
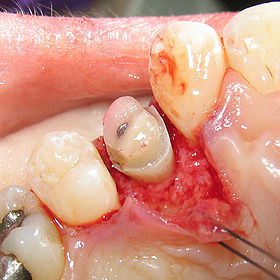
Crown lengthening
Encyclopedia
Dentist
A dentist, also known as a 'dental surgeon', is a doctor that specializes in the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of diseases and conditions of the oral cavity. The dentist's supporting team aides in providing oral health services...
to expose a greater amount of tooth
Tooth
Teeth are small, calcified, whitish structures found in the jaws of many vertebrates that are used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores, also use teeth for hunting or for defensive purposes. The roots of teeth are embedded in the Mandible bone or the Maxillary bone and are...
structure for the purpose of subsequently restoring the tooth prosthetically
Crown (dentistry)
A crown is a type of dental restoration which completely caps or encircles a tooth or dental implant. Crowns are often needed when a large cavity threatens the ongoing health of a tooth. They are typically bonded to the tooth using a dental cement. Crowns can be made from many materials, which...
. This is done by incising the gingival tissue
Gingiva
The gingiva , or gums, consists of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth.-General description:...
around a tooth and, after temporarily displacing the soft tissue, predictably removing a given height of alveolar bone
Dental alveolus
Dental alveolus are sockets in the jaws in which the roots of teeth are held in the alveolar process of maxilla with the periodontal ligament. The lay term for dental alveoli is tooth sockets...
from the circumference of the tooth or teeth being operated on. While many general dentists perform this procedure, they frequently refer such cases to periodontists.
Biologic width
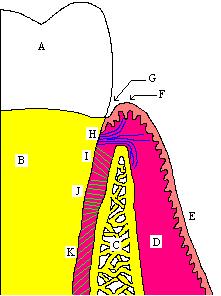
Biologic width is the distance established by "the junctional epithelium
Junctional epithelium
The junctional epithelium is that epithelium which lies at, and in health also defines, the base of the gingival sulcus. It attaches to the surface of the tooth with hemidesmosomes and is, on average, roughly 1 mm in width, constituting about one half of the biologic width.The junctional...
and connective tissue attachment
Gingival fibers
The gingival fibers are the connective tissue fibers that inhabit the gingival tissue adjacent to teeth and help hold the tissue firmly against the teeth...
to the root surface" of a tooth
Tooth
Teeth are small, calcified, whitish structures found in the jaws of many vertebrates that are used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores, also use teeth for hunting or for defensive purposes. The roots of teeth are embedded in the Mandible bone or the Maxillary bone and are...
. This distance is important to consider when fabricating dental restoration
Dental restoration
A dental restoration or dental filling is a dental restorative material used to restore the function, integrity and morphology of missing tooth structure. The structural loss typically results from caries or external trauma. It is also lost intentionally during tooth preparation to improve the...
s, because they must respect the natural architecture of the gingival attachment if harmful consequences are to be avoided.
Based on the 1961 paper by Gargulio, the mean biologic width was determined to be 2.04 mm, of which 1.07 mm is occupied by the connective tissue attachment
Periodontal ligament
The periodontal fiber or periodontal ligament, commonly abbreviated as the PDL, is a group of specialized connective tissue fibers that essentially attach a tooth to the alveolar bone within which it sits...
and another approximate 0.97 mm is occupied by the junctional epithelium
Junctional epithelium
The junctional epithelium is that epithelium which lies at, and in health also defines, the base of the gingival sulcus. It attaches to the surface of the tooth with hemidesmosomes and is, on average, roughly 1 mm in width, constituting about one half of the biologic width.The junctional...
. Because it is impossible to perfectly restore a tooth to the precise coronal edge of the junctional epithelium, it is often recommended to remove enough bone to have 3mm between the restorative margin and the crest of alveolar bone. When restorations do not take these considerations into account and violate biologic width, three things tend to occur:
- chronic painPainPain is an unpleasant sensation often caused by intense or damaging stimuli such as stubbing a toe, burning a finger, putting iodine on a cut, and bumping the "funny bone."...
