
Cuckoo hashing
Encyclopedia

Computer programming
Computer programming is the process of designing, writing, testing, debugging, and maintaining the source code of computer programs. This source code is written in one or more programming languages. The purpose of programming is to create a program that performs specific operations or exhibits a...
for resolving hash collision
Hash collision
Not to be confused with wireless packet collision.In computer science, a collision or clash is a situation that occurs when two distinct pieces of data have the same hash value, checksum, fingerprint, or cryptographic digest....
s of values of hash function
Hash function
A hash function is any algorithm or subroutine that maps large data sets to smaller data sets, called keys. For example, a single integer can serve as an index to an array...
s in a table
Hash table
In computer science, a hash table or hash map is a data structure that uses a hash function to map identifying values, known as keys , to their associated values . Thus, a hash table implements an associative array...
. Cuckoo hashing was first described by Rasmus Pagh and Flemming Friche Rodler in 2001. The name derives from the behavior of some species of cuckoo
Cuckoo
The cuckoos are a family, Cuculidae, of near passerine birds. The order Cuculiformes, in addition to the cuckoos, also includes the turacos . Some zoologists and taxonomists have also included the unique Hoatzin in the Cuculiformes, but its taxonomy remains in dispute...
, where the cuckoo chick pushes the other eggs or young out of the nest when it hatches.
Theory
The basic idea is to use two hash functions instead of only one. This provides two possible locations in the hash table for each keyUnique key
In relational database design, a unique key can uniquely identify each row in a table, and is closely related to the Superkey concept. A unique key comprises a single column or a set of columns. No two distinct rows in a table can have the same value in those columns if NULL values are not used...
. In one of the commonly used variants of the algorithm, the hash table is split into two smaller tables of equal size, and each hash function provides an index into one of these two tables.
When a new key is inserted, a greedy algorithm
Greedy algorithm
A greedy algorithm is any algorithm that follows the problem solving heuristic of making the locally optimal choice at each stagewith the hope of finding the global optimum....
is used: The new key is inserted in one of its two possible locations, "kicking out", that is, displacing, any key that might already reside in this location. This displaced key is then inserted in its alternative location, again kicking out any key that might reside there, until a vacant position is found, or the procedure enters an infinite loop
Infinite loop
An infinite loop is a sequence of instructions in a computer program which loops endlessly, either due to the loop having no terminating condition, having one that can never be met, or one that causes the loop to start over...
. In the latter case, the hash table
Hash table
In computer science, a hash table or hash map is a data structure that uses a hash function to map identifying values, known as keys , to their associated values . Thus, a hash table implements an associative array...
is rebuilt in-place
In-place algorithm
In computer science, an in-place algorithm is an algorithm which transforms input using a data structure with a small, constant amount of extra storage space. The input is usually overwritten by the output as the algorithm executes...
using new hash function
Hash function
A hash function is any algorithm or subroutine that maps large data sets to smaller data sets, called keys. For example, a single integer can serve as an index to an array...
s.
Lookup requires inspection of just two locations in the hash table, which takes constant time in the worst case (see Big O notation
Big O notation
In mathematics, big O notation is used to describe the limiting behavior of a function when the argument tends towards a particular value or infinity, usually in terms of simpler functions. It is a member of a larger family of notations that is called Landau notation, Bachmann-Landau notation, or...
). This is in contrast to many other hash table algorithms, which may not have a constant worst-case bound on the time to do a lookup.
It can also be shown that insertions succeed in expected constant time, even considering the possibility of having to rebuild the table, as long as the number of keys is kept below half of the capacity of the hash table, i.e., the load factor is below 50%. One method of proving this uses the theory of random graph
Random graph
In mathematics, a random graph is a graph that is generated by some random process. The theory of random graphs lies at the intersection between graph theory and probability theory, and studies the properties of typical random graphs.-Random graph models:...
s: one may form an undirected graph called the "Cuckoo Graph" that has a vertex for each hash table location, and an edge for each hashed value, with the endpoints of the edge being the two possible locations of the value. Then, the greedy insertion algorithm for adding a set of values to a cuckoo hash table succeeds if and only if the Cuckoo Graph for this set of values is a pseudoforest
Pseudoforest
In graph theory, a pseudoforest is an undirected graph in which every connected component has at most one cycle. That is, it is a system of vertices and edges connecting pairs of vertices, such that no two cycles of consecutive edges share any vertex with each other, nor can any two cycles be...
