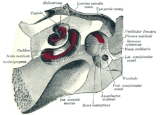
Cupula
Encyclopedia
The cupula is a structure in the vestibular system
, providing proprioception
.
The cupula is located within the ampullae
of each of the three semicircular canals. As fluid rushes by the cupula, hair cell
s within it sense rotational acceleration, and transmit the corresponding signal to the brain through the vestibulocochlear nerve
(CN VIII)
In their natural orientation within the head, the cupulae are located on the medial aspect of the semicircular canals. In this orientation, the kinocilia rest on the posterior aspect of the cupula.
Buoyancy Hypothesis
The Buoyancy Hypothesis posits that alcohol causes vertigo
by affecting the neutral buoyancy of the cupula within the surrounding fluid called the endolymph
. Linear accelerations (such as that of gravity) should not in theory effect a movement of the cupula when it is neutrally buoyant. The Buoyancy Hypothesis assumes that alcohol, with a different specific gravity from that of the cupula/endolymph, diffuses at different rates into the cupula and the surrounding endolymph. The result is a temporary density gradient between the cupula and endolymph, and a consequent (erroneous) sensitivity to linear accelerations such as that of gravity by a system normally signalling rotational accelerations. This sensation is commonly referred to as "the spins" .
Vestibular system
The vestibular system, which contributes to balance in most mammals and to the sense of spatial orientation, is the sensory system that provides the leading contribution about movement and sense of balance. Together with the cochlea, a part of the auditory system, it constitutes the labyrinth of...
, providing proprioception
Proprioception
Proprioception , from Latin proprius, meaning "one's own" and perception, is the sense of the relative position of neighbouring parts of the body and strength of effort being employed in movement...
.
The cupula is located within the ampullae
Osseous ampullae
The bony semicircular canals are three in number, superior, posterior, and lateral, and are situated above and behind the vestibule. They are unequal in length, compressed from side to side, and each describes the greater part of a circle. Each measures about 0.8 mm...
of each of the three semicircular canals. As fluid rushes by the cupula, hair cell
Hair cell
Hair cells are the sensory receptors of both the auditory system and the vestibular system in all vertebrates. In mammals, the auditory hair cells are located within the organ of Corti on a thin basilar membrane in the cochlea of the inner ear...
s within it sense rotational acceleration, and transmit the corresponding signal to the brain through the vestibulocochlear nerve
Vestibulocochlear nerve
The vestibulocochlear nerve is the eighth of twelve cranial nerves, and is responsible for transmitting sound and equilibrium information from the inner ear to the brain...
(CN VIII)
In their natural orientation within the head, the cupulae are located on the medial aspect of the semicircular canals. In this orientation, the kinocilia rest on the posterior aspect of the cupula.
Effects of alcohol
Further reading: Short-term effects of alcohol#vertigoBuoyancy Hypothesis
The Buoyancy Hypothesis posits that alcohol causes vertigo
Vertigo (medical)
Vertigo is a type of dizziness, where there is a feeling of motion when one is stationary. The symptoms are due to a dysfunction of the vestibular system in the inner ear...
by affecting the neutral buoyancy of the cupula within the surrounding fluid called the endolymph
Endolymph
Endolymph is the fluid contained in the membranous labyrinth of the inner ear. It is also called Scarpa's fluid, after Antonio Scarpa.-Composition:...
. Linear accelerations (such as that of gravity) should not in theory effect a movement of the cupula when it is neutrally buoyant. The Buoyancy Hypothesis assumes that alcohol, with a different specific gravity from that of the cupula/endolymph, diffuses at different rates into the cupula and the surrounding endolymph. The result is a temporary density gradient between the cupula and endolymph, and a consequent (erroneous) sensitivity to linear accelerations such as that of gravity by a system normally signalling rotational accelerations. This sensation is commonly referred to as "the spins" .
External links
- http://faculty.une.edu/com/abell/histo/CristaAmp.jpg
- http://www.kumc.edu/instruction/medicine/anatomy/histoweb/eye_ear/ear04.htm
- http://www.anatomyatlases.org/MicroscopicAnatomy/Section16/Plate16314.shtml
- http://education.vetmed.vt.edu/Curriculum/VM8054/Labs/Lab11/Ear/EXAMPLES/Excrista.htm