- chronic inflammationInflammationInflammation is part of the complex biological response of vascular tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. Inflammation is a protective attempt by the organism to remove the injurious stimuli and to initiate the healing process...
of the gingiva - unpredictable loss of alveolar bone
Ferrule effect
In addition to crown lengthening to establish a proper biologic width, a 2 mm height of tooth structure should be available to allow for a ferrule effect. A ferrule, in respect to teeth, is a band that encircles the external dimension of residual tooth structure, not unlike the metal bands that exist around a barrel. Sufficient vertical height of tooth structure that will be grasped by the future crown is necessary to allow for a ferrule effect of the future prosthetic crown; it has been shown to significantly reduce the incidence of fracture in the endodontically treated tooth. Because beveled tooth structure is not parallel to the vertical axis of the tooth, it does not properly contribute to ferrule height; thus, a desire to bevel the crown margin by 1 mm would require an additional 1 mm of bone removal in the crown lengthening procedure. Frequently, however, restorations are performed without such a bevel.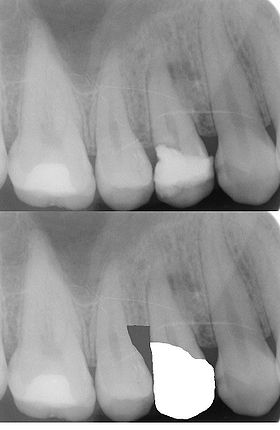
Crown-to-root ratio
The alveolar boneDental alveolus
Dental alveolus are sockets in the jaws in which the roots of teeth are held in the alveolar process of maxilla with the periodontal ligament. The lay term for dental alveoli is tooth sockets...
surrounding one tooth will naturally surround an adjacent tooth, and removing bone for a crown lengthening procedure will effectively damage the bony support of adjacent teeth to some inevitable extent, as well as unfavorably increase the crown-to-root ratio
Crown-to-root ratio
Crown-to-root-ratio is the ratio of the length of the part of a tooth that appears above the alveolar bone versus what lies below it. It is an important consideration in the diagnosis, treatment planning and restoration of teeth, one that hopefully guides the plan of treatment to the proper end...
. Additionally, once bone is removed, it is almost impossible to regain it to previous levels, and in case a patient would like to have an implant placed in the future, there might not be enough bone in the region once a crown lengthening procedure has been completed. Thus, it would be prudent for patients to thoroughly discuss all of their treatment planning options with their dentist before undergoing an irreversible procedure such as crown lengthening.
Treatment planning
Crown lengthening is often done in conjunction with a few other expensive and time-consuming procedures of which the combined goal is to improve the prosthetic forecast of a tooth. If a tooth, because of its relative lack of solid tooth structure, also requires a post and corePost and core
A post and core is a dental restoration used to sufficiently build-up tooth structure for future restoration with a crown when there is not enough tooth structure to properly retain the crown, due to loss of tooth structure to either decay or fracture...
, and thus, endodontic treatment, the total combined time, effort and cost of the various procedures, as well as the impaired prognosis due to the combined inherent failure rates of each procedure, might combine to make it reasonable to have the tooth extracted. If the patient and the extraction site make for eligible candidates, it might be possible to have an implant
Dental implant
A dental implant is a "root" device, usually made of titanium, used in dentistry to support restorations that resemble a tooth or group of teeth to replace missing teeth....
placed and restored with more esthetic, timely, inexpensive and reliable results. It is important to consider the many options available during the treatment planning stages of dental care.
A better alternative to surgical crown lengthening is orthodontic forced eruption, it is simple, it is non-invasive, does not remove or damage the bone and is cost effective. The tooth is extruded a couple of millimeters with simple bracketing of adjacent teeth and using light forces this will only take a couple of months. A simple fiberotomy is performed after crown lengthening and is easily performed by the general dentist. In many cases such as this one shown, surgery and extraction may be avoided if patient is treated orthodontically rather than periodontally.