, a graph with at most one cycle in each of its connected component
Connected component (graph theory)
In graph theory, a connected component of an undirected graph is a subgraph in which any two vertices are connected to each other by paths, and which is connected to no additional vertices. For example, the graph shown in the illustration on the right has three connected components...
s. This property is true with high probability for a random graph in which the number of edges is less than half the number of vertices.
Example
The following hashfunctions are given: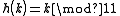
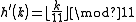
Cycle
If you now wish to insert the element 6, then you get into a cycle. In the last row of the table we find the same initial situation as at the beginning again.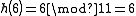
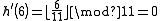
| considered key | table 1 | table 2 | ||
| old value | new value | old value | new value | |
| 6 | 50 | 6 | 53 | 50 |
| 53 | 75 | 53 | 67 | 75 |
| 67 | 100 | 67 | 105 | 100 |
| 105 | 6 | 105 | 3 | 6 |
| 3 | 36 | 3 | 39 | 36 |
| 39 | 105 | 39 | 100 | 105 |
| 100 | 67 | 100 | 75 | 67 |
| 75 | 53 | 75 | 50 | 53 |
| 50 | 39 | 50 | 36 | 39 |
| 36 | 3 | 36 | 6 | 3 |
| 6 | 50 | 6 | 53 | 50 |
Generalizations and applications
Generalizations of cuckoo hashing that use more than 2 alternative hash functions can be expected to utilize a larger part of the capacity of the hash table efficiently while sacrificing some lookup and insertion speed. Using just three hash functions increases the load to 91%. Another generalization of cuckoo hashing consists in using more than one key per bucket. Using just 2 keys per bucket permits a load factor above 80%.Other algorithms that use multiple hash functions include the Bloom filter
Bloom filter
A Bloom filter, conceived by Burton Howard Bloom in 1970, is a space-efficient probabilistic data structure that is used to test whether an element is a member of a set. False positives are possible, but false negatives are not; i.e. a query returns either "inside set " or "definitely not in set"...
. Cuckoo hashing can be used to implement a data structure equivalent to a Bloom filter. A simplified generalization of cuckoo hashing called skewed-associative cache is used in some CPU caches.
A study by Zukowski et al. has shown that cuckoo hashing is much faster than chained hashing for small, cache
CPU cache
A CPU cache is a cache used by the central processing unit of a computer to reduce the average time to access memory. The cache is a smaller, faster memory which stores copies of the data from the most frequently used main memory locations...
-resident hash tables on modern processors. Kenneth Ross has shown bucketized versions of cuckoo hashing (variants that use buckets that contain more than one key) to be faster than conventional methods also for large hash tables, when space utilization is high. The performance of the bucketized cuckoo hash table was investigated further by Askitis,
with its performance compared against alternative hashing schemes.
A survey by Mitzenmacher
Michael Mitzenmacher
Michael D. Mitzenmacher is an American computer scientist working in algorithms. Heis professor of computer science in theSchool of Engineering and Applied Sciences at Harvard University and area dean of computer science since July 2010.-Education:...
presents open problems related to cuckoo hashing as of 2009.
See also
- Perfect hashing
- Linear probingLinear probingLinear probing is a scheme in computer programming for resolving hash collisions of values of hash functions by sequentially searching the hash table for a free location. This is accomplished using two values - one as a starting value and one as an interval between successive values in modular...
- Double hashingDouble hashingDouble hashing is a computer programming technique used in hash tables to resolve hash collisions, cases when two different values to be searched for produce the same hash key...
- Hash collisionHash collisionNot to be confused with wireless packet collision.In computer science, a collision or clash is a situation that occurs when two distinct pieces of data have the same hash value, checksum, fingerprint, or cryptographic digest....
- Hash functionHash functionA hash function is any algorithm or subroutine that maps large data sets to smaller data sets, called keys. For example, a single integer can serve as an index to an array...
- Quadratic probingQuadratic probingQuadratic probing is a scheme in computer programming for resolving collisions in hash tables.It is an open addressing method to handle overflows after a collision takes place in some bucket of a hash table....

