
Crystal Ball function
Encyclopedia
The Crystal Ball function, named after the Crystal Ball
Collaboration (hence the capitalized initial letters), is a probability density function
commonly used to model various lossy processes in high-energy physics. It consists of a Gaussian core portion and a power-law low-end tail, below a certain threshold. The function itself and its first derivative
are both continuous
.
The Crystal Ball function is given by:
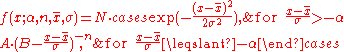
where
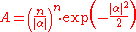 ,
,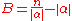 ,
,
 is a normalization factor and
is a normalization factor and  ,
,  ,
, 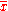 and
and  are parameters which are fitted with the data.
are parameters which are fitted with the data.
Crystal Ball (detector)
The Crystal Ball is a hermetic particle detector used initially with the SPEAR particle accelerator at the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center beginning in 1979. It was designed to detect neutral particles and was used to discover the ηc meson. Its central section was a spark chamber surrounded by...
Collaboration (hence the capitalized initial letters), is a probability density function
Probability density function
In probability theory, a probability density function , or density of a continuous random variable is a function that describes the relative likelihood for this random variable to occur at a given point. The probability for the random variable to fall within a particular region is given by the...
commonly used to model various lossy processes in high-energy physics. It consists of a Gaussian core portion and a power-law low-end tail, below a certain threshold. The function itself and its first derivative
Derivative
In calculus, a branch of mathematics, the derivative is a measure of how a function changes as its input changes. Loosely speaking, a derivative can be thought of as how much one quantity is changing in response to changes in some other quantity; for example, the derivative of the position of a...
are both continuous
Continuous function
In mathematics, a continuous function is a function for which, intuitively, "small" changes in the input result in "small" changes in the output. Otherwise, a function is said to be "discontinuous". A continuous function with a continuous inverse function is called "bicontinuous".Continuity of...
.
The Crystal Ball function is given by:
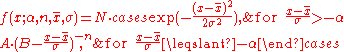
where
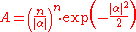 ,
,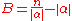 ,
, is a normalization factor and
is a normalization factor and  ,
,  ,
,  and
and  are parameters which are fitted with the data.
are parameters which are fitted with the data.External links
- J. E. Gaiser, Appendix-F Charmonium Spectroscopy from Radiative Decays of the J/Psi and Psi-Prime, Ph.D. Thesis, SLAC-R-255 (1982). (This is a 205 page document in .pdf form – the function is defined on p. 178.)
- M. J. Oreglia, A Study of the Reactions psi prime --> gamma gamma psi, Ph.D. Thesis, SLAC-R-236 (1980), Appendix D.
- T. Skwarnicki, Ph.D Thesis, DESY F31-86-02(1986), Appendix E.

