future cashflows can be reinvested) or the fact that bonds usually mature at par value, which can be an important component of a bond's return.
Relationship between yield to maturity and coupon rate
The concept of current yield is closely related to other bond concepts, including yield to maturityYield to maturity
The Yield to maturity or redemption yield of a bond or other fixed-interest security, such as gilts, is the internal rate of return earned by an investor who buys the bond today at the market price, assuming that the bond will be held until maturity, and that all coupon and principal payments...
, and coupon yield. When a bond sells at;
- a discount: YTM > current yield > coupon yield
- a premium: coupon yield > current yield > YTM
- parPar valuePar value, in finance and accounting, means stated value or face value. From this comes the expressions at par , over par and under par ....
: YTM = current yield = coupon yield.
Current Yield = Total Yield - Capital Gains Yield
The current yield is the annual payment divided by the price.
Algebraically expressed as Y = R/P, where Y is yield, R is the annual payment, and P represents price. This creation shows the fine line between high and low returns over more than one period. A high yield will produce a relative payment and a low yield will do the same. When the yields of several periods are compared a higher yield will show a higher payment with less risk associated. This equates to investors expecting a higher yield over a length of investing. The possibility of market risks are ignored.
Example Calculation
To calculate the current yield of a bond with a face value of $100 and a coupon rate of 5.00% that is selling at $95.00 (clean, not including accrued interest), use: